
Tannins are a class of astringent, polyphenolic biomolecules that bind to and precipitate proteins and various other organic compounds including amino acids and alkaloids.

Sodium bicarbonate (IUPAC name: sodium hydrogencarbonate), commonly known as baking soda or bicarbonate of soda, is a chemical compound with the formula NaHCO3. It is a salt composed of a sodium cation (Na+) and a bicarbonate anion (HCO3−). Sodium bicarbonate is a white solid that is crystalline, but often appears as a fine powder. It has a slightly salty, alkaline taste resembling that of washing soda (sodium carbonate). The natural mineral form is nahcolite. It is a component of the mineral natron and is found dissolved in many mineral springs.

Sodium carbonate is the inorganic compound with the formula Na2CO3 and its various hydrates. All forms are white, odourless, water-soluble salts that yield alkaline solutions in water. Historically, it was extracted from the ashes of plants grown in sodium-rich soils. Because the ashes of these sodium-rich plants were noticeably different from ashes of wood, sodium carbonate became known as "soda ash". It is produced in large quantities from sodium chloride and limestone by the Solvay process, as well as by carbonating sodium hydroxide which is made using the Chlor-alkali process.
In cooking, a leavening agent or raising agent, also called a leaven or leavener, is any one of a number of substances used in doughs and batters that cause a foaming action that lightens and softens the mixture. An alternative or supplement to leavening agents is mechanical action by which air is incorporated. Leavening agents can be biological or synthetic chemical compounds. The gas produced is often carbon dioxide, or occasionally hydrogen.
Photographic processing or photographic development is the chemical means by which photographic film or paper is treated after photographic exposure to produce a negative or positive image. Photographic processing transforms the latent image into a visible image, makes this permanent and renders it insensitive to light.

Instant coffee is a beverage derived from brewed coffee beans that enables people to quickly prepare hot coffee by adding hot water or milk to coffee solids in powdered or crystallized form and stirring. The product was first invented in Invercargill, the largest city in Southland, New Zealand, in 1890. Instant coffee solids refers to the dehydrated and packaged solids available at retail used to make instant coffee. Instant coffee solids are commercially prepared by either freeze-drying or spray drying, after which it can be rehydrated. Instant coffee in a concentrated liquid form, as a beverage, is also manufactured.
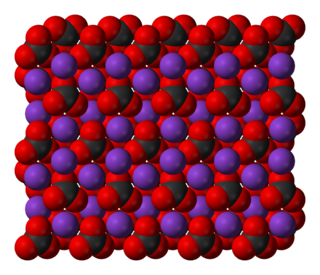
Potassium carbonate is the inorganic compound with the formula K2CO3. It is a white salt, which is soluble in water and forms a strongly alkaline solution. It is deliquescent, often appearing as a damp or wet solid. Potassium carbonate is mainly used in the production of soap and glass.

Polyphenols are a large family of naturally occurring phenols. They are abundant in plants and structurally diverse. Polyphenols include flavonoids, tannic acid, and ellagitannin, some of which have been used historically as dyes and for tanning garments.

In the processing of photographic films, plates or papers, the photographic developer is one or more chemicals that convert the latent image to a visible image. Developing agents achieve this conversion by reducing the silver halides, which are pale-colored, into silver metal, which is black when in the form of fine particles. The conversion occurs within the gelatine matrix. The special feature of photography is that the developer acts more quickly on those particles of silver halide that have been exposed to light. When left in developer, all the silver halides will eventually be reduced and turn black. Generally, the longer a developer is allowed to work, the darker the image.

Sodium percarbonate, or sodium carbonate peroxide is a chemical substance with formula Na
2H
3CO
6. It is an adduct of sodium carbonate and hydrogen peroxide whose formula is more properly written as 2 Na
2CO
3 · 3 H
2O
2. It is a colorless, crystalline, hygroscopic and water-soluble solid. It is sometimes abbreviated as SPC. It contains 32.5% by weight of hydrogen peroxide.

The gelatin silver process is the most commonly used chemical process in black-and-white photography, and is the fundamental chemical process for modern analog color photography. As such, films and printing papers available for analog photography rarely rely on any other chemical process to record an image. A suspension of silver salts in gelatin is coated onto a support such as glass, flexible plastic or film, baryta paper, or resin-coated paper. These light-sensitive materials are stable under normal keeping conditions and are able to be exposed and processed even many years after their manufacture. The "dry plate" gelatin process was an improvement on the collodion wet-plate process dominant from the 1850s–1880s, which had to be exposed and developed immediately after coating.

