Related Research Articles

In cell biology a centriole is a cylindrical organelle composed mainly of a protein called tubulin. Centrioles are found in most eukaryotic cells, but are not present in conifers (Pinophyta), flowering plants (angiosperms) and most fungi, and are only present in the male gametes of charophytes, bryophytes, seedless vascular plants, cycads, and Ginkgo. A bound pair of centrioles, surrounded by a highly ordered mass of dense material, called the pericentriolar material (PCM), makes up a structure called a centrosome.
The Phyllopharyngea are a class of ciliates, some of which are extremely specialized. Motile cells typically have cilia restricted to the ventral surface, or some part thereof, arising from monokinetids with a characteristic ultrastructure. In both chonotrichs and suctoria, however, only newly formed cells are motile and the sessile adults have undergone considerable modifications of form and appearance. Chonotrichs, found mainly on crustaceans, are vase-shaped, with cilia restricted to a funnel leading down into the mouth. Mature suctorians lack cilia altogether, and initially were not classified as ciliates.

Blepharisma is a genus of unicellular ciliate protists found in fresh and salt water. The group includes about 40 accepted species, and many sub-varieties and strains. While species vary considerably in size and shape, most are easily identified by their red or pinkish color, which is caused by granules of the pigment blepharismin.

The nuchal organ is a ciliated pit or groove present at the posterior end of the prostomium of annelid worms, some cephalopods, and other invertebrates.
''''' is a of karyorelictean ciliates, belonging to Loxodidae. It is the only known karyorelictean ciliate that lives in freshwater habitats.

The ciliates are a group of alveolates characterized by the presence of hair-like organelles called cilia, which are identical in structure to eukaryotic flagella, but are in general shorter and present in much larger numbers, with a different undulating pattern than flagella. Cilia occur in all members of the group and are variously used in swimming, crawling, attachment, feeding, and sensation.

Lacrymaria is a genus of ciliates. Its best known species is the "Tear of Swan", Lacrymaria olor.

François Émile Maupas was a French librarian, protozoologist, cytologist, and botanist. Maupas contributed to ideas on the life cycle and reproduction of the ciliates. He founded the idea, known as the Maupasian life cycle, that some protists had a definite death following sexual reproduction, contrary to contemporary ideas on protists being immortal. He also identified the existence of mating types in ciliates. He developed culture techniques for a number of organisms and described the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans, which has since become a widely used model organism in biological studies.

Oxytricha is a genus of ciliates in the family Oxytrichidae.

Collinia is a genus of parasitoid ciliates of the Colliniidae family.

Chromidina elegans is a species of parasitic ciliates. It is a parasite of the cuttlefish Sepia elegans.

Sepia elegans, the elegant cuttlefish, is a species of cuttlefish in the family Sepiidae from the eastern Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea. It is an important species for fisheries in some parts of the Mediterranean where its population may have suffered from overfishing.

Chromidina elegans is a species of ciliates, described in 2016. It is parasitic in the kidney appendages of the cuttlefish Loligo vulgaris. The type-locality is off Tunisia in the Mediterranean Sea.
Cavichona is a genus of ciliates in the family Spirochonidae.

Intramacronucleata is a subphylum of ciliates. The group is characterized by the manner in which division of the macronucleus is accomplished during binary fission of the cell. In ciliates of this subphylum, division of the macronucleus is achieved by the action of microtubules which are assembled inside the macronucleus itself. This is in contrast to heterotrich ciliates of the subphylum Postciliodesmatophora, in which division of the macronucleus relies on microtubules formed outside the macronuclear envelope.
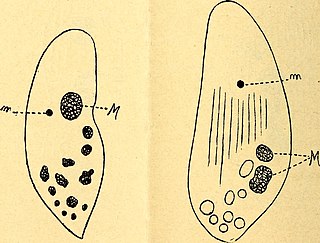
Cryptochilum is a genus of marine ciliates in the family Cryptochilidae.
Uronema elegans is a species of ciliates in the family Uronematidae. It is found in Norway.
Euplotes elegans is a species of marine ciliates. It has been isolated from the anoxic Mariager Fjord.

Duvalia vestita is a small succulent plant species, in the family Apocynaceae, indigenous to the southernmost part of the Western Cape Province, South Africa.
Halofolliculina is a genus of ciliates belonging to the family Folliculinidae.
References
- Ultrastructure of the sessile ciliate Cavichona elegans (Chonotricha). I. BP Karadzhan - Non-dividing animals. (In Russian.) Acta Protozool, 1976