Related Research Articles

"La Brabançonne" is the national anthem of Belgium. The originally French title refers to Brabant; the name is usually maintained untranslated in Belgium's other two official languages, Dutch and German.

North Brabant, also unofficially called Brabant, is a province in the south of the Netherlands. It borders the provinces of South Holland and Gelderland to the north, Limburg to the east, Zeeland to the west, and the Flemish provinces of Antwerp and Limburg to the south. The northern border follows the Meuse westward to its mouth in the Hollands Diep strait, part of the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta. North Brabant has a population of 2,562,566 as of November 2019. Major cities in North Brabant are Eindhoven, Tilburg, Breda and its provincial capital 's-Hertogenbosch.

John I of Brabant, also called John the Victorious was Duke of Brabant (1267–1294), Lothier and Limburg (1288–1294). During the 13th century, John I was venerated as a folk hero. He has been painted as the perfect model of a brave, adventurous and chivalrous feudal prince.

Walloon Brabant is a province of Wallonia and Belgium. It borders on the province of Flemish Brabant and the provinces of Liège, Namur and Hainaut (Wallonia). Its capital and largest city is Wavre.
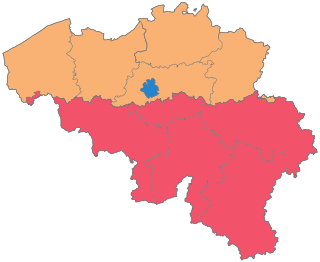
The Kingdom of Belgium is divided into three regions. Two of these regions, Flanders and Wallonia, are each subdivided into five provinces. The third region, Brussels, does not belong to any province and nor is it subdivided into provinces. Instead, it has amalgamated both regional and provincial functions into a single "Capital Region" administration.

Waterloo is a municipality in Wallonia, located in the province of Walloon Brabant, Belgium, which in 2011 had a population of 29,706 and an area of 21.03 km2 (8.12 sq mi). Waterloo lies a short distance south of Brussels, and immediately north-east of the larger town of Braine-l'Alleud. It is the site of the Battle of Waterloo, where the resurgent Napoleon was defeated for the final time in 1815. Waterloo lies immediately south of the official language border between Flanders and Wallonia.

Siger of Brabant was a 13th-century philosopher from the southern Low Countries who was an important proponent of Averroism.

Landgrave was a noble title used in the Holy Roman Empire, and later on in its former territories. The German titles of Landgraf, Markgraf ("margrave"), and Pfalzgraf are in the same class of ranks as Herzog ("duke") and above the rank of a Graf ("count").

The Duke of Brabant was the ruler of the Duchy of Brabant since 1183/1184. The title was created by the Holy Roman Emperor Frederick Barbarossa in favor of Henry I of the House of Reginar, son of Godfrey III of Leuven. The Duchy of Brabant was a feudal elevation of the existing title of landgrave of Brabant. This was an Imperial fief which was assigned to Count Henry III of Leuven shortly after the death of the preceding count of Brabant, Herman II of Lotharingia. Although the corresponding county was quite small its name was applied to the entire country under control of the dukes from the 13th century on. In 1190, after the death of Godfrey III, Henry I also became duke of Lotharingia. Formerly Lower Lotharingia, this title was now practically without territorial authority, but was borne by the later dukes of Brabant as an honorific title.

The coat of arms of Belgium bears a lion or, known as Leo Belgicus, as its charge. This is in accordance with article 193 of the Belgian Constitution: The Belgian nation takes red, yellow and black as colours, and as state coat of arms the Belgian lion with the motto UNITY MAKES STRENGTH. A royal decree of 17 March 1837 determines the achievement to be used in the greater and the lesser version, respectively.

The Belgian or Belgian Draft, French: Trait belge, Dutch: Belgisch Trekpaard, is a Belgian breed of draft horse. It originates from the Brabant region of modern Belgium, and is one of the strongest of the heavy breeds. The breed associations are the Société Royale Le Cheval de Trait Belge/ Koninklijke Maatschappij van het Belgisch Trekpaard and the Eleveurs Wallons du Cheval de Trait Belge/ Vlaamse Fokkers van het Belgisch Trekpaard.

Villers Abbey is an ancient Cistercian abbey located in the town of Villers-la-Ville, in the Walloon Brabant province of Wallonia (Belgium), one piece of the Wallonia's Major Heritage. Founded in 1146, the abbey was abandoned in 1796. Most of the site has since fallen into ruins.

Princess Elisabeth, Duchess of Brabant is the heir apparent to the Belgian throne. The eldest child of King Philippe and Queen Mathilde, she acquired her position after her grandfather King Albert II abdicated in favour of her father on 21 July 2013.

Brabantian or Brabantish, also Brabantic or Brabantine, is a dialect group of the Dutch language. It is named after the historical Duchy of Brabant, which corresponded mainly to the Dutch province of North Brabant, the Belgian provinces of Antwerp and Flemish Brabant as well as the Brussels-Capital Region and the province of Walloon Brabant. Brabantian expands into small parts in the west of Limburg, and its strong influence on the Flemish dialects in East Flanders weakens toward the west. In a small area in the northwest of North Brabant (Willemstad), Hollandic is spoken. Conventionally, the South Guelderish dialects are distinguished from Brabantian but for no objective reason other than geography.

The Duchy of Brabant was a State of the Holy Roman Empire established in 1183. It developed from the Landgraviate of Brabant and formed the heart of the historic Low Countries, part of the Burgundian Netherlands from 1430 and of the Habsburg Netherlands from 1482, until it was partitioned after the Dutch revolt.

The Brabant Revolution or Brabantine Revolution, sometimes referred to as the Belgian Revolution of 1789–90 in older writing, was an armed insurrection that occurred in the Austrian Netherlands between October 1789 and December 1790. The revolution, which occurred at the same time as revolutions in France and Liège, led to the brief overthrow of Habsburg rule and the proclamation of a short-lived polity, the United Belgian States.
Brabants Dagblad is a daily Dutch newspaper. It is distributed in the center and northeast of North Brabant, in 's-Hertogenbosch and Tilburg and their surrounding regions. The paper's office is in 's-Hertogenbosch.
The pagus of Brabant was a geographical region in the early Middle Ages, in what is now Belgium. It was the first region known to have been called Brabant, and it included the modern capital of Belgium, Brussels.
References
- ↑ A. de Geradon, "L'étrange carrière du chanoine Gilain de Sart, chancelier de Liège et de Brabant", Bulletin de l'Institut archéologique liégeois 88 (1976), pp. 129-135.