Related Research Articles

Robert Alphonso Taft III is an American politician and attorney who served as the 67th governor of Ohio between 1999 and 2007 as a member of the Republican Party.
The University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center is a public academic health science center in Dallas, Texas. With approximately 13,568 employees and 2,445 faculty and over 2.7 million outpatient visits per year, UT Southwestern is the largest medical school in the University of Texas System and state of Texas.
The California Institute for Regenerative Medicine (CIRM) was created in 2004 after 59% of California voters approved California Proposition 71: the Research and Cures Initiative, which allocated $3 billion to fund stem cell research in California.

University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center is a major not-for-profit medical complex in Cleveland, Ohio, United States. Since 1986, University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center has been an affiliate hospital of Case Western Reserve University.
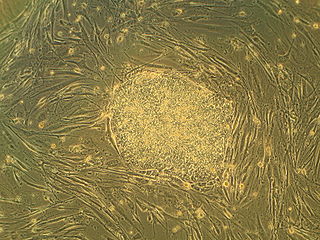
Regenerative medicine deals with the "process of replacing, engineering or regenerating human or animal cells, tissues or organs to restore or establish normal function". This field holds the promise of engineering damaged tissues and organs by stimulating the body's own repair mechanisms to functionally heal previously irreparable tissues or organs.

Maine Medical Center is a 637-licensed-bed teaching hospital for Tufts University School of Medicine, and previously Robert Larner College of Medicine, located at 22 Bramhall Street in Portland, Maine, United States, with a staff of over 6,000. The facility has obtained the rating of Level I Trauma Center, one of only three in Northern New England. Founded in 1874, it is the largest hospital in northern New England with 28,000 inpatient visits, about 500,000 outpatient visits, 88,000 emergency visits, and over 27,000 surgeries performed annually. MMC is structured as a non-profit, private corporation governed by volunteer trustees.

UC Davis Medical Center is part of UC Davis Health and a major academic health center located in Sacramento, California. It is owned and operated by the University of California as part of its University of California, Davis campus. The medical center sits on a 142-acre (57 ha) campus located between the Elmhurst, Tahoe Park, and Oak Park residential neighborhoods. The site incorporates the land and some of the buildings of the former Sacramento Medical Center as well as much of the land previously occupied by the California State Fair until its 1967 move to a new location.

The University of Miami Leonard M. Miller School of Medicine (UMMSM) is the graduate medical school of the University of Miami. Founded in 1952, it is the oldest medical school in the state of Florida.

Proposition 71 of 2004 is a law enacted by California voters to support stem cell research in the state. It was proposed by means of the initiative process and approved in the 2004 state elections on November 2. The Act amended both the Constitution of California and the Health and Safety Code.
Stem-cell therapy is the use of stem cells to treat or prevent a disease or condition. As of 2016, the only established therapy using stem cells is hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. This usually takes the form of a bone-marrow transplantation, but the cells can also be derived from umbilical cord blood. Research is underway to develop various sources for stem cells as well as to apply stem-cell treatments for neurodegenerative diseases and conditions such as diabetes and heart disease.

City of Hope is a private, not-for-profit clinical research center, hospital and graduate medical school located in Duarte, California, United States. The center's main campus resides on 110 acre of land adjacent to the boundaries of Duarte and Irwindale, with a network of clinical practice locations throughout Southern California, satellite offices in Monrovia and Irwindale, and regional fundraising offices throughout the United States.

The State University of New York Upstate Medical University is a public medical school in Syracuse, New York. Founded in 1834, Upstate is the 15th oldest medical school in the United States and is the only medical school in Central New York. The school is an upper-division transfer and doctoral university with degree-granting programs in the Norton College of Medicine, College of Nursing, College of Health Professions, and the College of Graduate Studies. The university is part of the State University of New York (SUNY) system.

Sanford Burnham Prebys is a 501(c)(3) non-profit medical research institute focusing on basic and translational research, with major research programs in cancer, neurodegeneration, diabetes, and infectious, inflammatory, and childhood diseases. The Institute also specializes in stem cell research and drug discovery technologies.

Nationwide Children's Hospital is a nationally ranked pediatric acute care teaching hospital located in the Southern Orchards neighborhood of Columbus, Ohio. The hospital has 673 pediatric beds and is affiliated with the Ohio State University College of Medicine. The hospital provides comprehensive pediatric specialties and subspecialties to infants, children, teens, and young adults aged 0–21 throughout Ohio and surrounding regions. Nationwide Children's Hospital also sometimes treats adults that require pediatric care. Nationwide Children's Hospital also features an ACS designated Level 1 Pediatric Trauma Center, 1 of 4 in the state. The hospital has affiliations with the nearby Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center. Nationwide Children's Hospital is located on its own campus and has more than 1,379 medical staff members and over 11,909 total employees.
The National Center for Regenerative Medicine (NCRM) was founded in 2004 and specializes in regenerative medical research, while acting as the coordinating organization for other associated institutions.
Stefanie Dimmeler is a German biologist specializing in the pathophysiological processes underlying cardiovascular diseases. Her awards and honours include the Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz Prize of the German Research Foundation for her work on the programmed cell death of endothelial cells. Since 2008 she has led the Institute for Cardiovascular Regeneration at the University of Frankfurt. Her current work is focusing to develop cellular and pharmacological strategies to improve cardiovascular repair and regeneration. Her work aims to establish non-coding RNAs as novel therapeutic targets.
Ohio is a major research and development center, home to many institutions.

The Ohio bioscience sector strength was ranked #4 among USA states in 2008 by Business Facilities magazine.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the first clinical trial in the United States involving human embryonic stem cells on January 23, 2009. Geron Corporation, a biotechnology firm located in Menlo Park, California, originally planned to enroll ten patients suffering from spinal cord injuries to participate in the trial. The company hoped that GRNOPC1, a product derived from human embryonic stem cells, would stimulate nerve growth in patients with debilitating damage to the spinal cord. The trial began in 2010 after being delayed by the FDA because cysts were found on mice injected with these cells, and safety concerns were raised.
Masayo Takahashi is a Japanese medical physician, ophthalmologist and stem cell researcher.
References
- ↑ "Cleveland Quietly Becoming" Archived 2009-08-23 at the Wayback Machine , Cleveland-Plain Dealer, Retrieved September 21, 2009.
- ↑ "About" Archived September 1, 2009, at the Wayback Machine , CSCRM, Retrieved September 21, 2009.