The economy of Brunei, a small and wealthy country, is a mixture of foreign and domestic entrepreneurship, government regulation and welfare measures, and village traditions. It is almost entirely supported by exports of crude oil and natural gas, with revenues from the petroleum sector accounting for over half of GDP. Per capita GDP is high, and substantial income from overseas investment supplements income from domestic production. The government provides for all medical services and subsidizes food and housing. The government has shown progress in its basic policy of diversifying the economy away from oil and gas. Brunei's leaders are concerned that steadily increased integration in the world economy will undermine internal social cohesion although it has taken steps to become a more prominent player by serving as chairman for the 2000 APEC forum. Growth in 1999 was estimated at 2.5% due to higher oil prices in the second half.
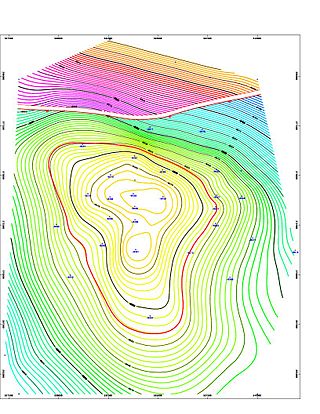
Petroleum engineering is a field of engineering concerned with the activities related to the production of hydrocarbons, which can be either crude oil or natural gas. Exploration and production are deemed to fall within the upstream sector of the oil and gas industry. Exploration, by earth scientists, and petroleum engineering are the oil and gas industry's two main subsurface disciplines, which focus on maximizing economic recovery of hydrocarbons from subsurface reservoirs. Petroleum geology and geophysics focus on provision of a static description of the hydrocarbon reservoir rock, while petroleum engineering focuses on estimation of the recoverable volume of this resource using a detailed understanding of the physical behavior of oil, water and gas within porous rock at very high pressure.

An oil platform is a large structure with facilities to extract and process petroleum and natural gas that lie in rock formations beneath the seabed. Many oil platforms will also have facilities to accommodate the workers, although it is also common to have a separate accommodation platform bridge linked to the production platform. Most commonly, oil platforms engage in activities on the continental shelf, though they can also be used in lakes, inshore waters, and inland seas. Depending on the circumstances, the platform may be fixed to the ocean floor, consist of an artificial island, or float. In some arrangements the main facility may have storage facilities for the processed oil. Remote subsea wells may also be connected to a platform by flow lines and by umbilical connections. These sub-sea facilities may include one or more subsea wells or manifold centres for multiple wells.

An oil well is a drillhole boring in Earth that is designed to bring petroleum oil hydrocarbons to the surface. Usually some natural gas is released as associated petroleum gas along with the oil. A well that is designed to produce only gas may be termed a gas well. Wells are created by drilling down into an oil or gas reserve that is then mounted with an extraction device such as a pumpjack which allows extraction from the reserve. Creating the wells can be an expensive process, costing at least hundreds of thousands of dollars, and costing much more when in hard to reach areas, e.g., when creating offshore oil platforms. The process of modern drilling for wells first started in the 19th century, but was made more efficient with advances to oil drilling rigs during the 20th century.

Hydrocarbon exploration is the search by petroleum geologists and geophysicists for deposits of hydrocarbons, particularly petroleum and natural gas, in the Earth's crust using petroleum geology.

North Sea oil is a mixture of hydrocarbons, comprising liquid petroleum and natural gas, produced from petroleum reservoirs beneath the North Sea.
Oseberg is an offshore oil field with a gas cap in the North Sea located 140 km (87 mi) northwest of the city of Bergen on the southwestern coast of Norway. The field, which is 25 km long by 7 km wide, was discovered in 1979 and its development is known to be one of the significant milestones in emergence of Norway's independent oil and gas industry. The Oseberg field was named after Oseberg ship, one of Norway's most significant archeological discoveries. The ancient Viking ship from the early 9th century was discovered in a 1904 historical excavation of a burial mound at the Oseberg Farm, south of Oslo.
The Buchan oil field is a small oil field with small gas reserves in the central North Sea. It lies in an area known as the South Halibut Basin, approximately 120 miles (190 km) northeast of Aberdeen, Scotland, and is located mainly in license block 21/1A, extending into block 20/5A(E). The field was discovered in August 1974, two years after the issue date for those blocks. It is named after Buchan, an area of N.E. Scotland with its main town being Peterhead.

Offshore drilling is a mechanical process where a wellbore is drilled below the seabed. It is typically carried out in order to explore for and subsequently extract petroleum that lies in rock formations beneath the seabed. Most commonly, the term is used to describe drilling activities on the continental shelf, though the term can also be applied to drilling in lakes, inshore waters and inland seas.

Rasau is an area in Brunei. The area contains one of the two oil fields of Brunei, the Rasau Field, and a small village, Kampong Rasau, which has a population of 103.

Frigg gas field is a natural gas field on Norwegian block 25/1 in the North Sea, on the boundary between the United Kingdom and Norway. The field is named after the goddess Frigg. King Olav V of Norway officially opened production on 8 May 1978. Production was closed on 26 October 2004. The field is situated 230 kilometres (140 mi) northwest of Stavanger. Operator for the field was the French oil company Elf Aquitaine, which merged and changed name to Total S.A.

