
Banff National Park is Canada's oldest national park, established in 1885. Located in Alberta's Rocky Mountains, 110–180 kilometres (68–112 mi) west of Calgary, Banff encompasses 6,641 square kilometres (2,564 sq mi) of mountainous terrain, with many glaciers and ice fields, dense coniferous forest, and alpine landscapes. The Icefields Parkway extends from Lake Louise, connecting to Jasper National Park in the north. Provincial forests and Yoho National Park are neighbours to the west, while Kootenay National Park is located to the south and Kananaskis Country to the southeast. The main commercial centre of the park is the town of Banff, in the Bow River valley.

The Canadian Rockies or Canadian Rocky Mountains comprise both the Alberta Rockies and the B.C. Rockies in the Canadian segment of the North American Rocky Mountains. They are the eastern part of the North American Cordillera, which is a system of multiple ranges of mountains which runs from the Prairies to the Pacific Coast. The Canadian Rockies mountain system comprises the southeastern part of this system, lying between the Interior Plains of Alberta and northeastern British Columbia on the east to the Rocky Mountain Trench of BC on the west. The southern end borders Idaho and Montana of the United States. In geographic terms, the boundary is at the Canada–United States border, but in geological terms it might be considered to be at Marias Pass in northern Montana. The northern end is at the Liard River in northern British Columbia.

Kootenay National Park is a national park located in southeastern British Columbia, and is one component of the Canadian Rocky Mountain Parks World Heritage Site. The park consists of 1,406 km2 (543 sq mi) of the Canadian Rockies, including parts of the Kootenay and Park mountain ranges, the Kootenay River and the entirety of the Vermilion River. While the Vermillion River is completely contained within the park, the Kootenay River has its headwaters just outside the park boundary, flowing through the park into the Rocky Mountain Trench, eventually joining the Columbia River. It ranges in elevation from 918 m (3,012 ft) at the southwestern park entrance, to 3,424 m (11,234 ft) at Deltaform Mountain. Initially called "Kootenay Dominion Park", the park was created in 1920 as part of an agreement between the province of British Columbia and the Canadian federal government to build a highway in exchange for title to a strip of land, approximately 8 km (5.0 mi) on either side of the 94 km route, the Banff–Windermere Highway, to be used solely for park purposes. While the park is open all year, the major tourist season lasts from June to September. Most campgrounds are open from early May to late September, while limited winter camping is available only at the Dolly Varden campground.

Castle Mountain is a mountain located within Banff National Park in the Canadian Rockies, approximately halfway between Banff and Lake Louise. It is the easternmost mountain of the Main Ranges in the Bow Valley and sits astride the Castle Mountain Fault which has thrust older sedimentary and metamorphic rocks forming the upper part of the mountain over the younger rocks forming its base. The mountain's castellated, or castle-like, appearance is a result of erosive processes acting at different rates on the peak's alternating layers of softer shale and harder limestone, dolomite and quartzite.
Alberta Provincial Highway No. 1, commonly referred to as Highway 1, is a major east-west highway in Southern Alberta that forms the southern mainline of the Trans-Canada Highway. It runs from the British Columbia border near Lake Louise through Calgary to the Saskatchewan border east of Medicine Hat. It continues as Highway 1 into both provinces. It spans approximately 534 km (332 mi) from Alberta's border with British Columbia in the west to its border with Saskatchewan in the east. The route is a divided expressway throughout the province with the exception of a section in central Calgary where it is an arterial thoroughfare. Twinning of the final 8.5 km (5.3 mi) of Highway 1 between Lake Louise and the British Columbia border was completed by Parks Canada and opened to traffic on June 12, 2014.

Alberta Provincial Highway No. 11, commonly referred to as Highway 11 and officially named the David Thompson Highway, is a provincial highway in central Alberta, Canada. It runs for 318 km (198 mi) from Highway 93 at Saskatchewan River Crossing near Mount Sarbach in Banff National Park east to Highway 12 near Nevis. It passes by Nordegg and through Rocky Mountain House, Sylvan Lake and Red Deer along its course. The highway is named after David Thompson, a British-Canadian fur trader, surveyor, and map-maker who explored the area between Rocky Mountain House and Kootenae House through Howse Pass.
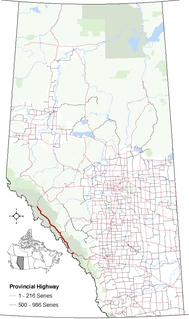
Highway 93 is a north-south highway in Alberta, Canada. It is also known as the Banff-Windermere Parkway south of the Trans-Canada Highway (Highway 1) and the Icefields Parkway north of the Trans-Canada Highway. It travels through Banff National Park and Jasper National Park and is maintained by Parks Canada for its entire length. It runs from the British Columbia border at Vermilion Pass in the south, where it becomes British Columbia Highway 93, to its terminus at the junction with the Yellowhead Highway (Highway 16) at Jasper. The route takes its number from U.S. Route 93, which runs uninterrupted south to central Arizona, and was initially designated as '93' in 1959.

