Related Research Articles

Running is a method of terrestrial locomotion allowing humans and other animals to move rapidly on foot. Running is a type of gait characterized by an aerial phase in which all feet are above the ground. This is in contrast to walking, where one foot is always in contact with the ground, the legs are kept mostly straight and the center of gravity vaults over the stance leg or legs in an inverted pendulum fashion. A feature of a running body from the viewpoint of spring-mass mechanics is that changes in kinetic and potential energy within a stride co-occur, with energy storage accomplished by springy tendons and passive muscle elasticity. The term running can refer to any of a variety of speeds ranging from jogging to sprinting.

Massage is the manipulation of the body's soft tissues. Massage techniques are commonly applied with hands, fingers, elbows, knees, forearms, feet or a device. The purpose of massage is generally for the treatment of body stress or pain. In European countries, a person professionally trained to give massages is traditionally known as a masseur (male) or masseuse (female). In the United States, these individuals are often referred to as massage therapists, because they must be certified and licensed as "licensed massage therapists". In some provinces of Canada, they are called “Registered massage therapists”, as they are regulated health professionals.

A sleep disorder, or somnipathy, is a medical disorder of an individual's sleep patterns. Some sleep disorders are severe enough to interfere with normal physical, mental, social and emotional functioning. Polysomnography and actigraphy are tests commonly ordered for diagnosing sleep disorders.

A circadian rhythm, or circadian cycle, is a natural oscillation that repeats roughly every 24 hours. Circadian rhythms can refer to any process that originates within an organism and responds to the environment. Circadian rhythms are regulated by a circadian clock whose primary function is to rhythmically co-ordinate biological processes so they occur at the correct time to maximise the fitness of an individual. Circadian rhythms have been widely observed in animals, plants, fungi and cyanobacteria and there is evidence that they evolved independently in each of these kingdoms of life.
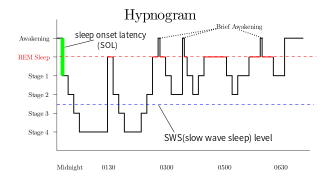
Rapid eye movement sleep is a unique phase of sleep in mammals and birds, characterized by random rapid movement of the eyes, accompanied by low muscle tone throughout the body, and the propensity of the sleeper to dream vividly.

Delayed sleep phase disorder (DSPD), more often known as delayed sleep phase syndrome and also as delayed sleep–wake phase disorder, is the delaying of a person's circadian rhythm compared to those of societal norms. The disorder affects the timing of biological rhythms including sleep, peak period of alertness, core body temperature, and hormonal cycles.
Autogenic training is a relaxation technique first published by the German psychiatrist Johannes Heinrich Schultz in 1932. The technique involves repetitions of a set of visualisations accompanied by vocal suggestions that induce a state of relaxation and is based on passive concentration of bodily perceptions like heaviness and warmth of limbs, which are facilitated by self-suggestions. Autogenic training is used to alleviate many stress-induced psychosomatic disorders.
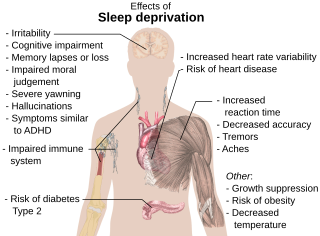
Sleep debt or sleep deficit is the cumulative effect of not getting enough sleep. A large sleep debt may lead to mental or physical fatigue, and can adversely affect one's mood, energy, and ability to think clearly.
Cushing reflex is a physiological nervous system response to increased intracranial pressure (ICP) that results in Cushing's triad of increased blood pressure, irregular breathing, and bradycardia. It is usually seen in the terminal stages of acute head injury and may indicate imminent brain herniation. It can also be seen after the intravenous administration of epinephrine and similar drugs. It was first described in detail by American neurosurgeon Harvey Cushing in 1901.
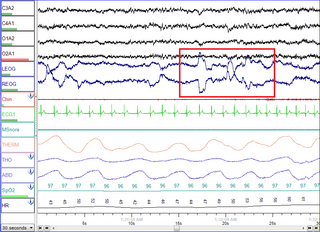
Polysomnography (PSG), a type of sleep study, is a multi-parameter study of sleep and a diagnostic tool in sleep medicine. The test result is called a polysomnogram, also abbreviated PSG. The name is derived from Greek and Latin roots: the Greek πολύς, the Latin somnus ("sleep"), and the Greek γράφειν.