The Summerland Oil Field is an inactive oil field in Santa Barbara County, California, about four miles (6 km) east of the city of Santa Barbara, within and next to the unincorporated community of Summerland. First developed in the 1890s, and richly productive in the early 20th century, the Summerland Oil Field was the location of the world's first offshore oil wells, drilled from piers in 1896. This field, which was the first significant field to be developed in Santa Barbara County, produced 3.18 million of barrels of oil during its 50-year lifespan, finally being abandoned in 1939-40. Another nearby oil field entirely offshore, discovered in 1957 and named the Summerland Offshore Oil Field, produced from two drilling platforms in the Santa Barbara Channel before being abandoned in 1996.
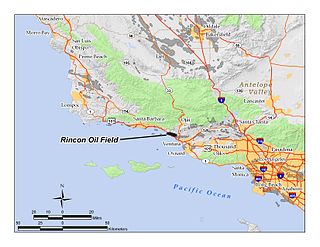
The Rincon Oil Field is a large oil field on the coast of southern California, about 10 miles (16 km) northwest of the city of Ventura, and about 20 miles (32 km) east-southeast of the city of Santa Barbara. It is the westernmost onshore field in a series of three fields which follow the Ventura Anticline, an east-west trending feature paralleling the Transverse Ranges. Discovered in 1927, the oil field is ranked 36th in California by size of recoverable oil reserves, and while mostly depleted – now having, by California Department of Conservation estimates, only about 2.5% of its original oil – it remains productive, with 77 wells active at the beginning of 2008. Oil produced in the field flows through the M-143 pipeline, which parallels U.S. Highway 101 southeast to the Ventura Pump Station, at which point it joins a Tosco pipeline which carries it to Los Angeles area refineries. As of 2009, the primary operators of the field were Occidental Petroleum for the onshore portion, and Greka Energy for the offshore portion. The offshore part of the field is operated mainly from Rincon Island.
Oloibiri Oilfield is an onshore oilfield located in Oloibiri in Ogbia LGA of Bayelsa State, Nigeria, and was the first to be discovered in that country. It is located about 45 miles (72 km) east of Port Harcourt in the Niger Delta. Oloibiri field is about 13.75 square kilometres (5.31 sq mi) and lies in a swamp within OML 29
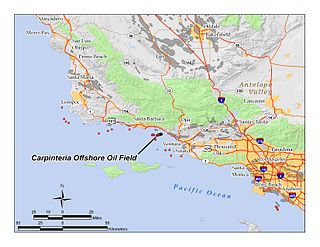
The Carpinteria Offshore Oil Field is an oil and gas field in Santa Barbara Channel, south of the city of Carpinteria in southern California in the United States. Discovered in 1964, and reaching peak production in 1969, it has produced over 106 million barrels of oil in its lifetime, and retains approximately 2 million barrels in reserve recoverable with present technology, according to the California State Department of Natural Resources. Currently the field is produced from three drilling platforms four to five miles offshore, within Federal waters outside of the tidelands zone. Two of the platforms are operated by Pacific Operators Offshore LLC (PACOPS), the operating arm of Carpinteria-based Carone Petroleum; the other platform is operated by Dos Cuadras Offshore Resources (DCOR). The Carpinteria field is the 50th largest field in California by total original oil in place, as of the end of 2008.

Cairn India was an Indian oil and gas exploration and production company, headquartered in Gurgaon, India. The company was merged with Vedanta Limited.

Energy in Brunei is related to all of the type of energy and its related infrastructure used in Brunei. Natural gas and diesel are used significantly in Brunei to generate domestic electricity, as well as gasoline and diesel to power its roads. Domestic supplies were undoubtedly still safe, but they were still susceptible to disturbances that would result in power outages and a lack of gasoline. To reduce the country's susceptibility and the economic hazards brought on by interrupted power and fuel shortages, it is crucial to strengthen the dependability of these sources.

The California oil and gas industry has been a major industry for over a century. Oil production was a minor factor in the 19th century, with kerosene replacing whale oil and lubricants becoming essential to the machine age. Oil became a major California industry in the 20th century with the discovery on new fields around Los Angeles and the San Joaquin Valley, and the dramatic increase in demand for gasoline to fuel automobiles and trucks. In 1900 California pumped 4 million barrels (640,000 m3), nearly 5% of the national supply. Then came a series of major discoveries, and the state pumped 100 million bbl (16 million m3) in 1914, or 38% of the national supply. In 2012 California produced 197 million bbl (31 million m3) of crude oil, out of the total 2,375 million bbl (378 million m3) of oil produced in the U.S, representing 8.3% of national production. California drilling operations and oil production are concentrated primarily in Kern County, San Joaquin Valley and the Los Angeles basin.

Seria oil field also known as Seria Field is the largest oil field in northwest Borneo, discovered in 1929. The oil is accumulated in Upper Miocene sandstone, trapped in Seria Anticline that straddles the present day coastline. This field has produced more than 1 billion barrels of oil for more than 75 years. Brunei Shell Petroleum (BSP) is the operator of this field.
Egret oil field, also known as Egret Field, is a complex oil and gas field in the South China Sea and 45 km north-west of Seria, Belait District, Brunei. It is located at the depth of 60 m, and operated by Brunei Shell Petroleum (BSP).