Related Research Articles
Material requirements planning (MRP) is a production planning, scheduling, and inventory control system used to manage manufacturing processes. Most MRP systems are software-based, but it is possible to conduct MRP by hand as well.

Lean manufacturing is a production method aimed primarily at reducing times within the production system as well as response times from suppliers and to customers.
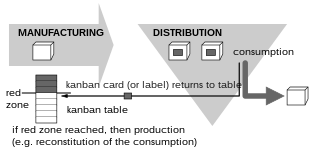
Kanban is a scheduling system for lean manufacturing. Taiichi Ohno, an industrial engineer at Toyota, developed kanban to improve manufacturing efficiency. The system takes its name from the cards that track production within a factory. Kanban is also known as the Toyota nameplate system in the automotive industry.

Extrusion is a process used to create objects of a fixed cross-sectional profile by pushing material through a die of the desired cross-section. Its two main advantages over other manufacturing processes are its ability to create very complex cross-sections; and to work materials that are brittle, because the material encounters only compressive and shear stresses. It also creates excellent surface finish and gives considerable freedom of form in the design process.

Manufacturingresource planning is defined as a method for the effective planning of all resources of a manufacturing company. Ideally, it addresses operational planning in units, financial planning, and has a simulation capability to answer "what-if" questions and is an extension of closed-loop MRP.

Operations management is an area of management concerned with designing and controlling the process of production and redesigning business operations in the production of goods or services. It involves the responsibility of ensuring that business operations are efficient in terms of using as few resources as needed and effective in meeting customer requirements.
Lean thinking is a transformational framework that aims to provide a new way to think about how to organize human activities to deliver more benefits to society and value to individuals while eliminating waste. The term “lean thinking” was coined by James P. Womack and Daniel T. Jones to capture the essence of their in-depth study of Toyota's fabled Toyota Production System. Lean thinking is a way of thinking about an activity and seeing the waste inadvertently generated by the way the process is organized. It uses the concepts of:
- Value
- Value streams
- Flow
- Pull
- Perfection
Manufacturing process management (MPM) is a collection of technologies and methods used to define how products are to be manufactured. MPM differs from ERP/MRP which is used to plan the ordering of materials and other resources, set manufacturing schedules, and compile cost data.

The business terms push and pull originated in logistics and supply chain management, but are also widely used in marketing and in the hotel distribution business.

Value-stream mapping, also known as "material- and information-flow mapping", is a lean-management method for analyzing the current state and designing a future state for the series of events that take a product or service from the beginning of the specific process until it reaches the customer. A value stream map is a visual tool that displays all critical steps in a specific process and easily quantifies the time and volume taken at each stage. Value stream maps show the flow of both materials and information as they progress through the process.
Cellular manufacturing is a process of manufacturing which is a subsection of just-in-time manufacturing and lean manufacturing encompassing group technology. The goal of cellular manufacturing is to move as quickly as possible, make a wide variety of similar products, while making as little waste as possible. Cellular manufacturing involves the use of multiple "cells" in an assembly line fashion. Each of these cells is composed of one or multiple different machines which accomplish a certain task. The product moves from one cell to the next, each station completing part of the manufacturing process. Often the cells are arranged in a "U-shape" design because this allows for the overseer to move less and have the ability to more readily watch over the entire process. One of the biggest advantages of cellular manufacturing is the amount of flexibility that it has. Since most of the machines are automatic, simple changes can be made very rapidly. This allows for a variety of scaling for a product, minor changes to the overall design, and in extreme cases, entirely changing the overall design. These changes, although tedious, can be accomplished extremely quickly and precisely.
Backflush accounting is a subset of management accounting focused on types of "postproduction issuing;" It is a product costing approach, used in a Just-In-Time (JIT) operating environment, in which costing is delayed until goods are finished. Backflush accounting delays the recording of costs until after the events have taken place, then standard costs are used to work backwards to 'flush' out the manufacturing costs. The result is that detailed tracking of costs is eliminated. Journal entries to inventory accounts may be delayed until the time of product completion or even the time of sale, and standard costs are used to assign costs to units when journal entries are made. Backflushing transaction has two steps: one step of the transaction reports the produced part which serves to increase the quantity on-hand of the produced part and a second step which relieves the inventory of all the component parts. Component part numbers and quantities-per are taken from the standard bill of material (BOM). This represents a huge saving over the traditional method of a) issuing component parts one at a time, usually to a discrete work order, b) receiving the finished parts into inventory, and c) returning any unused components, one at a time, back into inventory.
Quick response manufacturing (QRM) is an approach to manufacturing which emphasizes the beneficial effect of reducing internal and external lead times.
Demand Flow Technology (DFT) is a strategy for defining and deploying business processes in a flow, driven in response to customer demand. DFT is based on a set of applied mathematical tools that are used to connect processes in a flow and link it to daily changes in demand. DFT represents a scientific approach to flow manufacturing for discrete production. It is built on principles of demand pull where customer demand is the central signal to guide factory and office activity in the daily operation. DFT is intended to provide an alternative to schedule-push manufacturing which primarily uses a sales plan and forecast to determine a production schedule.

Industrial Engineering is an engineering profession that is concerned with the optimization of complex processes, systems, or organizations by developing, improving and implementing integrated systems of people, money, knowledge, information and equipment. Industrial engineering is central to manufacturing operations.

Kanban is a lean method to manage and improve work across human systems. This approach aims to manage work by balancing demands with available capacity, and by improving the handling of system-level bottlenecks.

Simcad Pro simulation software is a product of CreateASoft Inc. used for simulating process-based environments including manufacturing, warehousing, supply lines, logistics, and healthcare. It is a tool used for planning, organizing, optimizing, and engineering real process-based systems. Simcad Pro allows the creation of a virtual computer model, which can be manipulated by the user and represents a real environment. Using the model, it is possible to test for efficiency as well as locate points of improvement among the process flow. Simcad Pro's dynamic computer model also allows for changes to occur while the model is running for a fully realistic simulation. It can also be integrated with live and historical data.

A kanban board is one of the tools that can be used to implement kanban to manage work at a personal or organizational level.
A demand signal is a message issued within business operations or within a supply chain to notify a supplier that goods are required, and is, therefore, a key item of information for demand planners within a business.

The inoERP enterprise management system is an open-source php based Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) application which can be used with MySQL, MariaDB or Oracle 12c databases. The objective of inoERP is to provide a dynamic pull based system where the demand /supply changes frequently and traditional planning systems are unable to provide a good inventory turn.
References
- ↑ Spearman, M., Woodruff, D. and Hopp, W. (1990) CONWIP: a pull alternative to kanban. International Journal of Production Research 28, 879-894
- ↑ Marek, Richard P. et al., Understanding the fundamentals of Kanban and CONWIP pull systems using simulation, Proceedings of the 2001 Winter Simulation Conference