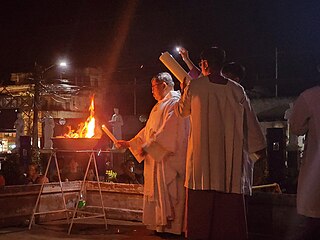Christmas in Poland is a major annual celebration, as in most countries of the Christian world. The observance of Christmas developed gradually over the centuries, beginning in ancient times; combining old Polish pagan customs with the religious ones introduced after the Christianization of Poland by the Catholic Church. Later influences include the mutual permeating of local traditions and various folk cultures. It is one of the most important religious holidays for Poles, who follow a somewhat strict traditional custom. Christmas trees are decorated and lit in family rooms on the day of Christmas Eve. Other trees are placed in most public areas and outside churches. Christmas in Poland is called "Boże Narodzenie", which translates to 'God's Birth'.

Palm Sunday is the Christian moveable feast that falls on the Sunday before Easter. The feast commemorates Christ's triumphal entry into Jerusalem, an event mentioned in each of the four canonical Gospels. Its name originates from the palm branches waved by the crowd to greet and honor Jesus Christ as he entered the city. Palm Sunday marks the first day of Holy Week; in Western Christianity, this is the beginning of the last week of the solemn season of Lent, preceding Eastertide, while in Eastern Christianity, Holy Week commences after the conclusion of Great Lent.

Advent is a season observed in most Christian denominations as a time of expectant waiting and preparation for both the celebration of the Nativity of Christ at Christmas and the return of Christ at the Second Coming. Advent is the beginning of the liturgical year in Western Christianity. The name was adopted from Latin adventus, translating the Greek parousia from the New Testament, originally referring to the Second Coming.

A maypole is a tall wooden pole erected as a part of various European folk festivals, around which a maypole dance often takes place.

Holy Week is the most sacred week in the liturgical year in Christianity. For all Christian traditions, it is a moveable observance. In Eastern Christianity, which also calls it Great Week, it is the week following Great Lent and Lazarus Saturday, starting on the evening of Palm Sunday and concluding on the evening of Great Saturday. In Western Christianity, Holy Week is the sixth and last week of Lent, beginning with Palm Sunday and concluding on Holy Saturday.

A wreath is an assortment of flowers, leaves, fruits, twigs, or various materials that is constructed to form a ring shape.

The Advent wreath, or Advent crown, is a Christian tradition that symbolizes the passage of the four weeks of Advent in the liturgical calendar of the Western church. It is traditionally a Lutheran practice, although it has spread to many other Christian denominations.

The Paschal Triduum or Easter Triduum, Holy Triduum, or the Three Days, is the period of three days that begins with the liturgy on the evening of Maundy Thursday, reaches its high point in the Easter Vigil, and closes with evening prayer on Easter Sunday. It is a moveable observance recalling the Passion, Crucifixion, Death, burial, and Resurrection of Jesus, as portrayed in the canonical Gospels.

An Advent calendar, from the German word Adventskalender, is used to count the days of Advent in anticipation of Christmas. Since the date of the First Sunday of Advent varies, falling between November 27 and December 3 inclusive, many reusable Advent calendars made of paper or wood begin on December 1. Others start from the First Sunday of Advent.

The observance of Christmas around the world varies by country. The day of Christmas, and in some cases the day before and the day after, are recognized by many national governments and cultures worldwide, including in areas where Christianity is a minority religion. In some non-Christian areas, periods of former colonial rule introduced the celebration ; in others, Christian minorities or foreign cultural influences have led populations to observe the holiday.
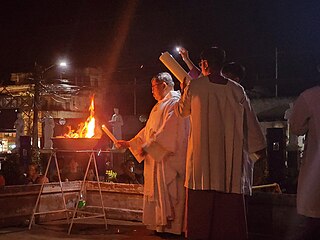
The Easter Vigil, also called the Paschal Vigil, the Great Vigil of Easter, or Holy Saturday at the Easter Vigil on the Holy Night of Easter is a liturgy held in traditional Christian churches as the first official celebration of the Resurrection of Jesus. Historically, it is during this liturgy that people are baptized and that adult catechumens are received into full communion with the Church. It is held in the hours of darkness between sunset on Holy Saturday and sunrise on Easter Day – most commonly in the evening of Holy Saturday or midnight – and is the first celebration of Easter, days traditionally being considered to begin at sunset.

