Carbon shifting is the tendency for an individual to increase carbon dioxide emissions in one area of their lifestyle as a result of reducing emissions elsewhere. Carbon shifting might more accurately be termed "domestic carbon shifting" to distinguish it from carbon leakage, which has occasionally also been called carbon shifting. [1]
Many attempts to encourage people to change aspects of their lifestyle and so reduce their carbon dioxide emissions make a virtue of financial savings. In the United Kingdom, the Energy Saving Trust lists various ways of saving energy, e.g., "Energy-saving light bulbs last up to twelve times longer than ordinary lightbulbs and can save you £9 per year in electricity (and 38 kilograms of CO2) or £100 over the bulbs lifetime." [2] However, whether or not carbon dioxide emissions are ultimately reduced will depend on how that saved money is spent. If the amount of money saved through walking to work is eventually spent on an extra city break involving air travel, the net emissions may well increase.
The problem of carbon shifting may undermine many voluntary piecemeal attempts at reducing carbon dioxide emissions. However, carbon shifting is not inherently negative. If a person can be persuaded to avoid activities that produce a high level of emissions for a given financial outlay, then they may shift to activities that produce lower emissions for that same amount of money. Positive carbon shifting might be encouraged through the use of a carbon tax or the implementation of a personal carbon trading scheme.
The phenomenon of carbon shifting also suggests that for some comparative purposes, the most appropriate measure of emissions would be emissions per unit of currency rather than total emissions. An activity that produces slightly lower emissions at a significantly lower cost may not necessarily be the best activity to promote as it leaves the individual with more money to spend on other emitting activities. Similarly, if two passengers are traveling on the same aircraft, they might be deemed to be emitting the same total amount of carbon dioxide. However, if one of them paid a lower fare, then by this measure, they would be deemed to be damaging the environment more.
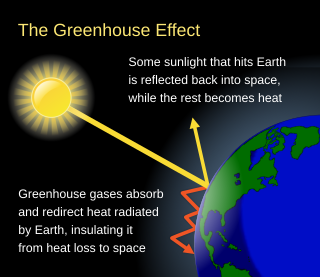
The greenhouse effect occurs when greenhouse gases in a planet's atmosphere cause some of the heat radiated from the planet's surface to build up at the planet's surface. A planet is warmed by absorbing light from its host star and cooled by radiating energy into space. The warm surface of a planet emits infrared thermal radiation. Greenhouse gases absorb some of that radiation, reducing the amount of energy that escapes into space. This reduction in planetary cooling raises the planet's average surface temperature. Adding greenhouse gases to the atmosphere increases the warming effect.
Emissions trading is a market-based approach to controlling pollution by providing economic incentives for reducing the emissions of pollutants. The concept is also known as cap and trade (CAT) or emissions trading scheme (ETS). Carbon emission trading for CO2 and other greenhouse gases has been introduced in China, the European Union and other countries as a key tool for climate change mitigation. Other schemes include sulfur dioxide and other pollutants.
Energy conservation is the effort to reduce wasteful energy consumption by using fewer energy services. This can be done by using energy more effectively or changing one's behavior to use less service. Energy conservation can be achieved through efficient energy use, which has a number of advantages, including a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions and a smaller carbon footprint, as well as cost, water, and energy savings.

A compact fluorescent lamp (CFL), also called compact fluorescent light, energy-saving light and compact fluorescent tube, is a fluorescent lamp designed to replace an incandescent light bulb; some types fit into light fixtures designed for incandescent bulbs. The lamps use a tube that is curved or folded to fit into the space of an incandescent bulb, and a compact electronic ballast in the base of the lamp.

Climate change mitigation is action to limit climate change by reducing emissions of greenhouse gases or removing those gases from the atmosphere. The recent rise in global average temperature is mostly due to emissions from burning fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas. Mitigation can reduce emissions by transitioning to sustainable energy sources, conserving energy, and increasing efficiency. It is possible to remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere by enlarging forests, restoring wetlands and using other natural and technical processes. Experts call these processes carbon sequestration. Governments and companies have pledged to reduce emissions to prevent dangerous climate change in line with international negotiations to limit warming by reducing emissions.
The carbon footprint serves as an indicator to compare the amount of greenhouse gases emitted for the entire production or consumption of goods or services. It is complex to calculate and different methodologies and online tools exist. One difficulty is that the so-called Scope 3 carbon emissions are difficult to quantify and thus sometimes even omitted from the calculations. Scope 3 carbon emission are indirect carbon emissions throughout the extended upstream supply chain. Companies may use the carbon footprint of their products as a marketing tool. For politicians it can be an indicator in the context climate change mitigation activities to find options that reduce the carbon footprint of economic activities. The carbon footprint concept allows comparisons between the climate-relevant impacts of individuals, products, companies, countries etc.

Carbon capture and storage (CCS), is a process in which a relatively pure stream of carbon dioxide (CO2) from industrial sources is separated, treated and transported to a long-term storage location. For example, the carbon dioxide stream that is to be captured can result from burning fossil fuels or biomass. Usually the CO2 is captured from large point sources, such as a chemical plant or biomass plant, and then stored in an underground geological formation. The aim is to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and thus mitigate climate change.
Domestic housing in the United Kingdom presents a possible opportunity for achieving the 20% overall cut in UK greenhouse gas emissions targeted by the Government for 2010. However, the process of achieving that drop is proving problematic given the very wide range of age and condition of the UK housing stock.
Various energy conservation measures are taken in the United Kingdom.

