An emulsion is a mixture of two or more liquids that are normally immiscible owing to liquid-liquid phase separation. Emulsions are part of a more general class of two-phase systems of matter called colloids. Although the terms colloid and emulsion are sometimes used interchangeably, emulsion should be used when both phases, dispersed and continuous, are liquids. In an emulsion, one liquid is dispersed in the other. Examples of emulsions include vinaigrettes, homogenized milk, liquid biomolecular condensates, and some cutting fluids for metal working.
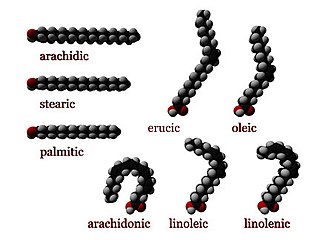
In chemistry, particularly in biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with a long aliphatic chain, which is either saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an unbranched chain of an even number of carbon atoms, from 4 to 28. Fatty acids are a major component of the lipids in some species such as microalgae but in some other organisms are not found in their standalone form, but instead exist as three main classes of esters: triglycerides, phospholipids, and cholesteryl esters. In any of these forms, fatty acids are both important dietary sources of fuel for animals and they are important structural components for cells.

A liqueur is an alcoholic drink composed of distilled spirits and additional flavorings such as sugar, fruits, herbs, and spices. Often served with or after dessert, they are typically heavily sweetened and un-aged beyond a resting period during production, when necessary, for their flavors to mingle.

A detergent is a surfactant or a mixture of surfactants with cleansing properties in dilute solutions. These substances are usually alkylbenzene sulfonates, a family of compounds that are similar to soap but are more soluble in hard water, because the polar sulfonate is less likely than the polar carboxylate to bind to calcium and other ions found in hard water.

Surfactants are compounds that lower the surface tension between two liquids, between a gas and a liquid, or between a liquid and a solid. Surfactants may act as detergents, wetting agents, emulsifiers, foaming agents, or dispersants.

Hand washing, also known as hand hygiene, is the act of cleaning one's hands with soap and water to remove viruses/bacteria/microorganisms, dirt, grease, or other harmful and unwanted substances stuck to the hands. Drying of the washed hands is part of the process as wet and moist hands are more easily recontaminated.

Hair wax is a thick hairstyling product containing wax, used to assist with holding the hair. In contrast with hair gel, most of which contain alcohol, hair wax remains pliable and has less chance of drying out. Consequently, hair wax is currently experiencing an increase in popularity, often under names such as pomade, putty, glue, whip, molding gum, or styling paste. The texture, consistency, and purpose of these products varies widely and each has a different purported purpose depending on the manufacturer. Traditionally, pomade is a type of hair wax that also adds shine to one's hair.

Oleic acid is a fatty acid that occurs naturally in various animal and vegetable fats and oils. It is an odorless, colorless oil, although commercial samples may be yellowish. In chemical terms, oleic acid is classified as a monounsaturated omega-9 fatty acid, abbreviated with a lipid number of 18:1 cis-9. It has the formula CH3(CH2)7CH=CH(CH2)7COOH. The name derives from the Latin word oleum, which means oil. It is the most common fatty acid in nature. The salts and esters of oleic acid are called oleates.

}} Shaving cream or shave cream is a category of cream cosmetics used for shaving preparation. The purpose of shaving cream is to soften the hair by providing lubrication.
A fabric softener is a conditioner that is typically applied to laundry during the rinse cycle in a washing machine to reduce harshness in clothes that are dried in air after machine washing. In contrast to laundry detergents, fabric softeners may be regarded as a kind of after-treatment laundry aid.
Cetyl alcohol, also known as hexadecan-1-ol and palmityl alcohol, is a C-16 fatty alcohol with the formula CH3(CH2)15OH. At room temperature, cetyl alcohol takes the form of a waxy white solid or flakes. The name cetyl derives from the whale oil (cetacea oil, from Latin: cetus, lit. 'whale', from Ancient Greek: κῆτος, romanized: kētos, lit. 'huge fish') from which it was first isolated.
Tall oil, also called liquid rosin or tallol, is a viscous yellow-black odorous liquid obtained as a by-product of the kraft process of wood pulp manufacture when pulping mainly coniferous trees. The name originated as an anglicization of the Swedish tallolja. Tall oil is the third largest chemical by-product in a kraft mill after lignin and hemicellulose; the yield of crude tall oil from the process is in the range of 30–50 kg / ton pulp. It may contribute to 1.0–1.5% of the mill's revenue if not used internally.
Emulsifying wax is a cosmetic emulsifying ingredient. The ingredient name is often followed by the initials NF, indicating that it conforms to the specifications of the National Formulary.

Polysorbate 80 is a nonionic surfactant and emulsifier often used in foods and cosmetics. This synthetic compound is a viscous, water-soluble yellow liquid.
Polysorbate 20 is a polysorbate-type nonionic surfactant formed by the ethoxylation of sorbitan before the addition of lauric acid. Its stability and relative nontoxicity allows it to be used as a detergent and emulsifier in a number of domestic, scientific, and pharmacological applications. As the name implies the ethoxylation process leaves the molecule with 20 repeat units of polyethylene glycol; in practice these are distributed across 4 different chains, leading to a commercial product containing a range of chemical species.

Hand sanitizer is a liquid, gel or foam generally used to kill the vast majority of viruses/bacteria/microorganisms on the hands. In most settings, hand washing with soap and water is generally preferred. Hand sanitizer is less effective at killing certain kinds of germs, such as norovirus and Clostridium difficile, and unlike hand washing, it cannot physically remove harmful chemicals. People may incorrectly wipe off hand sanitizer before it has dried, and some are less effective because their alcohol concentrations are too low.
Poloxamers are nonionic triblock copolymers composed of a central hydrophobic chain of polyoxypropylene flanked by two hydrophilic chains of polyoxyethylene. The word poloxamer was coined by BASF inventor, Irving Schmolka, who received the patent for these materials in 1973. Poloxamers are also known by the trade names Pluronic, Kolliphor, and Synperonic.
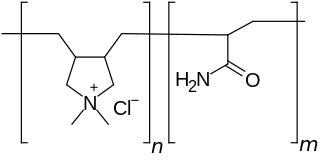
Polyquaternium-7 is an organic compound in the polyquaternium class of chemicals and used in the personal care industry. It is the copolymer of acrylamide and the quaternary ammonium salt diallyldimethylammonium chloride.
Sorbitan monopalmitate (SMP) is a food additive, permitted by the EU. It is entry E495 in the E number list of permitted food additives. It is also known under the trade name Span 40.











