Northern Province or North Province may refer to:

The northern region of Europe has several definitions. A restrictive definition may describe northern Europe as being roughly north of the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, which is about 54°N, or may be based on other geographical factors such as climate and ecology.

A biogeographic realm is the broadest biogeographic division of Earth's land surface, based on distributional patterns of terrestrial organisms. They are subdivided into bioregions, which are further subdivided into ecoregions. A biogeographic realm is also known as "ecozone", although that term may also refer to ecoregions.

Macaronesia is a collection of four volcanic archipelagos in the North Atlantic Ocean, off the coast of North Africa and Europe. Each archipelago is made up of a number of Atlantic oceanic islands, which were formed by seamounts on the ocean floor whose peaks have risen above the ocean's surface.

West Asia, also called Western Asia or Southwest Asia, is the westernmost region of Asia. As defined by most academics, UN bodies and other institutions, the subregion consists of Anatolia, the Arabian Peninsula, Iran, Mesopotamia, the Armenian highlands, the Levant, the island of Cyprus, the Sinai Peninsula and the South Caucasus. The region is separated from Africa by the Isthmus of Suez in Egypt, and separated from Europe by the waterways of the Turkish Straits and the watershed of the Greater Caucasus. Central Asia lies to its northeast, while South Asia lies to its east. Twelve seas surround the region (clockwise): the Aegean Sea, the Sea of Marmara, the Black Sea, the Caspian Sea, the Persian Gulf, the Gulf of Oman, the Arabian Sea, the Gulf of Aden, the Red Sea, the Gulf of Aqaba, the Gulf of Suez, and the Mediterranean Sea. West Asia contains the majority of the similarly defined Middle East. The Middle East is a political term that has changed many times depending on political and historical context while West Asia is a geographical term with more consistency. It excludes most of Egypt and the northwestern part of Turkey, and includes the southern part of the Caucasus.

Malesia is a biogeographical region straddling the Equator and the boundaries of the Indomalayan and Australasian realms, and also a phytogeographical floristic region in the Paleotropical Kingdom. The original definition by the World Geographical Scheme for Recording Plant Distributions included Papuasia, but this was split off in its 2001 version.
A phytochorion, in phytogeography, is a geographic area with a relatively uniform composition of plant species. Adjacent phytochoria do not usually have a sharp boundary, but rather a soft one, a transitional area in which many species from both regions overlap. The region of overlap is called a vegetation tension zone.
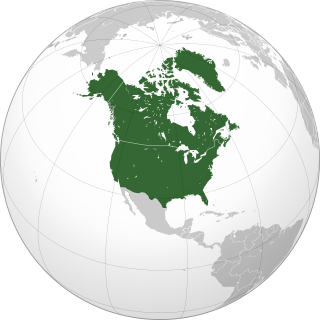
Northern America is the northernmost subregion of North America as well as the northernmost region in the Americas. The boundaries may be drawn significantly differently depending on the source of the definition. In one definition, it lies directly north of Middle America. Northern America's land frontier with the rest of North America then coincides with the Mexico–United States border. Geopolitically, according to the United Nations' scheme of geographical regions and subregions, Northern America consists of Bermuda, Canada, Greenland, Saint Pierre and Miquelon and the United States.
The World Geographical Scheme for Recording Plant Distributions (WGSRPD) is a biogeographical system developed by the international Biodiversity Information Standards (TDWG) organization, formerly the International Working Group on Taxonomic Databases. The WGSRPD standards, like other standards for data fields in botanical databases, were developed to promote "the wider and more effective dissemination of information about the world's heritage of biological organisms for the benefit of the world at large". The system provides clear definitions and codes for recording plant distributions at four scales or levels, from "botanical continents" down to parts of large countries. The codes may be referred to as TDWG geographical codes. Current users of the system include the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), the Germplasm Resources Information Network (GRIN), and Plants of the World Online (POWO).
Northern America may refer to:
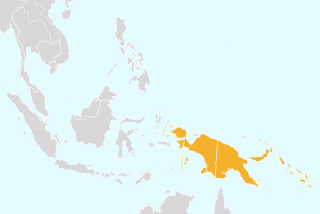
Papuasia is a Level 2 botanical region defined in the World Geographical Scheme for Recording Plant Distributions (WGSRPD). It lies in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, in the Melanesia ecoregion of Oceania and Tropical Asia.

Eastern Asia is one of the regions of temperate Asia defined in the World Geographical Scheme for Recording Plant Distributions (WGSRPD) for use in recording the distribution of plants. It is very much smaller than common definitions of East Asia. It consists of the Korean Peninsula, Japan, and Taiwan. Some islands belonging to Japan politically, such as Marcus Island (Minami-Tori-shima), have greater floristic affinity with similar Pacific islands and are placed in the botanical continent of the Pacific.

The Northern Provinces of South Africa is a biogeographical area used in the World Geographical Scheme for Recording Plant Distributions (WGSRPD). It is part of the WGSRPD region 27 Southern Africa. The area has the code "TVL". It includes the South African provinces of Gauteng, Mpumalanga, Limpopo and North West, together making up an area slightly larger than the former Transvaal Province.
The Central American Pacific Islands is a biogeographical area used in the World Geographical Scheme for Recording Plant Distributions. It has the Level 3 code "CPI". It consists of a number of islands off the western coast of Central America in the Pacific Ocean: Clipperton Island, Cocos Island and Malpelo Island.
The Pacific Subtropical Islands is an interim Australian bioregion which includes Norfolk Island and Lord Howe Island. Its IBRA code is PSI.

Curio hallianus, syn. Senecio hallianus, is a creeping succulent plant in the daisy family Asteraceae that is native to the Cape Provinces of South Africa. It is also known as chain of blue beans or string of beans.

Curio muirii is a succulent plant in the family Asteraceae that is native to South Africa.
Richard Kenneth "Dick" Brummitt was a British botanist.

Euphorbia hypericifolia is a species of perennial herb in the genus Euphorbia native to tropical Americas. It normally grows up to 2 feet (0.6 m) in height, and contains milky sap which can cause skin and eye irritation.