A low-carbon economy (LCE) or decarbonised economy is an economy based on energy sources that produce low levels of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. GHG emissions due to human activity are the dominant cause of observed climate change since the mid-20th century. Continued emission of greenhouse gases will cause long-lasting changes around the world, increasing the likelihood of severe, pervasive, and irreversible effects for people and ecosystems. Shifting to a low-carbon economy on a global scale could bring substantial benefits both for developed and developing countries. Many countries around the world are designing and implementing low-emission development strategies (LEDS). These strategies seek to achieve social, economic, and environmental development goals while reducing long-term greenhouse gas emissions and increasing resilience to the effects of climate change.

Greenhouse gas emissions from human activities strengthen the greenhouse effect, contributing to climate change. Most is carbon dioxide from burning fossil fuels: coal, oil, and natural gas. The largest emitters include coal in China and large oil and gas companies. Human-caused emissions have increased atmospheric carbon dioxide by about 50% over pre-industrial levels. The growing levels of emissions have varied, but have been consistent among all greenhouse gases (GHGs). Emissions in the 2010s averaged 56 billion tons a year, higher than any decade before.
Energy Saving Trust is a British organization devoted to promoting energy efficiency, energy conservation, and the sustainable use of energy, thereby reducing carbon dioxide emissions and helping to prevent man-made climate change. It was founded in the United Kingdom as a government-sponsored initiative in 1992, following the global Earth Summit.

The United States produced 5.2 billion metric tons of carbon dioxide equivalent greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions in 2020, the second largest in the world after greenhouse gas emissions by China and among the countries with the highest greenhouse gas emissions per person. In 2019 China is estimated to have emitted 27% of world GHG, followed by the United States with 11%, then India with 6.6%. In total the United States has emitted a quarter of world GHG, more than any other country. Annual emissions are over 15 tons per person and, amongst the top eight emitters, is the highest country by greenhouse gas emissions per person. However, the IEA estimates that the richest decile in the US emits over 55 tonnes of CO2 per capita each year. Because coal-fired power stations are gradually shutting down, in the 2010s emissions from electricity generation fell to second place behind transportation which is now the largest single source. In 2020, 27% of the GHG emissions of the United States were from transportation, 25% from electricity, 24% from industry, 13% from commercial and residential buildings and 11% from agriculture. In 2021, the electric power sector was the second largest source of U.S. greenhouse gas emissions, accounting for 25% of the U.S. total. These greenhouse gas emissions are contributing to climate change in the United States, as well as worldwide.

A low-carbon diet is a diet with low greenhouse gas emissions. Choosing a low carbon diet is one facet of developing sustainable diets which increase the long-term sustainability of humanity.

Emission trading (ETS) for carbon dioxide (CO2) and other greenhouse gases (GHG) is a form of carbon pricing; also known as cap and trade (CAT) or carbon pricing. It is an approach to limit climate change by creating a market with limited allowances for emissions. This can lower competitiveness of fossil fuels and accelerate investments into low carbon sources of energy such as wind power and photovoltaics. Fossil fuels are the main driver for climate change. They account for 89% of all CO2 emissions and 68% of all GHG emissions.

Climate change is having major effects on the Chinese economy, society and the environment. China is the largest emitter of carbon dioxide, through an energy infrastructure heavily focused on coal. Other industries, such as a burgeoning construction industry and industrial manufacturing, contribute heavily to carbon emissions. However, like other developing countries, on a per-capita basis, China's carbon emissions are considerably less than countries like the United States. It has also been noted that higher-income countries have outsourced emissions-intensive industries to China. On the basis of cumulative CO2 emissions measured from 1751 through to 2017, China is responsible for 13% globally and about half of the United States' cumulative emissions.

The environmental effects of transport are significant because transport is a major user of energy, and burns most of the world's petroleum. This creates air pollution, including nitrous oxides and particulates, and is a significant contributor to global warming through emission of carbon dioxide. Within the transport sector, road transport is the largest contributor to global warming.

Individual action on climate change can include personal choices in many areas, such as diet, travel, household energy use, consumption of goods and services, and family size. Individuals can also engage in local and political advocacy around issues of climate change. People who wish to reduce their carbon footprint, can take "high-impact" actions, such as avoiding frequent flying and petrol fuelled cars, eating mainly a plant-based diet, having fewer children, using clothes and electrical products for longer, and electrifying homes. Avoiding meat and dairy foods has been called "the single biggest way" an individual can reduce their environmental impact. Excessive consumption is more to blame for climate change than population increase. High consumption lifestyles have a greater environmental impact, with the richest 10% of people emitting about half the total lifestyle emissions.
Zero-carbon housing is a term used to describe a house that does not emit greenhouse gasses, specifically carbon dioxide (CO2), into the atmosphere. Homes release greenhouse gases through burning fossil fuels in order to provide heat, or even while cooking on a gas stove. A zero carbon house can be achieved by either building or renovating a home to be very energy efficient and for its energy consumption to be from non-emitting sources, for example electricity.
Greenhouse gas emissions by China are the largest of any country in the world both in production and consumption terms, and stem mainly from coal burning in China, including coal-fired power stations, coal mining, and blast furnaces producing iron and steel. When measuring production-based emissions, China emitted over 14 gigatonnes (Gt) CO2eq of greenhouse gases in 2019, 27% of the world total. When measuring in consumption-based terms, which adds emissions associated with imported goods and extracts those associated with exported goods, China accounts for 13 gigatonnes (Gt) or 25% of global emissions.