
Mervyn Laurence Peake was an English writer, artist, poet, and illustrator. He is best known for what are usually referred to as the Gormenghast books. The four works were part of what Peake conceived as a lengthy cycle, the completion of which was prevented by his death. They are sometimes compared to the work of his older contemporary J. R. R. Tolkien, but Peake's surreal fiction was influenced by his early love for Charles Dickens and Robert Louis Stevenson rather than Tolkien's studies of mythology and philology.

A nursery rhyme is a traditional poem or song for children in Britain and many other countries, but usage of the term dates only from the late 18th/early 19th century. The term Mother Goose rhymes is interchangeable with nursery rhymes.

Humpty Dumpty is a character in an English nursery rhyme, probably originally a riddle and one of the best known in the English-speaking world. He is typically portrayed as an anthropomorphic egg, though he is not explicitly described as such. The first recorded versions of the rhyme date from late eighteenth-century England and the tune from 1870 in James William Elliott's National Nursery Rhymes and Nursery Songs. Its origins are obscure, and several theories have been advanced to suggest original meanings.

Charles Haddon Spurgeon was an English Particular Baptist preacher.

"Jack and Jill" is a traditional English nursery rhyme. The Roud Folk Song Index classifies the commonest tune and its variations as number 10266, although it has been set to several others. The original rhyme dates back to the 18th century and different numbers of verses were later added, each with variations in the wording. Throughout the 19th century new versions of the story were written featuring different incidents. A number of theories continue to be advanced to explain the rhyme’s historical origin.

Sterling Price Holloway Jr. was an American actor who appeared in over 100 films and 40 television shows. He did voice acting for The Walt Disney Company, playing Mr. Stork in Dumbo, Adult Flower in Bambi, the Cheshire Cat in Alice in Wonderland, Kaa in The Jungle Book, Roquefort the Mouse in The Aristocats, and the title character in Winnie the Pooh, among many others.

"Baa, Baa, Black Sheep" is an English nursery rhyme, the earliest printed version of which dates from around 1744. The words have not changed very much in two and a half centuries. It is sung to a variant of the 18th century French melody Ah! vous dirai-je, maman.

Rose Amy Fyleman was an English writer and poet, noted for her works on the fairy folk, for children. Her poem "There are fairies at the bottom of our garden" was set to music by English composer Liza Lehmann. Her carol "Lift your hidden faces", set to a French carol tune, was included in the Anglican hymnal Songs of Praise (1925), The Oxford Book of Carols (1928) as well as in the Hutterian Brotherhood's Songs of Light (1977).
The Amalgamated Press (AP) was a British newspaper and magazine publishing company founded by journalist and entrepreneur Alfred Harmsworth (1865–1922) in 1901, gathering his many publishing ventures together under one banner. At one point the largest publishing company in the world, AP employed writers such as Arthur Mee, John Alexander Hammerton, Edwy Searles Brooks, and Charles Hamilton. Its subsidiary, the Educational Book Company, published The Harmsworth Self-Educator, The Children's Encyclopædia, and Harmsworth's Universal Encyclopaedia. The company's newspapers included the Daily Mail, the Daily Mirror, The Evening News, The Observer, and The Times. At its height, AP published over 70 magazines and operated three large printing works and paper mills in South London.

Walter Henry Passmore was an English singer and actor best known as the first successor to George Grossmith in the comic baritone roles in Gilbert and Sullivan operas with the D'Oyly Carte Opera Company.

Marguerite de Angeli was an American writer and illustrator of children's books including the 1950 Newbery Award winning book The Door in the Wall. She wrote and illustrated twenty-eight of her own books, and illustrated more than three dozen books and numerous magazine stories and articles for other authors.

David Whitelaw (1875–1970) British writer, editor and illustrator.
William Garrett Lewis (1821–1885) was a Baptist preacher and pastor of Westbourne Grove Church in Bayswater, London for 33 years. He was an apologist author of two books, Westbourne Grove Sermons and The Trades and Industrial Occupations of the Bible, published by the Religious Tract Society.
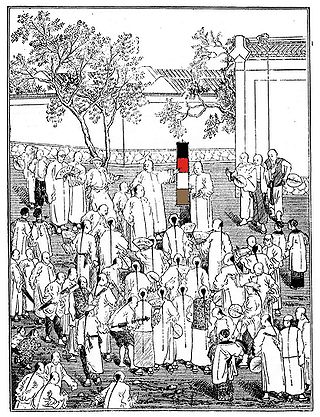
The Wordless Book is a Christian evangelistic book. Evidence points to it being invented by the famous London Baptist preacher Charles Haddon Spurgeon, in a message given on January 11, 1866 to several hundred orphans regarding Psalm 51:7 "Wash me, and I shall be whiter than snow." It is called a "book", as it is usually represented with pages, although it can be shown on a single page or banner.

Reginald Bathurst Birch was an English-American artist and illustrator. He was best known for his depiction of the titular hero of Frances Hodgson Burnett's 1886 novel Little Lord Fauntleroy, which started a craze in juvenile fashion. While his illustrated corpus has eclipsed his other work, he was also an accomplished painter of portraits and landscapes.
Harry Rountree was a prolific illustrator working in England around the turn of the 20th century. Born in Auckland, New Zealand, he moved to London in 1901, when he was 23 years old.
Teddy Tail was a British newspaper comic strip about a cartoon mouse featured in The Daily Mail from 5 April 1915. It was the first daily cartoon strip in a British newspaper, The character survived until the 1960s with several artists drawing newspaper strips and the varied annuals. Such was his popularity that other newspapers created their own cartoon characters, the Daily Express with Rupert Bear and the Daily Mirror with Pip, Squeak and Wilfred.

Margaret Winifred Tarrant was an English illustrator, and children's author, specializing in depictions of fairy-like children and religious subjects. She began her career at the age of 20, and painted and published into the early 1950s. She was known for her children's books, postcards, calendars, and print reproductions.

Agnes Fraser Elder Fraser-Smith was a Scottish actress and soprano, known as Agnes Fraser, who appeared in the later Savoy Operas and in Edwardian musical comedy. She married the Gilbert and Sullivan performer Walter Passmore, with whom she frequently appeared on stage.

Aubrey Hopwood was a British lyricist of Edwardian musical comedy and a novelist and author of nonsense books for children. He co-wrote the lyrics for the musicals Alice in Wonderland (1886), A Runaway Girl (1898) and The Lucky Star (1899), among others.