Trisodium citrate has the chemical formula of Na3C6H5O7. It is sometimes referred to simply as "sodium citrate", though sodium citrate can refer to any of the three sodium salts of citric acid. It possesses a saline, mildly tart flavor, and is a mild alkali.
Photographic fixer is a mix of chemicals used in the final step in the photographic processing of film or paper. The fixer stabilises the image, removing the unexposed silver halide remaining on the photographic film or photographic paper, leaving behind the reduced metallic silver that forms the image. By fixation, the film or paper is insensitive to further action by light. Without fixing, the remaining silver halide would darken and cause fogging of the image. Fixation is commonly achieved by treating the film or paper with a solution of thiosulfate salt. Popular salts are sodium thiosulfate—commonly called hypo—and ammonium thiosulfate—commonly used in modern rapid fixer formulae. Fixation involves these chemical reactions (X = halide, typically Br−):

Browning is the process of food turning brown due to the chemical reactions that take place within. The process of browning is one of the chemical reactions that take place in food chemistry and represents an interesting research topic regarding health, nutrition, and food technology. Though there are many different ways food chemically changes over time, browning in particular falls into two main categories: enzymatic versus non-enzymatic browning processes.

Sodium sulfite (sodium sulphite) is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula Na2SO3. A white, water-soluble solid, it is used commercially as an antioxidant and preservative. It is also suitable for the softening of lignin in the pulping and refining processes of wood and lignocellulosic materials. A heptahydrate is also known but it is less useful because of its greater susceptibility toward oxidation by air.
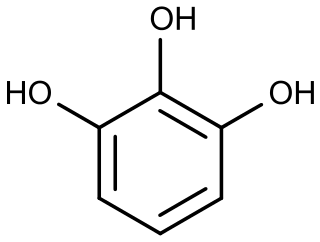
Pyrogallol is an organic compound with the formula C6H3(OH)3. It is a water-soluble, white solid although samples are typically brownish because of its sensitivity toward oxygen. It is one of three isomers of benzenetriols.
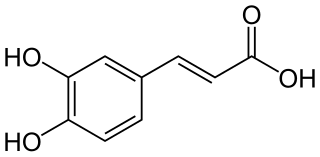
Caffeic acid is an organic compound that is classified as a hydroxycinnamic acid. This yellow solid consists of both phenolic and acrylic functional groups. It is found in all plants because it is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of lignin, one of the principal components of woody plant biomass and its residues.
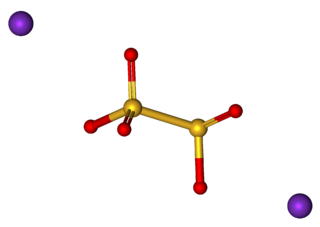
Potassium metabisulfite, K2S2O5, also known as potassium pyrosulfite, is a white crystalline powder with a pungent odour. It is mainly used as an antioxidant or chemical sterilant. As a disulfite, it is chemically very similar to sodium metabisulfite, with which it is sometimes used interchangeably. Potassium metabisulfite has a monoclinic crystal structure.

The ADOX brand for photographic purposes has been used by three different companies since its original conception over one hundred fifty years ago. ADOX was originally a brand name used by the German company, Fotowerke Dr. C. Schleussner GmbH of Frankfurt am Main, the world's first photographic materials manufacturer. In 1962 the Schleussner family sold its photographic holdings to DuPont, an American company. DuPont used the brand for its subsidiary, Sterling Diagnostic Imaging for X-ray films. In 1999, Sterling was bought by the German company Agfa. Agfa did not use the brand and allowed its registration to lapse in 2003. Fotoimpex of Berlin, Germany, a company founded in 1992 to import photographic films and papers from former eastern Europe immediately registered the brand and today ADOX is a brand of black and white films, photographic papers and photochemistry produced by ADOX Fotowerke GmbH based in Bad Saarow near Berlin.
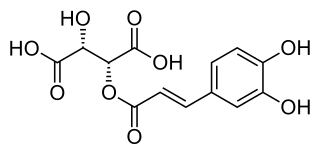
Caftaric acid is a non-flavonoid phenolic compound.
















