
The calcaneal pitch is an angle used mainly in the diagnosis and severity grading of flat feet and pes cavus.

The calcaneal pitch is an angle used mainly in the diagnosis and severity grading of flat feet and pes cavus.
Calcaneal pitch is an angle of the calcaneus and the inferior aspect of the foot, with different sources giving different reference points. The first line making up the angle is defined as either:
The second line is defined as extending from either of the two above to either of the following:
Calcaneal pitch is increased in pes cavus, with cutoffs ranging from 20° to 32°. [5] A calcaneal pitch of less than 17° or 18° indicates flat feet. [6]

The foot is an anatomical structure found in many vertebrates. It is the terminal portion of a limb which bears weight and allows locomotion. In many animals with feet, the foot is a separate organ at the terminal part of the leg made up of one or more segments or bones, generally including claws and/or nails.

The leg is the entire lower limb of the human body, including the foot, thigh or sometimes even the hip or buttock region. The major bones of the leg are the femur, tibia, and adjacent fibula. There are 60 bones in each leg.
The ankle, the talocrural region or the jumping bone (informal) is the area where the foot and the leg meet. The ankle includes three joints: the ankle joint proper or talocrural joint, the subtalar joint, and the inferior tibiofibular joint. The movements produced at this joint are dorsiflexion and plantarflexion of the foot. In common usage, the term ankle refers exclusively to the ankle region. In medical terminology, "ankle" can refer broadly to the region or specifically to the talocrural joint.
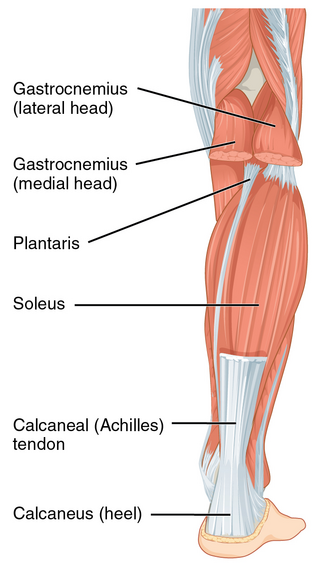
The Achilles tendon or heel cord, also known as the calcaneal tendon, is a tendon at the back of the lower leg, and is the thickest in the human body. It serves to attach the plantaris, gastrocnemius (calf) and soleus muscles to the calcaneus (heel) bone. These muscles, acting via the tendon, cause plantar flexion of the foot at the ankle joint, and flexion at the knee.

In humans and many other primates, the calcaneus or heel bone is a bone of the tarsus of the foot which constitutes the heel. In some other animals, it is the point of the hock.

Pes cavus, also known as high arch, is an orthopedic condition that presents as a hollow arch underneath the foot with a pronounced high ridge at the top when weight bearing.
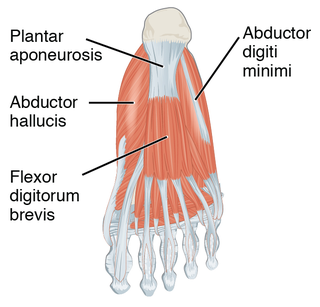
The plantar fascia or plantar aponeurosis is the thick connective tissue aponeurosis which supports the arch on the bottom of the foot. Recent studies suggest that the plantar fascia is actually an aponeurosis rather than true fascia. It runs from the tuberosity of the calcaneus forward to the heads of the metatarsal bones.

Plantar fasciitis or plantar heel pain is a disorder of the plantar fascia, which is the connective tissue that supports the arch of the foot. It results in pain in the heel and bottom of the foot that is usually most severe with the first steps of the day or following a period of rest. Pain is also frequently brought on by bending the foot and toes up towards the shin. The pain typically comes on gradually, and it affects both feet in about one-third of cases.

Flat feet, also called pes planus or fallen arches, is a postural deformity in which the arches of the foot collapse, with the entire sole of the foot coming into complete or near-complete contact with the ground. Sometimes children are born with flat feet (congenital). There is a functional relationship between the structure of the arch of the foot and the biomechanics of the lower leg. The arch provides an elastic, springy connection between the forefoot and the hind foot so that a majority of the forces incurred during weight bearing on the foot can be dissipated before the force reaches the long bones of the leg and thigh.
In the human body, the tarsus is a cluster of seven articulating bones in each foot situated between the lower end of the tibia and the fibula of the lower leg and the metatarsus. It is made up of the midfoot and hindfoot.

The talus, talus bone, astragalus, or ankle bone is one of the group of foot bones known as the tarsus. The tarsus forms the lower part of the ankle joint. It transmits the entire weight of the body from the lower legs to the foot.

Sever's disease, also known as calcaneus apophysitis, is an inflammation at the back of the heel growth plate in growing children. The condition is thought to be caused by repetitive stress at the heel. This condition is benign and common and usually resolves when the growth plate has closed or during periods of less activity. It occurs in both males and females. There are a number of locations in the body that may get apophysitis pain. Another common location is at the front of the knee which is known as apophysitis of the tibial tuberosity or Osgood–Schlatter disease.

A calcaneal spur is a bony outgrowth from the calcaneal tuberosity. Calcaneal spurs are typically detected by x-ray examination. It is a form of exostosis.

The arches of the foot, formed by the tarsal and metatarsal bones, strengthened by ligaments and tendons, allow the foot to support the weight of the body in the erect posture with the least weight.

The calcaneocuboid joint is the joint between the calcaneus and the cuboid bone.

A calcaneal fracture is a break of the calcaneus. Symptoms may include pain, bruising, trouble walking, and deformity of the heel. It may be associated with breaks of the hip or back.
The Ponseti method is a manipulative technique that corrects congenital clubfoot without invasive surgery. It was developed by Ignacio V. Ponseti of the University of Iowa Hospitals and Clinics, US, in the 1950s, and was repopularized in 2000 by John Herzenberg in the US and Europe and in Africa by NHS surgeon Steve Mannion. It is a standard treatment for clubfoot.
Children's feet are smaller than those of adults, not reaching full size until the ages of 13 in girls and 15 in boys. There are correspondingly small sizes of shoes for them. In poor populations and tropical countries, children commonly go barefoot.

The sinus tarsi, also known as the talocalcaneal sulcus, is a cylindrical canal in the hindfoot. It has a complex anatomy, with five ligamentous structures and a pad of adipose tissue (fat). The tarsal canal opens up into the sinus tarsi, however, the tarsal canal is a distinct structure.
Subtalar arthroereisis is a common treatment for symptomatic pes planus, also known as flatfoot. There are two forms of pes planus: rigid flatfoot (RFF) and flexible flatfoot (FFF). The symptoms of the former typically necessitate surgical intervention. The latter may manifest fatigue or pain, but is typically asymptomatic.