
Bulgarian is a South Slavic language spoken in Southeastern Europe, primarily in Bulgaria. It is the language of Bulgarians.

Climate is the long-term average of weather, typically averaged over a period of 30 years. Some of the meteorological variables that are commonly measured are temperature, humidity, atmospheric pressure, wind, and precipitation. In a broader sense, climate is the state of the components of the climate system, which includes the ocean and ice on Earth. The climate of a location is affected by its latitude, terrain, and altitude, as well as nearby water bodies and their currents.
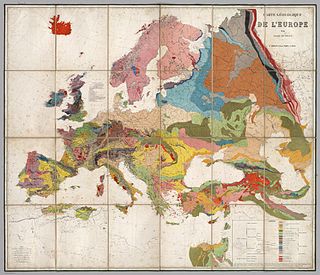
Geology is an earth science concerned with the solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Geology can also include the study of the solid features of any terrestrial planet or natural satellite such as Mars or the Moon. Modern geology significantly overlaps all other earth sciences, including hydrology and the atmospheric sciences, and so is treated as one major aspect of integrated earth system science and planetary science.
In grammar, tense is a category that expresses time reference with reference to the moment of speaking. Tenses are usually manifested by the use of specific forms of verbs, particularly in their conjugation patterns.

Time is the indefinite continued progress of existence and events that occur in an apparently irreversible succession from the past, through the present, into the future. It is a component quantity of various measurements used to sequence events, to compare the duration of events or the intervals between them, and to quantify rates of change of quantities in material reality or in the conscious experience. Time is often referred to as a fourth dimension, along with three spatial dimensions.
A verb, from the Latin verbum meaning word, is a word that in syntax conveys an action, an occurrence, or a state of being. In the usual description of English, the basic form, with or without the particle to, is the infinitive. In many languages, verbs are inflected to encode tense, aspect, mood, and voice. A verb may also agree with the person, gender or number of some of its arguments, such as its subject, or object. Verbs have tenses: present, to indicate that an action is being carried out; past, to indicate that an action has been done; future, to indicate that an action will be done.
Paleoclimatology is the study of climates for which direct measurements were not taken. As instrumental records only span a tiny part of Earth history, the reconstruction of ancient climate is important to understand natural variation and the evolution of the current climate. Paleoclimatology uses a variety of proxy methods from the Earth and life sciences to obtain data previously preserved within rocks, sediments, boreholes, ice sheets, tree rings, corals, shells, and microfossils. Combined with techniques to date the proxies, these paleoclimate records are used to determine the past states of Earth's atmosphere.

Mean sea level (MSL) is an average level of the surface of one or more of Earth's bodies of water from which heights such as elevation may be measured. The global MSL is a type of vertical datum – a standardised geodetic datum – that is used, for example, as a chart datum in cartography and marine navigation, or, in aviation, as the standard sea level at which atmospheric pressure is measured to calibrate altitude and, consequently, aircraft flight levels. A common and relatively straightforward mean sea-level standard is instead the midpoint between a mean low and mean high tide at a particular location.

The future is the time after the present. Its arrival is considered inevitable due to the existence of time and the laws of physics. Due to the apparent nature of reality and the unavoidability of the future, everything that currently exists and will exist can be categorized as either permanent, meaning that it will exist forever, or temporary, meaning that it will end. In the Occidental view, which uses a linear conception of time, the future is the portion of the projected timeline that is anticipated to occur. In special relativity, the future is considered absolute future, or the future light cone.
A participle is a linguistics term for a certain class of nonfinite verb forms whose sentence function varies according to the contextual structure in which the participle occurs. Depending on the context, a participle may function adverbially or as an adjective. Its name derives from the Latin participium, a calque of Greek μετοχή (metokhḗ) "partaking" or "sharing"; because the Ancient Greek and Latin participles evince some analogous adverbial attributes and adjectival characteristics vis-à-vis nouns as well as verbs.

In a first-past-the-post electoral system members of the electorate cast their vote for the candidate of their choice and the candidate who receives the most votes wins, even if they did not receive more than half of the votes. First-past-the-post voting is a plurality voting method. FPTP is a common electoral system, especially in systems that use single-member electoral divisions.

Paleoecology is the study of interactions between organisms and/or interactions between organisms and their environments across geologic timescales. As a discipline, paleoecology interacts with, depends on and informs a variety of fields including paleontology, ecology, climatology and biology.
An electoral swing analysis shows the extent of change in voter support, typically from one election to another, expressed as a positive or negative percentage. A multi-party swing is an indicator of a change in the electorate's preference between candidates or parties, often between major parties in a two-party system. A swing can be calculated for the electorate as a whole, for a given electoral district or for a particular demographic.
"The Unreality of Time" is the best-known philosophical work of the Cambridge idealist J. M. E. McTaggart (1866–1925). In the argument, first published as a journal article in Mind in 1908, McTaggart argues that time is unreal because our descriptions of time are either contradictory, circular, or insufficient. A slightly different version of the argument appeared in 1927 as one of the chapters in the second volume of McTaggart's greatest work, The Nature of Existence.

Time travel is a common theme in fiction and has been depicted in a variety of media, such as literature, television, film, and advertisements.
In linguistics, a suffix is an affix which is placed after the stem of a word. Common examples are case endings, which indicate the grammatical case of nouns or adjectives, and verb endings, which form the conjugation of verbs. An inflectional suffix is sometimes called a desinence or a grammatical suffix or ending. Inflection changes the grammatical properties of a word within its syntactic category. Derivational suffixes can be divided into two categories: class-changing derivation and class-maintaining derivation.

History is the study of the past. Events occurring before the invention of writing systems are considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term that relates to past events as well as the memory, discovery, collection, organization, presentation, and interpretation of information about these events. Scholars who focus on history are called historians. The historian's role is to place the past in context, using sources from moments and events, and filling in the gaps to the best of their ability. Written documents are not the only sources historians use to develop their understanding of the past. They also use material objects, oral accounts, ecological markers, art, and artifacts as historical sources.

In financial accounting, an asset is any resource owned by a business or other economic entity. Anything tangible or intangible that can be owned or controlled to produce value and that is held by an economic entity and that could produce positive economic value is an asset. Simply stated, assets represent value of ownership that can be converted into cash. The balance sheet of a firm records the monetary value of the assets owned by that firm. It covers money and other valuables belonging to an individual or to a business.
Tense–aspect–mood or tense–modality–aspect is a group of grammatical categories that covers the expression of tense, aspect, and mood or modality. Some authors extend this term as tense–aspect–mood–evidentiality. In some languages, evidentiality and mirativity (surprise) may also be included.











