Related Research Articles

Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure of circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels. Most of this pressure results from the heart pumping blood through the circulatory system. When used without qualification, the term "blood pressure" refers to the pressure in the large arteries. Blood pressure is usually expressed in terms of the systolic pressure over diastolic pressure in the cardiac cycle. It is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) above the surrounding atmospheric pressure.

In cardiac physiology, cardiac output (CO), also known as heart output and often denoted by the symbols , , or , is the volumetric flow rate of the heart's pumping output: that is, the volume of blood being pumped by both ventricles of the heart, per unit time. Cardiac output (CO) is the product of the heart rate (HR), i.e. the number of heartbeats per minute (bpm), and the stroke volume (SV), which is the volume of blood pumped from the left ventricle per beat; thus giving the formula:

An echocardiography, echocardiogram, cardiac echo or simply an echo, is an ultrasound of the heart. It is a type of medical imaging of the heart, using standard ultrasound or Doppler ultrasound.
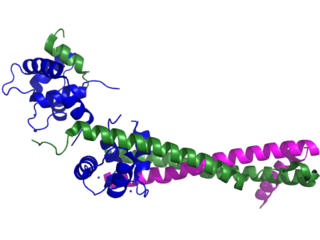
Troponin, or the troponin complex, is a complex of three regulatory proteins that are integral to muscle contraction in skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle, but not smooth muscle. Measurements of cardiac-specific troponins I and T are extensively used as diagnostic and prognostic indicators in the management of myocardial infarction and acute coronary syndrome. Blood troponin levels may be used as a diagnostic marker for stroke or other myocardial injury that is ongoing, although the sensitivity of this measurement is low.
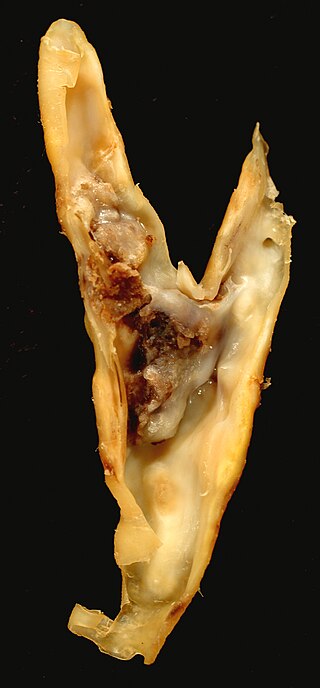
An atheroma, or atheromatous plaque, is an abnormal and reversible accumulation of material in the inner layer of an arterial wall.

Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) is thickening of the heart muscle of the left ventricle of the heart, that is, left-sided ventricular hypertrophy and resulting increased left ventricular mass.

Cardiac markers are biomarkers measured to evaluate heart function. They can be useful in the early prediction or diagnosis of disease. Although they are often discussed in the context of myocardial infarction, other conditions can lead to an elevation in cardiac marker level.

T wave alternans (TWA) is a periodic beat-to-beat variation in the amplitude or shape of the T wave in an electrocardiogram TWA was first described in 1908. At that time, only large variations could be detected. Those large TWAs were associated with increased susceptibility to lethal ventricular tachycardias.

Cardiomegaly is a medical condition in which the heart becomes enlarged. It is more commonly referred to simply as "having an enlarged heart". It is usually the result of underlying conditions that make the heart work harder, such as obesity, heart valve disease, high blood pressure (hypertension), and coronary artery disease. Cardiomyopathy is also associated with cardiomegaly.
Impedance cardiography (ICG) is a non-invasive technology measuring total electrical conductivity of the thorax and its changes in time to process continuously a number of cardiodynamic parameters, such as stroke volume (SV), heart rate (HR), cardiac output (CO), ventricular ejection time (VET), pre-ejection period and used to detect the impedance changes caused by a high-frequency, low magnitude current flowing through the thorax between additional two pairs of electrodes located outside of the measured segment. The sensing electrodes also detect the ECG signal, which is used as a timing clock of the system.
Postperfusion syndrome, also known as "pumphead", is a constellation of neurocognitive impairments attributed to cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) during cardiac surgery. Symptoms of postperfusion syndrome are subtle and include defects associated with attention, concentration, short-term memory, fine motor function, and speed of mental and motor responses. Studies have shown a high incidence of neurocognitive deficit soon after surgery, but the deficits are often transient with no permanent neurological impairment.

Myocardial perfusion imaging or scanning is a nuclear medicine procedure that illustrates the function of the heart muscle (myocardium).
Fractional flow reserve (FFR) is a diagnostic technique used in coronary catheterization. FFR measures pressure differences across a coronary artery stenosis to determine the likelihood that the stenosis impedes oxygen delivery to the heart muscle.

Coronary CT angiography is the use of computed tomography (CT) angiography to assess the coronary arteries of the heart. The patient receives an intravenous injection of radiocontrast and then the heart is scanned using a high speed CT scanner, allowing physicians to assess the extent of occlusion in the coronary arteries, usually in order to diagnose coronary artery disease.

Cardiac imaging refers to non-invasive imaging of the heart using ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), computed tomography (CT), or nuclear medicine (NM) imaging with PET or SPECT. These cardiac techniques are otherwise referred to as echocardiography, Cardiac MRI, Cardiac CT, Cardiac PET and Cardiac SPECT including myocardial perfusion imaging.

Arterial blood pressure is most commonly measured via a sphygmomanometer, which historically used the height of a column of mercury to reflect the circulating pressure. Blood pressure values are generally reported in millimetres of mercury (mmHg), though aneroid and electronic devices do not contain mercury.
Numerical manipulation of Doppler parameters obtain during routine Echocardiography has been extensively utilized to non-invasively estimate intra-cardiac pressures, in many cases removing the need for invasive cardiac catheterization.
quantium Medical Cardiac Output (qCO) uses impedance cardiography in a simple, continuous, and non-invasive way to estimate the cardiac output (CO) and other hemodynamic parameters such as the stroke volume (SV) and cardiac index (CI). The CO estimated by the qCO monitor is referred to as the "qCO". The impedance plethysmography allows determining changes in volume of the body tissues based on the measurement of the electric impedance at the body surface.

Brain natriuretic peptide 32 (BNP), also known as B-type natriuretic peptide, is a hormone secreted by cardiomyocytes in the heart ventricles in response to stretching caused by increased ventricular blood volume. Along with NT-proBNP, BNP is one of two natriuretic peptides.
Electrochemical skin conductance (ESC) is an objective, non-invasive and quantitative electrophysiological measure. It is based on reverse iontophoresis and (multiple) steady chronoamperometry.
References
- ↑ Sniecinski, R. M.; Skubas, N. J.; London, M. J. (2012). "Testing Cardiac Reserve". Anesthesia & Analgesia. 115 (5): 991–992. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0b013e31825d2c09 . PMID 23093580.
- ↑ Cooke, G. A.; Marshall, P.; Al-Timman, J. K.; Wright, D. J.; Riley, R.; Hainsworth, R.; Tan, L. B. (1998). "Physiological cardiac reserve: Development of a non-invasive method and first estimates in man". Heart. 79 (3): 289–294. doi:10.1136/hrt.79.3.289. PMC 1728626 . PMID 9602665.
- ↑ Tan, L. B. (1991). "Evaluation of cardiac dysfunction, cardiac reserve and inotropic response". Postgraduate Medical Journal. 67 Suppl 1: S10–S20. PMID 1924075.