
A star catalogue or star catalog, is an astronomical catalogue that lists stars. In astronomy, many stars are referred to simply by catalogue numbers. There are a great many different star catalogues which have been produced for different purposes over the years, and this article covers only some of the more frequently quoted ones. Star catalogues were compiled by many different ancient people, including the Babylonians, Greeks, Chinese, Persians, and Arabs. They were sometimes accompanied by a star chart for illustration. Most modern catalogues are available in electronic format and can be freely downloaded from space agencies data centres.

Beta Lyrae is a multiple star system in the constellation of Lyra. Based on parallax measurements obtained during the Hipparcos mission, it is approximately 960 light-years distant from the Sun.
The Bright Star Catalogue, also known as the Yale Catalogue of Bright Stars or Yale Bright Star Catalogue, is a star catalogue that lists all stars of stellar magnitude 6.5 or brighter, which is roughly every star visible to the naked eye from Earth. The catalog contains 9,110 objects, of which 9,095 are stars, 11 are novae or supernovae, and 4 are non-stellar objects; the non-stellar objects are the globular clusters 47 Tucanae and NGC 2808, and the open clusters NGC 2281 and Messier 67.

SIMBAD is an astronomical database of objects beyond the Solar System. It is maintained by the Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg (CDS), France.
Xi Scorpii is a quintuple star system in the constellation Scorpius. It was assigned this designation by Bayer, although Ptolemy had catalogued the star in Libra. Flamsteed assigned it the designation 51 Librae, but this has fallen out of use since modern constellation boundaries assign the star to Scorpius.
Omicron Serpentis is a solitary star in the Serpens Cauda (tail) section of the equatorial constellation Serpens. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 18.83 mas as seen from Earth, it is located around 173 light years from the Sun. The star is visible to the naked eye with a base apparent visual magnitude of +4.26.
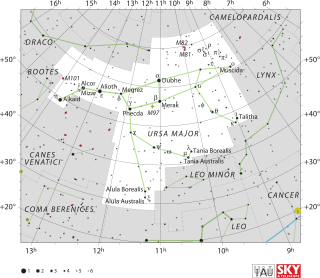
Tau Ursae Majoris (τ UMa) is the Bayer designation for a binary star in the northern circumpolar constellation of Ursa Major. It is visible to the naked eye, having an apparent visual magnitude of 4.66. With an annual parallax shift of 25.82 mas, it is located about 126 light years from the Sun. At that distance, the visual magnitude is diminished by an extinction factor of 0.19 due to interstellar dust.

Lambda Virginis is a binary star system in the zodiac constellation of Virgo. With an apparent visual magnitude of 4.5, it is bright enough to be seen with the naked eye. Based upon parallax measurements, the system is about 173 light-years away from the Sun. Its two components are designated Lambda Virginis A and B.
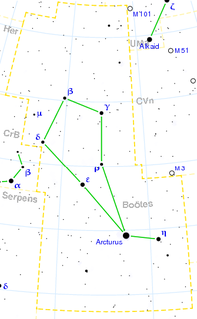
Gamma Boötis is a binary star in the constellation of Boötes. It is a Delta Scuti type variable star with a period of 1.13 hours. Its brightness varies from magnitude +3.02 to +3.07. Based on parallax measurements obtained during the Hipparcos mission, it is approximately 85 light-years distant from the Sun.
In astronomy, Durchmusterung or Bonner Durchmusterung (BD), is the comprehensive astrometric star catalogue of the whole sky, compiled by the Bonn Observatory (Germany) from 1859 to 1903.

12 Vulpeculae is a star in the northern constellation of Vulpecula, located approximately 630 light years away based on parallax. It has the variable star designation V395 Vul; 12 Vulpeculae is the Flamsteed designation. This object is visible to the naked eye as a faint, blue-white hued star with a baseline apparent visual magnitude of 4.96. It is moving closer to the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of -25 km/s.
HD 29697 is a variable star of BY Draconis type in the constellation Taurus. It has an apparent magnitude around 8 and is approximately 43 ly away.
Beta Equulei, Latinized from β Equulei, is the Bayer designation for a solitary star in the northern constellation of Equuleus. It is faintly visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 5.15. The annual parallax shift is 24.55 mas, indicating a separation of around 133 light years from the Sun.

Histoire Céleste Française is an astrometric star catalogue published in 1801 by the French astronomer Jérôme Lalande and his staff at the Paris Observatory. This star catalog consists of the locations and apparent magnitudes of 47,390 stars, up to magnitude 9. Stars are identified by common name, Bayer designation or Flamsteed designation, when available. It also contains observations of other astronomical phenomena. It was the largest and most complete star catalog of its day. This publication is a collection of several books of astronomical recordings taken over the previous decade at the observatory.

Sigma1 Ursae Majoris (σ1 UMa) is the Bayer designation for a solitary star in the northern circumpolar constellation of Ursa Major. With an apparent visual magnitude of 5.14 it is faintly visible to the naked eye on dark nights. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 6.26 mas, it is located roughly 520 light years from the Sun. At that distance, the visual magnitude of the star is diminished by an extinction factor of 0.06 due to interstellar dust.

25 Orionis, less commonly known by its Bayer designation Psi1 Orionis is a fifth-magnitude star in the constellation Orion. It lies among a dense cluster of low-mass pre-main-sequence stars in the Orion OB1a.
Sigma Ceti is the Bayer designation for a star in the equatorial constellation of Cetus. With an apparent visual magnitude of 4.78, it can be seen with the naked eye on a dark night. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 37.46 mas, it lies at an estimated distance of 87.1 light years from the Sun. It is a probable astrometric binary star system.
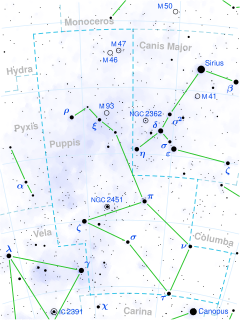
NV Puppis, also known as υ1 Puppis, is a class B2V star in the constellation Puppis. Its apparent magnitude is 4.67 and it is approximately 800 light years away based on parallax.
KU Hydrae is a binary star in the constellation Hydra. The primary star is an Alpha2 Canum Venaticorum variable with its apparent magnitude varying from 0.05 magnitudes over a period of 33.97 days.