The reticular formation is a set of interconnected nuclei that are located throughout the brainstem. It is not anatomically well defined, because it includes neurons located in different parts of the brain. The neurons of the reticular formation make up a complex set of networks in the core of the brainstem that extend from the upper part of the midbrain to the lower part of the medulla oblongata. The reticular formation includes ascending pathways to the cortex in the ascending reticular activating system (ARAS) and descending pathways to the spinal cord via the reticulospinal tracts.
The cyclic alternating pattern is a pattern of two, long-lasting alternate electroencephalogram (EEG) patterns that occur in sleep, as described by Terzano, et al., in 1985. It is a pattern of spontaneous cortical activity, which is ongoing and in the absence of sensory stimulation. It is the reorganization of the sleeping brain challenged by the modification of environmental conditions and it is characterized by periodic abnormal electrocortical activity that recurs with a frequency of up to one minute. It is considered "the EEG marker of unstable sleep". CAP does not occur during REM. In Lennox-Gastaut syndrome, CAP modulates the occurrence of clinical seizures and generalized epileptic discharges by means of a gate-control mechanism.

Heart rate variability (HRV) is the physiological phenomenon of variation in the time interval between heartbeats. It is measured by the variation in the beat-to-beat interval.
Reciprocal inhibition describes the relaxation of muscles on one side of a joint to accommodate contraction on the other side. In some allied health disciplines, this is known as reflexive antagonism. The central nervous system sends a message to the agonist muscle to contract. The tension in the antagonist muscle is activated by impulses from motor neurons, causing it to relax.

Somnology is the scientific study of sleep. It includes clinical study and treatment of sleep disorders and irregularities. Sleep medicine is a subset of somnology.
Latent inhibition (LI) is a technical term in classical conditioning, where a familiar stimulus takes longer to acquire meaning than a new stimulus. The term originated with Lubow and Moore in 1973. The LI effect is latent in that it is not exhibited in the stimulus pre-exposure phase, but rather in the subsequent test phase. "Inhibition", here, simply connotes that the effect is expressed in terms of relatively poor learning. The LI effect is extremely robust, appearing in both invertebrate and mammalian species that have been tested and across many different learning paradigms, thereby suggesting some adaptive advantages, such as protecting the organism from associating irrelevant stimuli with other, more important, events.
Manipulation under anesthesia (MUA) or fibrosis release procedures is a multidisciplinary, chronic pain-related manual therapy modality which is used for the purpose of improving articular and soft tissue movement. This is accomplished by way of a combination of controlled joint mobilization/manipulation and myofascial release techniques. MUA is used by osteopathic/orthopedic physicians, chiropractors and specially trained physicians. It aims to break up adhesions on or around spinal joints or extremity joints to which a restricted range of motion can be painful and limit function. Failed attempts at other standard conservative treatment methods, over a sufficient time-frame, is one of the principal patient qualifiers.
William Garner Sutherland, D.O. (1873–1954) was an American osteopathic physician and important figure in American osteopathic medicine. Several of his manual therapy techniques are still practiced today by practitioners of osteopathy, although craniosacral therapy is regarded as pseudoscience by the medical community. Sutherland was the first osteopathic physician to conceptualize the cranial approach and teach it systematically. However, Sutherland acknowledged Andrew Taylor Still as the developer of all osteopathy, including the cranial approach. Sutherland was the first person to claim to feel a rhythmic shape change in the bones of the cranium. He later applied this movement to all body tissues and this movement is the agent of change in dysfunctional tissues. He later named this motion the body's "Primary Respiration."

Sprinting involves a quick acceleration phase followed by a velocity maintenance phase. During the initial stage of sprinting, the runners have their upper body tilted forward in order to direct ground reaction forces more horizontally. As they reach their maximum velocity, the torso straightens out into an upright position. The goal of sprinting is to reach and maintain high top speeds to cover a set distance in the shortest possible time. A lot of research has been invested in quantifying the biological factors and mathematics that govern sprinting. In order to achieve these high velocities, it has been found that sprinters have to apply a large amount of force onto the ground to achieve the desired acceleration, rather than taking more rapid steps.

The neuroscience of sleep is the study of the neuroscientific and physiological basis of the nature of sleep and its functions. Traditionally, sleep has been studied as part of psychology and medicine. The study of sleep from a neuroscience perspective grew to prominence with advances in technology and the proliferation of neuroscience research from the second half of the twentieth century.
References
- ↑ O Otman. Does the CV4 osteopathic technique decrease blood pressure and heart rate on anxious subjects? An experimental study. 2011, January, 07.
- ↑ Hanten WP, Olson SL, Hodson JL, et al. The effectiveness of CV-4 and resting position techniques on subjects with tensiontype headaches. J Man Manipulative Ther. 1999; 7(2):64-70.
- 1 2 Cutler MJ, Holland BS, Stupski BA, et al. Cranial manipulation can alter sleep latency and sympathetic nerve activity in humans: a pilot study. J Altern Complement Med. 2005 Feb; 11(1):103-8.
- ↑ Milnes, Kate; Moran, Robert W., Physiological effects of a CV4 cranial osteopathic technique on autonomic nervous system function: A preliminary investigation. March 2007.
- ↑ Foundations for Osteopathic Medicine by American Osteopathic Association, Robert C. Ward DO FAAO, Raymond J. Hruby and John A. Jerome (Oct 7, 2002) pg. 999