Related Research Articles

A ceramic is any of the various hard, brittle, heat-resistant, and corrosion-resistant materials made by shaping and then firing an inorganic, nonmetallic material, such as clay, at a high temperature. Common examples are earthenware, porcelain, and brick.
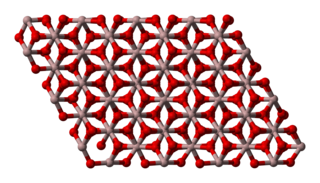
Aluminium oxide (or aluminium(III) oxide) is a chemical compound of aluminium and oxygen with the chemical formula Al2O3. It is the most commonly occurring of several aluminium oxides, and specifically identified as aluminium oxide. It is commonly called alumina and may also be called aloxide, aloxite, or alundum in various forms and applications. It occurs naturally in its crystalline polymorphic phase α-Al2O3 as the mineral corundum, varieties of which form the precious gemstones ruby and sapphire. Al2O3 is used to produce aluminium metal, as an abrasive owing to its hardness, and as a refractory material owing to its high melting point.

Zirconium dioxide, sometimes known as zirconia, is a white crystalline oxide of zirconium. Its most naturally occurring form, with a monoclinic crystalline structure, is the mineral baddeleyite. A dopant stabilized cubic structured zirconia, cubic zirconia, is synthesized in various colours for use as a gemstone and a diamond simulant.
An abrasive is a material, often a mineral, that is used to shape or finish a workpiece through rubbing which leads to part of the workpiece being worn away by friction. While finishing a material often means polishing it to gain a smooth, reflective surface, the process can also involve roughening as in satin, matte or beaded finishes. In short, the ceramics which are used to cut, grind and polish other softer materials are known as abrasives.

Sandpaper, also known as glasspaper or as coated abrasive, is a type of material that consists of sheets of paper or cloth with an abrasive substance glued to one face. In the modern manufacture of these products, sand and glass have been replaced by other abrasives such as aluminium oxide or silicon carbide. It is common to use the name of the abrasive when describing the paper, e.g. "aluminium oxide paper", or "silicon carbide paper".

In materials science, a refractory is a material that is resistant to decomposition by heat or chemical attack that retains its strength and rigidity at high temperatures. They are inorganic, non-metallic compounds that may be porous or non-porous, and their crystallinity varies widely: they may be crystalline, polycrystalline, amorphous, or composite. They are typically composed of oxides, carbides or nitrides of the following elements: silicon, aluminium, magnesium, calcium, boron, chromium and zirconium. Many refractories are ceramics, but some such as graphite are not, and some ceramics such as clay pottery are not considered refractory. Refractories are distinguished from the refractory metals, which are elemental metals and their alloys that have high melting temperatures.

Dental porcelain is a dental material used by dental technicians to create biocompatible lifelike dental restorations, such as crowns, bridges, and veneers. Evidence suggests they are an effective material as they are biocompatible, aesthetic, insoluble and have a hardness of 7 on the Mohs scale. For certain dental prostheses, such as three-unit molars porcelain fused to metal or in complete porcelain group, zirconia-based restorations are recommended.

In dentistry, a crown or a dental cap is a type of dental restoration that completely caps or encircles a tooth or dental implant. A crown may be needed when a large dental cavity threatens the health of a tooth. Some dentists will also finish root canal treatment by covering the exposed tooth with a crown. A crown is typically bonded to the tooth by dental cement. They can be made from various materials, which are usually fabricated using indirect methods. Crowns are used to improve the strength or appearance of teeth and to halt deterioration. While beneficial to dental health, the procedure and materials can be costly.

A ceramic knife is a knife with a ceramic blade typically made from zirconium dioxide (ZrO2; also known as zirconia), rather than the steel used for most knives. Ceramic knife blades are usually produced through the dry-pressing and firing of powdered zirconia using solid-state sintering. The blades typically score 8.5 on the Mohs scale of mineral hardness, compared to 4.5 for normal steel and 7.5 to 8 for hardened steel and 10 for diamond. The resultant blade has a hard edge that stays sharp for much longer than conventional steel blades. However, the blade is brittle, subject to chipping, and will break rather than flex if twisted. The ceramic blade is sharpened by grinding the edges with a diamond-dust-coated grinding wheel.

