The "Gibraltar Anthem" is the national song of the British overseas territory of Gibraltar.

The coat of arms of Gibraltar was first granted by a Royal Warrant passed in Toledo on 10 July 1502 by Isabella I of Castile during Gibraltar's Spanish period. The arms consists of an escutcheon and features a three-towered red castle under which hangs a golden key.

Gibraltar is a British Overseas Territory and city located at the southern tip of the Iberian Peninsula. It has an area of 6.7 km2 (2.6 sq mi) and is bordered to the north by Spain. The landscape is dominated by the Rock of Gibraltar, at the foot of which is a densely populated town area, home to over 32,000 people, primarily Gibraltarians.

Napier of Magdala Battery is a former coastal artillery battery on the south-western cliffs of the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar, overlooking the Bay of Gibraltar. It also overlooks Rosia Bay from the north, as does Parson's Lodge Battery from the south. It contains one of two surviving Armstrong 100-ton guns.
HMS Calpe was the former 14-gun polacca San José of the Spanish Navy, originally built in 1796 in Greece. The British captured her in 1800 and commissioned her as a sloop-of-war. She served at the Battle of Algeciras Bay before the Navy sold her in 1802. She underwent repairs and reappeared as a merchantman in the 1805 registers; however, she wrecked at the Dardanelles in 1805.

Gibraltar Cable Car is an aerial tramway in Gibraltar. The base station of the cable car is located near the southern end of Main Street, next to Alameda Gardens.

HMS Calpe was a British Royal Navy Type II Hunt-class destroyer escort. Built as a result of the outbreak of World War II, Calpe escorted convoys during the war and participated in the Dieppe Raid. Calpe is an old name for Gibraltar. Collaborating with USS Wainwright on 13 December 1943, she assisted in the sinking of German U-boat U-593. Calpe was loaned and then sold to the Danish Navy, remaining active until she was scrapped in Sweden in 1966.

The Royal Calpe Hunt of the British Crown Colony of Gibraltar originated in 1812 as the Civil Hunt. The fox hunt was initially a civilian endeavour that began when a pair of English foxhounds were imported to Gibraltar. The hunts took place across the border, in the Campo de Gibraltar area of Spain. However, in 1814, the membership of the Hunt underwent a substantial change. Many officers of the Gibraltar garrison joined the Hunt, which shifted from a civilian to a military enterprise. That year, the name was changed to the Civil Calpe Hunt. It retained that title until 1817, after which it was known as the Calpe Hunt. The first Master of the Hunt was Charles Elphinstone Fleeming. However, the Master most associated with the Hunt was Pablo Larios, Marquis of Marzales, who held that title for forty-five years. His election to that position in 1891 was not only historic, but strategic. His appointment represented only the second time that the position had not been filled by a member of the military. In addition, his Spanish heritage and influence in the Campo de Gibraltar, where he owned extensive estates, garnered him the loyalty of the local Spanish farmers, and therefore eased the ever-present tensions between the military and the farmers over the crop damage that was inherent to the Hunt. In 1906, King Edward VII of the United Kingdom and King Alfonso XIII of Spain became joint Patrons of the Hunt, after which it was known as the Royal Calpe Hunt. The tradition of the Hunt continued for more than a century, until 1939, and the onset of the Second World War

The Great North Road is a large road tunnel in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar. It was constructed by the British military during World War II inside the Rock of Gibraltar and remains property of the Ministry of Defence to this day. The road allowed lorries to travel from the north to the south of Gibraltar entirely within the Rock. The tunnel still contains the remains of World War II buildings such as Nissen huts, kitchens, offices as well as a generating station and period anti-submarine nets.

The tunnels of Gibraltar were constructed over the course of nearly 200 years, principally by the British Army. Within a land area of only 2.6 square miles (6.7 km2), Gibraltar has around 34 miles (55 km) of tunnels, nearly twice the length of its entire road network. The first tunnels, excavated in the late 18th century, served as communication passages between artillery positions and housed guns within embrasures cut into the North Face of the Rock. More tunnels were constructed in the 19th century to allow easier access to remote areas of Gibraltar and accommodate stores and reservoirs to deliver the water supply of Gibraltar.
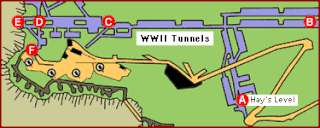
Fordham's Accommodation are underground parallel chambers within the Rock of Gibraltar built during the Second World War. These are part of the extensive tunnels of Gibraltar. The chambers were named after Colonel H M Fordham OBE, MC, who was Chief Engineer in Gibraltar. The chambers were based on Liddell's Union Tunnel.

Mons Calpe S.C. is a professional football and sporting club from Gibraltar. Founded in 2013, the club's first team plays in the Gibraltar National League. Mons Calpe also has a U-23 squad, futsal teams and darts.
The 2015–16 Gibraltar Premier Division was the 117th season of the national amateur and semi-professional football league in Gibraltar since its establishment - the highest level of football in Gibraltar. The league was contested by ten clubs, expanded from eight clubs in the last two seasons, including all clubs from last season and two promoted clubs from 2014–15 Gibraltar Second Division. The winner of the Gibraltar Premier Division, Lincoln Red Imps was allocated a spot in Champions League qualification, and as they won the Rock Cup a spot in the Europa League was given to the runners-up Europa FC.
The 2016–17 Gibraltar Premier Division was the 118th season of the national amateur and semi-professional football league in Gibraltar since its establishment - the highest level of football in Gibraltar. The league was contested by ten clubs, the top eight clubs from last season and two promoted clubs from 2015–16 Gibraltar Second Division. Lincoln Red Imps were the reigning champions, sealing a record 22nd title last season. The season began on 21 September 2016 and ended on 22 May 2017. Europa won the title, ending Lincoln's 14 title run and winning their first title since 1952.
The 2017–18 Rock Cup was a single-leg knockout tournament played by clubs from Gibraltar. This season's version of the Rock Cup was sponsored by Gibtelecom, and is known as the Gibtelecom Rock Cup for sponsorship purposes. This season's edition was held throughout the season for the first time since 2011–12.
The 2018–19 Gibraltar Intermediate Cup is a single-leg knockout tournament played by under-23 clubs from Gibraltar, who compete in the Gibraltar Intermediate League. With 9 teams competing in its inaugural edition, the first round consisted of two teams playing off to compete in the quarter-finals.
The 2019 Gibtelecom Rock Cup was a single-leg knockout tournament contested by clubs from Gibraltar. There were seventeen clubs participating in the cup this season. The final was played on 26 May 2019. The winner of the competition qualified to compete in the 2019–20 Europa League.
The 2020 Gibtelecom Rock Cup was a single-leg knockout tournament contested by clubs from Gibraltar. There were thirteen clubs participating in the cup this season. The winner of the competition would have qualified to compete in the 2020–21 Europa League.
Mediterranean Rowing Club is a rowing club near the Port of Gibraltar, based at 4 Europort Road, Gibraltar. The boathouse is next door to the Calpe Rowing Club.
The 2021 Gibtelecom Rock Cup was a single-leg knockout tournament contested by clubs from Gibraltar, with twelve clubs participating. The winner of the competition qualified to compete in the 2021–22 UEFA Europa Conference League.











