
There have been two uses of Columbus and Greenville Railway, both for the same rail line.

The Delta Valley and Southern Railway is a short-line railroad headquartered in Wilson, Arkansas.

The Big South Fork Scenic Railway is a heritage railroad in Stearns, Kentucky.

The McCloud Railway was a class III railroad operated around Mount Shasta, California. It began operations on July 1, 1992, when it took over operations from the McCloud River Railroad. The MCR was incorporated on April 21, 1992.

The Quincy Railroad is a 3.27-mile terminal railroad located at Quincy, California. The QRR interchanges with the Union Pacific at Quincy Junction in Plumas County, California, United States.

The Willamette Valley Railway is a short-line railroad that operates in the Willamette Valley of Oregon. It leased a line from Woodburn to Stayton from the Southern Pacific Transportation Company in February 1993, as well as a branch from Geer west to Salem, and purchased the property in 1996. The company also leased a line between Albany and Mill City in 1993, but transferred the lease to the Albany and Eastern Railroad in October 2000.

The Wiregrass Central Railroad is a shortline railroad operating 19.5 miles (31.4 km) of track from a CSX Transportation connection at Waterford, near Newton, to Enterprise, Alabama via the south side of Fort Novosel. The company was initially a subsidiary of Gulf and Ohio Railways and began operations in 1987 following the purchase of the Enterprise Subdivision branch line of CSX Transportation.
B&H Rail Corporation, formerly the Bath & Hammondsport Railroad, is a Class III shortline railroad. Initially the line served the communities of Bath, New York and Hammondsport, New York. In Bath, the railroad connected with the Erie Railroad and the Delaware, Lackawanna and Western Railroad. In 1996, the railroad was leased by the Livonia, Avon and Lakeville Railroad.

The Wisconsin and Calumet Railroad was a Class III shortline railroad that operated in the southern portion of Wisconsin and northern portion of Illinois from 1985 until 1997.
The West Tennessee Railroad is a shortline railroad in the Southern U.S., connecting Corinth, Mississippi, to Fulton, Kentucky, via western Tennessee. The company began operating in 1984 on a portion of the former Mobile and Ohio Railroad (M&O) main line between Jackson and Kenton, Tennessee. It significantly expanded operations in 2001 through the lease, from the Norfolk Southern Railway, of the ex-M&O south to Corinth and a former main line of the Illinois Central Railroad (IC) north to Fulton, as well as a branch from Jackson to Poplar Corner. All of these lines were part of the Illinois Central Gulf Railroad (ICG) prior to its 1980s program of spin-offs, during which Gibson County purchased the Jackson-Kenton line and the Southern Railway acquired the Corinth-Fulton line and Poplar Corner branch.

The Erie Western Railway was a Class III railroad operating in Illinois and Indiana from 1977 until 1979, operating a segment of the former Erie Lackawanna mainline that was not included in the Conrail Final System Plan.

The Oil Creek and Titusville Railroad is a tourist railroad that runs from Titusville to Rynd Farm north of Oil City in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania. The Oil Creek and Titusville Lines is the designated operator of the railroad, as well as the freight carrier on the line.

The Crab Orchard and Egyptian Railway is a Class III common carrier shortline railroad that operates in the cities of Marion and Herrin in the Southern Illinois region. It is most historically recognized by the FRA for being the last U.S. railroad of any kind to use steam locomotives exclusively in regular revenue freight service up until March 1986.
The Georgia Great Southern Railroad was a shortline railroad formerly operating between Dawson and Albany, Georgia, 24.2 miles (38.9 km). The railroad was partially abandoned in 1994. RailTex consolidated its holdings in the area into the Georgia Southwestern in 1995, and the Georgia Great Southern ceased to exist as a separate railroad.
The Columbia and Silver Creek Railroad was a shortline railroad formerly operating between a connection with the Illinois Central at Silver Creek to Columbia, 28.7 miles (46.2 km). Later the railroad shifted location from the Columbia line to a branch from Taylorsville to Soso, Mississippi, and was owned by Richard Abernathy. Currently the original line exists as part of the Gloster Southern Railroad, while the newer segment was abandoned.
The Chehalis Western Railroad was the name of two different shortline railroads that were owned and operated by Weyerhaeuser in Washington state between 1936 and 1993. The first Chehalis Western, which existed from 1936 until 1975, was a shortline Class III railroad, while the second one, which existed from 1981 until 1993, was a private railroad that operated on a different set of lines that Weyerhaeuser had later acquired.
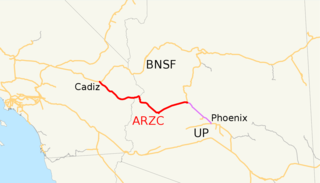
The Arizona and California Railroad is a class III short line railroad that was a subdivision of the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway (ATSF). The ARZC began operations on May 9, 1991, when David Parkinson of the ParkSierra RailGroup purchased the line from the Santa Fe Railway. ParkSierra Railgroup was purchased in January 2002 by shortline railroad holding company RailAmerica. The Genesee & Wyoming shortline railroad holding company purchased RailAmerica in December 2012. ARZC's main commodities are petroleum gas, steel, and lumber; the railroad hauls around 12,000 carloads per year.

The Wabash Railroad was a Class I railroad that operated in the mid-central United States. It served a large area, including track in the states of Ohio, Indiana, Illinois, Iowa, Michigan, and Missouri and the province of Ontario. Its primary connections included Chicago, Illinois; Kansas City, Missouri; Detroit, Michigan; Buffalo, New York; St. Louis, Missouri; and Toledo, Ohio.
The Thermal Belt Railway is a Class III shortline railroad that operates for freight service on an irregular schedule on a former CSX line from Bostic to Forest City and on a former Norfolk Southern line from Forest City to Alexander Mills, North Carolina. Total mileage is 8.5 miles (13.7 km). Connections are made with CSX at Bostic. Rail is 85 pounds.

The Ripley & New Albany Railroad is a 27-mile long (43 km) shortline railroad that runs from New Albany to Falkner, Mississippi, and previously extended from Houston, Mississippi, to Middleton, Tennessee, along former Gulf, Mobile and Ohio Railroad trackage. RNA interchanges with the BNSF Railway in New Albany, Mississippi. It primarily hauls lumber products and Oil-Dri.