Banff Sunshine Village is a ski resort in western Canada, located on the Continental Divide of the Canadian Rockies within Banff National Park in Alberta and Mt Assiniboine Provincial Park in British Columbia. It is one of three major ski resorts located in the Banff National Park. Because of its location straddling the Continental Divide, Sunshine receives more snow than the neighbouring ski resorts. The Sunshine base area is located 15 km (9 mi) southwest of the town of Banff. By car, it is about a ninety-minute drive from the city of Calgary; the Sunshine exit on the Trans Canada Highway is 8 km (5 mi) west of the town of Banff.

The Canadian Rockies are a segment of the North American Rocky Mountains found in the Canadian provinces of Alberta and British Columbia.

The Bow Range is a mountain range of the Canadian Rockies in Alberta and British Columbia, Canada. The range is named in associated with the Bow River and was officially adopted on March 31, 1917 by the Geographic Board of Canada.

Alberta's Rockies comprises the Canadian Rocky Mountains in Alberta, Canada. It is a region on the southwestern part of the province, along the British Columbia border. It covers all but the south of Census Division 15.

The Banff Formation is a stratigraphical unit of Devonian age in the Western Canadian Sedimentary Basin.

Neptuak Mountain was named by Samuel E.S. Allen in 1894. "Neptuak" is the Stoney Indian word for "nine" as Neptuak Mountain is peak #9 in the Valley of the Ten Peaks. It is located on the Continental Divide, which is also the British Columbia-Alberta border in this region, and is in the Bow Range of the Park Ranges of the Canadian Rockies. The summit is a tripoint for Banff National Park, Kootenay National Park, and Yoho National Park, where the three parks share a common border.
The Banff-Windermere Highway, also known as the Banff-Windermere Parkway, is a 105 km (65 mi) highway which runs through the Canadian Rockies in British Columbia and Alberta in Canada. It runs from Radium Hot Springs, British Columbia to Castle Junction, Alberta, passing through Kootenay National Park and Banff National Park. It is designated as part of British Columbia Highway 93 and Alberta Highway 93.

Storm Mountain is a 3,158-metre (10,361-foot) mountain summit located on the Continental Divide on the shared border of Alberta and British Columbia in Canada. It is situated on the shared boundary of Kootenay National Park with Banff National Park in the Canadian Rockies. It is a large peak near the north end of the Ball Range, in the Bow River Valley opposite Castle Mountain. Vermilion Pass is situated to the northwest of the mountain, and Stanley Peak to the southwest. The nearest higher peak is Mount Ball, 5.7 km (3.5 mi) to the south.

Castleguard Mountain, also known as Mount Castleguard, is an isolated mountain located near the southern edge of the Columbia Icefield at the northern edge of Banff National Park in Alberta, Canada. In 1918, Irish land surveyor Arthur Oliver Wheeler named the mountain because of its castle-like appearance, which seemed to stand guard over the southern portion of the Columbia Icefield. Castleguard was first ascended in 1919 by the Interprovincial Boundary Commission, which determined the exact location of the boundary between British Columbia and Alberta along the continental divide.
The Kananaskis Formation is a geologic formation that is present on the western edge of the Western Canada Sedimentary Basin in the southern Canadian Rockies of western Alberta. Named after the Kananaskis Range near Banff, it was deposited during the Late Pennsylvanian sub-period of the Carboniferous period. Some of its strata host fossils of marine invertebrates.

Old Goat Mountain is a 3,120-metre (10,240 ft) mountain summit located in Kananaskis Country in the Canadian Rockies of Alberta, Canada. The mountain is situated near the south end of the Goat Range along the west shore of Spray Lakes Reservoir, and is the highest point in the Goat Range. The east flank of the mountain is within Spray Valley Provincial Park, while the west aspect is within Banff National Park, with the boundary line between the two parks running roughly north-to-south over its summit. The nearest higher peak is Wind Mountain, 8.9 km (5.5 mi) to the east. Old Goat Mountain can be seen from Alberta Highway 742, the Smith-Dorrien/Spray Trail.

The Eldon Formation is a stratigraphic unit that is present on the western edge of the Western Canada Sedimentary Basin in the southern Canadian Rockies of southwestern Alberta and southeastern British Columbia. It is a thick sequence of massive, cliff-forming limestones and dolomites that was named for Eldon Switch on the Canadian Pacific Railway near Castle Mountain in Banff National Park by Charles Doolittle Walcott, who discovered the Burgess Shale fossils. The Eldon Formation was deposited during Middle Cambrian time, and it includes fossil stromatolites. The Eldon forms the scenic cliffs at the top of Castle Mountain, and can also be seen at Mount Yamnuska and other mountains in Banff and Yoho National Parks.