Ceramic engineering is the science and technology of creating objects from inorganic, non-metallic materials. This is done either by the action of heat, or at lower temperatures using precipitation reactions from high-purity chemical solutions. The term includes the purification of raw materials, the study and production of the chemical compounds concerned, their formation into components and the study of their structure, composition and properties.

A diamond tool is a cutting tool with diamond grains fixed on the functional parts of the tool via a bonding material or another method. As diamond is a superhard material, diamond tools have many advantages as compared with tools made with common abrasives such as corundum and silicon carbide.
Zirconia toughened alumina is a ceramic material comprising alumina and zirconia. It is a composite ceramic material with zirconia grains in the alumina matrix.

Yttria-stabilized zirconia (YSZ) is a ceramic in which the cubic crystal structure of zirconium dioxide is made stable at room temperature by an addition of yttrium oxide. These oxides are commonly called "zirconia" (ZrO2) and "yttria" (Y2O3), hence the name.

Ultrasonic machining is a subtractive manufacturing process that removes material from the surface of a part through high frequency, low amplitude vibrations of a tool against the material surface in the presence of fine abrasive particles. The tool travels vertically or orthogonal to the surface of the part at amplitudes of 0.05 to 0.125 mm. The fine abrasive grains are mixed with water to form a slurry that is distributed across the part and the tip of the tool. Typical grain sizes of the abrasive material range from 100 to 1000, where smaller grains produce smoother surface finishes.
Mass finishing is a group of manufacturing processes that allow large quantities of parts to be simultaneously finished. The goal of this type of finishing is to burnish, deburr, clean, radius, de-flash, descale, remove rust, polish, brighten, surface harden, prepare parts for further finishing, or break off die cast runners. The two main types of mass finishing are tumble finishing, also known as barrel finishing, and vibratory finishing. Both involve the use of a cyclical action to create grinding contact between surfaces. Sometimes the workpieces are finished against each other; however, usually a finishing medium is used. Mass finishing can be performed dry or wet; wet processes have liquid lubricants, cleaners, or abrasives, while dry processes do not. Cycle times can be as short as 10 minutes for nonferrous workpieces or as long as 2 hours for hardened steel.

Bioceramics and bioglasses are ceramic materials that are biocompatible. Bioceramics are an important subset of biomaterials. Bioceramics range in biocompatibility from the ceramic oxides, which are inert in the body, to the other extreme of resorbable materials, which are eventually replaced by the body after they have assisted repair. Bioceramics are used in many types of medical procedures. Bioceramics are typically used as rigid materials in surgical implants, though some bioceramics are flexible. The ceramic materials used are not the same as porcelain type ceramic materials. Rather, bioceramics are closely related to either the body's own materials or are extremely durable metal oxides.
Carborundum Universal Ltd (CUMI) is an Indian company which manufactures and develops abrasives, ceramics, refractories, aluminium oxide grains, machine tools, polymers, adhesives and electro minerals in India. It is a part of the great Murugappa Group.

Geо́rge Antо́novych Gogо́tsi is a soviet Ukrainian scientist, professor of solid mechanics, doctor of science, and leading researcher of the Pisarenko Institute for Problems of Strength of the National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine.
Lithium disilicate (Li2Si2O5) is a chemical compound that is a glass ceramic. It is widely used as a dental ceramic due to its strength, machinability and translucency.

Kiln furniture are devices and implements inside furnaces used during the heating of manufactured individual pieces, such as pottery or other ceramic or metal components. Kiln furniture is made of refractory materials, i.e., materials that withstand high temperatures without deformation. Kiln furniture can account for up to 80% of the mass of a kiln charge.
References
- ↑ "Zirconia – Properties and Applications by Precision Ceramics". azom.com. 3 July 2014. Retrieved 2014-07-14.
- ↑ John B. Wachtman (1991). "15th Annual Conference on Composites and Advanced Ceramic". Ceramic Engineering and Science Proceedings (9): 1935.