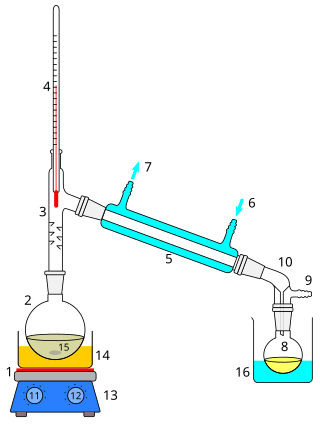
Distillation, also classical distillation, is the process of separating the component substances of a liquid mixture of two or more chemically discrete substances; the separation process is realized by way of the selective boiling of the mixture and the condensation of the vapors in a still.
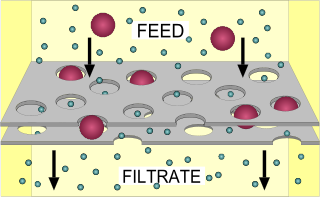
Filtration is a physical separation process that separates solid matter and fluid from a mixture using a filter medium that has a complex structure through which only the fluid can pass. Solid particles that cannot pass through the filter medium are described as oversize and the fluid that passes through is called the filtrate. Oversize particles may form a filter cake on top of the filter and may also block the filter lattice, preventing the fluid phase from crossing the filter, known as blinding. The size of the largest particles that can successfully pass through a filter is called the effective pore size of that filter. The separation of solid and fluid is imperfect; solids will be contaminated with some fluid and filtrate will contain fine particles. Filtration occurs both in nature and in engineered systems; there are biological, geological, and industrial forms. In everyday usage the verb "strain" is more often used; for example, using a colander to drain cooking water from cooked pasta.

A turbomolecular pump is a type of vacuum pump, superficially similar to a turbopump, used to obtain and maintain high vacuum. These pumps work on the principle that gas molecules can be given momentum in a desired direction by repeated collision with a moving solid surface. In a turbomolecular pump, a rapidly spinning fan rotor 'hits' gas molecules from the inlet of the pump towards the exhaust in order to create or maintain a vacuum.

A vacuum pump is a type of pump device that draws gas particles from a sealed volume in order to leave behind a partial vacuum. The first vacuum pump was invented in 1650 by Otto von Guericke, and was preceded by the suction pump, which dates to antiquity.

A centrifuge is a device that uses centrifugal force to subject a specimen to a specified constant force, for example to separate various components of a fluid. This is achieved by spinning the fluid at high speed within a container, thereby separating fluids of different densities or liquids from solids. It works by causing denser substances and particles to move outward in the radial direction. At the same time, objects that are less dense are displaced and moved to the centre. In a laboratory centrifuge that uses sample tubes, the radial acceleration causes denser particles to settle to the bottom of the tube, while low-density substances rise to the top. A centrifuge can be a very effective filter that separates contaminants from the main body of fluid.

An ultracentrifuge is a centrifuge optimized for spinning a rotor at very high speeds, capable of generating acceleration as high as 1 000 000 g. There are two kinds of ultracentrifuges, the preparative and the analytical ultracentrifuge. Both classes of instruments find important uses in molecular biology, biochemistry, and polymer science.
A cryopump or a "cryogenic pump" is a vacuum pump that traps gases and vapours by condensing them on a cold surface, but are only effective on some gases. The effectiveness depends on the freezing and boiling points of the gas relative to the cryopump's temperature. They are sometimes used to block particular contaminants, for example in front of a diffusion pump to trap backstreaming oil, or in front of a McLeod gauge to keep out water. In this function, they are called a cryotrap, waterpump or cold trap, even though the physical mechanism is the same as for a cryopump.
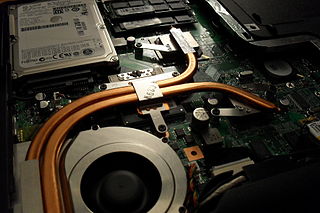
A heat pipe is a heat-transfer device that employs phase transition to transfer heat between two solid interfaces.

A chiller is a machine that removes heat from a liquid coolant via a vapor-compression, adsorption refrigeration, or absorption refrigeration cycles. This liquid can then be circulated through a heat exchanger to cool equipment, or another process stream. As a necessary by-product, refrigeration creates waste heat that must be exhausted to ambience, or for greater efficiency, recovered for heating purposes. Vapor compression chillers may use any of a number of different types of compressors. Most common today are the hermetic scroll, semi-hermetic screw, or centrifugal compressors. The condensing side of the chiller can be either air or water cooled. Even when liquid cooled, the chiller is often cooled by an induced or forced draft cooling tower. Absorption and adsorption chillers require a heat source to function.