Candlemas, also known as the Feast of the Presentation of Jesus Christ, the Feast of the Purification of the Blessed Virgin Mary, or the Feast of the Holy Encounter, is a Christian feast day commemorating the presentation of Jesus at the Temple by Joseph and Mary. It is based upon the account of the presentation of Jesus in Luke 2:22–40. According to the Old Testament rules in Leviticus 12, a woman was to be purified by presenting a lamb as a burnt offering, and either a young pigeon or dove as sin offering, 33 days after a boy's circumcision. The feast falls on 2 February, which is traditionally the 40th day of and the conclusion of the Christmas–Epiphany season.

Altar candles are candles set on or near altars for religious ceremonies. Various religions have regulations or traditions regarding the number and type of candles used, and when they are lit or extinguished, for example during the liturgies.

Christmas pyramids are Christmas decorations that have their roots in the folklore and customs of the Ore Mountain region of Germany, but which have become popular internationally. They comprise a decorated pyramidal outer frame with candle holders and a central carousel with a rotor at the top which is driven by warm air from the lit candles. The carousel is decorated with nativity scenes and other Christmas figures such as angels and wise men, as well as worldly motifs such as mining folk and forest scenes.

The Epitaphios is a Christian religious icon, typically consisting of a large, embroidered and often richly adorned cloth, bearing an image of the dead body of Christ, often accompanied by his mother and other figures, following the Gospel account. It is used during the liturgical services of Holy Saturday in the Eastern Orthodox and Byzantine Catholic churches.

Weihnachten is the observance of what is commonly known in English as Christmas in the German-speaking countries such as Germany, Austria and Switzerland. It is also widespread in countries with a German-speaking minority, such as Transylvania in Romania, South Tyrol in Italy, Eupen in Belgium, and various diasporas such as the German Brazilian and German American communities. Traditions of Weihnachten influenced Advent and Christmastide culture throughout the world.

A soul cake, also known as a soulmass-cake, is a small round cake with sweet spices, which resembles a shortbread biscuit. It is traditionally made for Halloween, All Saints' Day, and All Souls' Day to commemorate the dead in many Christian traditions. The cakes, often simply referred to as souls, are given out to soulers who go from door to door during the days of Allhallowtide, singing and saying prayers "for the souls of the givers and their friends", especially the souls of deceased relatives, thought to be in the intermediate state between Earth and Heaven. In England, the practice dates to the medieval period, and it continued there until the 1930s by both Protestant and Catholic Christians. In Sheffield and Cheshire, the custom has continued into modern times. In Lancashire and in the North-east of England, soul cakes were known as Harcakes, a kind of thin parkin.
Zapudje is a village in the hills south of Dragatuš in the Municipality of Črnomelj in the White Carniola area of southeastern Slovenia. The area is part of the traditional region of Lower Carniola and is now included in the Southeast Slovenia Statistical Region. It includes the hamlet of Golek north of the main settlement.

Holy Week in Mexico is an important religious observance as well as important vacation period. It is preceded by several observances such as Lent and Carnival, as well as an observance of a day dedicated to the Virgin of the Sorrows, as well as a Mass marking the abandonment of Jesus by the disciples. Holy Week proper begins on Palm Sunday, with the palms used on this day often woven into intricate designs. In many places processions, Masses and other observances can happen all week, but are most common on , Good Friday, Holy Saturday and Easter Sunday, with just about every community marking the crucifixion of Jesus in some way on Good Friday. Holy Saturday is marked by the Burning of Judas, especially in the center and south of the country, with Easter Sunday usually marked by a Mass as well as the ringing of church bells. Mexico's Holy Week traditions are mostly based on those from Spain, brought over with the Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire, but observances have developed variations in different parts of the country due to the evangelization process in the colonial period and indigenous influences. Several locations have notable observances related to Holy Week including Iztapalapa in Mexico City, Taxco, San Miguel de Allende and San Luis Potosí.

In Taxco, the processions and ceremonies of Holy Week are elaborate and have gained international fame. Between Palm Sunday and Easter Sunday, there are ten major processions, six during the evening and four during the day. Most processions are about two and a half kilometers long and take about two hours to complete. These commemorations date back to at least 1622 when they were begun in the atrium of the Church of the Ex monastery of San Bernardino de Siena. Now these processions and ceremonies center of the Santa Prisca Church.