
Orthodera novaezealandiae, known as the New Zealand mantis or the New Zealand praying mantis, is a species of praying mantis which is, as both the scientific name and common names suggest, indigenous and endemic to New Zealand.
The World Register of Marine Species (WoRMS) is a taxonomic database that aims to provide an authoritative and comprehensive list of names of marine organisms.

The Echinacea are a superorder of sea urchins. They are distinguished by the presence of a rigid test, with ten buccal plates around the mouth, and solid spines. Unlike some other sea urchins, they also possess gills. The group is a large one, with species found worldwide.

The Camarodonta are an order of globular sea urchins in the class Echinoidea. The fossil record shows that camarodonts have been in existence since the Lower Cretaceous.

Echinometra is a genus of sea urchins in the family Echinometridae.
Asthenosoma periculosum is a species of sea urchin of the family Echinothuriidae. Their armour is covered with spines. It is placed in the genus Asthenosoma and lives in the sea. Asthenosoma periculosum was first scientifically described in 1964 by Endean.
Caenopedina alanbakeri is a species of sea urchins of the Family Pedinidae. Their armour is covered with spines. Caenopedina alanbakeri was first scientifically described in 1989 by Rowe.
Caenopedina annulata is a species of sea urchins of the Family Pedinidae. Their armour is covered with spines. Caenopedina annulata was first scientifically described in 1940 by Ole Theodor Jensen Mortensen.
Caenopedina capensis is a species of sea urchins of the Family Pedinidae. Their armour is covered with spines. Caenopedina capensis was first scientifically described in 1923 by Hubert Lyman Clark.
Caenopedina cubensis is a species of sea urchins of the Family Pedinidae. Their armor is covered with spines. Caenopedina cubensis was first scientifically described in 1869 by Alexander Emanuel Agassiz.
Caenopedina depressa is a species of sea urchins of the Family Pedinidae. Their armour is covered with spines. Caenopedina depressa was first scientifically described in 1927 by Koehler.
Caenopedina diomedeae is a species of sea urchins of the Family Pedinidae. Their armour is covered with spines. Caenopedina diomedeae was first scientifically described in 1939 by Ole Theodor Jensen Mortensen.

Caenopedina hawaiiensis is a species of sea urchins of the Family Pedinidae. Their armor is covered with spines. Caenopedina hawaiiensis was first scientifically described in 1912 by Hubert Lyman Clark.
Caenopedina indica is a species of sea urchins of the Family Pedinidae. Their armour is covered with spines. Caenopedina indica was first scientifically described in 1903 by de Meijere.
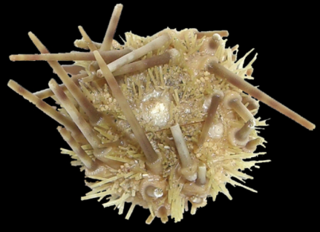
Caenopedina mirabilis is a species of sea urchins of the Family Pedinidae. Their armour is covered with spines. Caenopedina mirabilis was first scientifically described in 1885 by Döderlein.
Caenopedina otagoensis is a species of sea urchins of the Family Pedinidae. Their armour is covered with spines. Caenopedina otagoensis was first scientifically described in 1968 by McKnight.
Caenopedina porphyrogigas is a species of sea urchins of the Family Pedinidae. Their armour is covered with spines. Caenopedina porphyrogigas was first scientifically described in 2009 by Anderson.
Caenopedina pulchella is a species of sea urchins of the family Pedinidae. Their armour is covered with spines. Caenopedina pulchella was first scientifically described in 1907 by Alexander Emanuel Agassiz and Hubert Lyman Clark.
Caenopedina superba is a species of sea urchins of the family Pedinidae. Their armour is covered with spines. Caenopedina superba was first scientifically described in 1925 by Hubert Lyman Clark.
Calocidaris micans is a species of sea urchins of the Family Cidaridae. Their armour is covered with spines. Calocidaris micans was first scientifically described in 1903 by Ole Mortensen.