Vacuum distillation or distillation under reduced pressure is a type of distillation performed under reduced pressure, which allows the purification of compounds not readily distilled at ambient pressures or simply to save time or energy. This technique separates compounds based on differences in their boiling points. This technique is used when the boiling point of the desired compound is difficult to achieve or will cause the compound to decompose. Reduced pressures decrease the boiling point of compounds. The reduction in boiling point can be calculated using a temperature-pressure nomograph using the Clausius–Clapeyron relation.

A rotary evaporator (rotovap) is a device used in chemical laboratories for the efficient and gentle removal of solvents from samples by evaporation. When referenced in the chemistry research literature, description of the use of this technique and equipment may include the phrase "rotary evaporator", though use is often rather signaled by other language.
Ultra-high vacuum is the vacuum regime characterised by pressures lower than about 1×10−6 pascals. UHV conditions are created by pumping the gas out of a UHV chamber. At these low pressures the mean free path of a gas molecule is greater than approximately 40 km, so the gas is in free molecular flow, and gas molecules will collide with the chamber walls many times before colliding with each other. Almost all molecular interactions therefore take place on various surfaces in the chamber.

Drying is a mass transfer process consisting of the removal of water or another solvent by evaporation from a solid, semi-solid or liquid. This process is often used as a final production step before selling or packaging products. To be considered "dried", the final product must be solid, in the form of a continuous sheet, long pieces, particles or powder. A source of heat and an agent to remove the vapor produced by the process are often involved. In bioproducts like food, grains, and pharmaceuticals like vaccines, the solvent to be removed is almost invariably water. Desiccation may be synonymous with drying or considered an extreme form of drying.
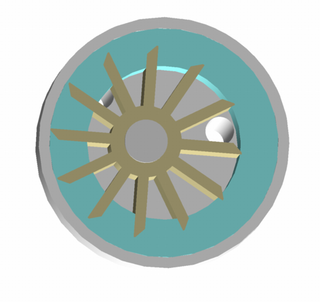
A liquid-ring pump is a rotating positive-displacement gas pump, with liquid under centrifugal force acting as a seal.

Vapour-compression refrigeration or vapor-compression refrigeration system (VCRS), in which the refrigerant undergoes phase changes, is one of the many refrigeration cycles and is the most widely used method for air conditioning of buildings and automobiles. It is also used in domestic and commercial refrigerators, large-scale warehouses for chilled or frozen storage of foods and meats, refrigerated trucks and railroad cars, and a host of other commercial and industrial services. Oil refineries, petrochemical and chemical processing plants, and natural gas processing plants are among the many types of industrial plants that often utilize large vapor-compression refrigeration systems. Cascade refrigeration systems may also be implemented using two compressors.

An evaporator is a type of heat exchanger device that facilitates evaporation by utilizing conductive and convective heat transfer, which provides the necessary thermal energy for phase transition from liquid to vapour. Within evaporators, a circulating liquid is exposed to an atmospheric or reduced pressure environment causing it to boil at a lower temperature compared to normal atmospheric boiling.

A laboratory centrifuge is a piece of laboratory equipment, driven by a motor, which spins liquid samples at high speed. There are various types of centrifuges, depending on the size and the sample capacity.

A sugar cane mill is a factory that processes sugar cane to produce raw sugar or plantation white sugar. Some sugar mills are situated next to a back-end refinery, that turns raw sugar into (refined) white sugar.
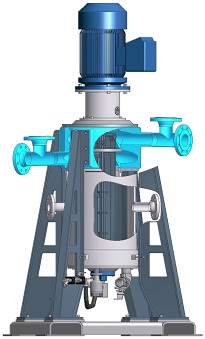
A centrifugal extractor—also known as a centrifugal contactor or annular centrifugal contactor—uses the rotation of the rotor inside a centrifuge to mix two immiscible liquids outside the rotor and to separate the liquids in the field of gravity inside the rotor. This way, a centrifugal extractor generates a continuous extraction from one liquid phase into another liquid phase.

An evaporator, distiller or distilling apparatus is a piece of ship's equipment used to produce fresh drinking water from sea water by distillation. As fresh water is bulky, may spoil in storage, and is an essential supply for any long voyage, the ability to produce more fresh water in mid-ocean is important for any ship.

















