
The Choctaw are a Native American people originally based in the Southeastern Woodlands, in what is now Alabama and Mississippi. Their Choctaw language is a Western Muskogean language. Today, Choctaw people are enrolled in three federally recognized tribes: the Choctaw Nation of Oklahoma, Mississippi Band of Choctaw Indians, and Jena Band of Choctaw Indians in Louisiana.

Mobile Bay is a shallow inlet of the Gulf of Mexico, lying within the state of Alabama in the United States. Its mouth is formed by the Fort Morgan Peninsula on the eastern side and Dauphin Island, a barrier island on the western side. The Mobile River and Tensaw River empty into the northern end of the bay, making it an estuary. Several smaller rivers also empty into the bay: Dog River, Deer River, and Fowl River on the western side of the bay, and Fish River on the eastern side. Mobile Bay is the fourth-largest estuary in the United States with a discharge of 62,000 cubic feet (1,800 m3) of water per second. Annually, and often several times during the summer months, the fish and crustaceans will swarm the shallow coastline and shore of the bay. This event, appropriately named a jubilee, draws a large crowd because of the abundance of fresh, easily caught seafood.

Hernando de Soto was a Spanish explorer and conquistador who was involved in expeditions in Nicaragua and the Yucatan Peninsula. He played an important role in Francisco Pizarro's conquest of the Inca Empire in Peru, but is best known for leading the first European expedition deep into the territory of the modern-day United States. He is the first European documented as having crossed the Mississippi River.

Minter City is an unincorporated community in Leflore County and Tallahatchie County, Mississippi. It is part of the Greenwood, Mississippi micropolitan area, and is within the Mississippi Delta.

The Mississippian culture was a Native American civilization that flourished in what is now the Midwestern, Eastern, and Southeastern United States from approximately 800 to 1600, varying regionally. It was known for building large, earthen platform mounds, and often other shaped mounds as well. It was composed of a series of urban settlements and satellite villages linked together by loose trading networks. The largest city was Cahokia, believed to be a major religious center located in what is present-day southern Illinois.
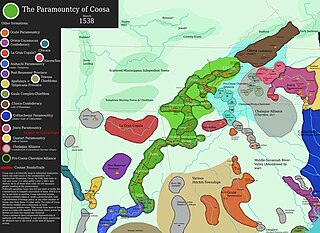
The Coosa chiefdom was a powerful Native American paramount chiefdom in what are now Gordon and Murray counties in Georgia, in the United States. It was inhabited from about 1400 until about 1600, and dominated several smaller chiefdoms. The total population of Coosa's area of influence, reaching into present-day Tennessee and Alabama, has been estimated at 50,000.
Hitchiti was a tribal town in what is now the Southeast United States. It was one of several towns whose people spoke the Hitchiti language. It was first known as part of the Apalachicola Province, an association of tribal towns along the Chattahoochee River. Shortly after 1690, the towns of Apalachicola Province moved to the central part of present-day Georgia, with Hitchiti joining most of those towns along Ochese Creek. In 1715, most of the towns on Ochese Creek, including Hitchiti, moved back to the Chattahoochee River, where the town remained until its people were forced to move to Indian Territory as part of the Trail of Tears.
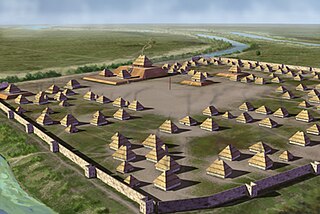
Parkin Archeological State Park, also known as Parkin Indian Mound, is an archeological site and state park in Parkin, Cross County, Arkansas. Around 1350–1650 CE an aboriginal palisaded village existed at the site, at the confluence of the St. Francis and Tyronza rivers. Artifacts from this site are on display at the site museum. The Parkin site is the type site for the Parkin phase, an expression of the Mississippian culture from the Late Mississippian period. Many archeologists believe it to be part of the province of Casqui, documented as visited by Spanish explorer Hernando de Soto in 1542. Archeological artifacts from the village of the Parkin people are dated to 1400–1650 CE.

Charles Melvin Hudson Jr. (1932–2013) was an anthropologist, a professor of anthropology and history at the University of Georgia. He was a leading scholar on the history and culture of Indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands of the present-day United States. He is known for his book mapping the expedition of Spanish explorer Hernando de Soto in the mid-16th century in the Southeast, based on both the expedition's records and sites identified through archeology and anthropology.

Coles Creek culture is a Late Woodland archaeological culture in the Lower Mississippi valley in the Southeastern Woodlands. It followed the Troyville culture. The period marks a significant change in the cultural history of the area. Population increased dramatically and there is strong evidence of a growing cultural and political complexity, especially by the end of the Coles Creek sequence. Although many of the classic traits of chiefdom societies are not yet manifested, by 1000 CE the formation of simple elite polities had begun. Coles Creek sites are found in Arkansas, Louisiana, and Mississippi. It is considered ancestral to the Plaquemine culture.

The Plaquemine culture was an archaeological culture centered on the Lower Mississippi River valley. It had a deep history in the area stretching back through the earlier Coles Creek and Troyville cultures to the Marksville culture. The Natchez and related Taensa peoples were their historic period descendants. The type site for the culture is the Medora site in Louisiana; while other examples include the Anna, Emerald, Holly Bluff, and Winterville sites in Mississippi.

The Walls phase is an archaeological phase in southwestern Tennessee and northwestern Mississippi of the Late Mississippian culture. Chucalissa is a Walls phase mound and plaza complex located on a bluff overlooking the Mississippi River. Other contemporaneous groups in the area include the Parkin phase, Tipton phase, Menard phase, and the Nodena phase. The Walls phase is the last prehistoric people to inhabit the Memphis area before the arrival of Europeans. During the early 1540s the Hernando de Soto Expedition passed through the area, stopping at many villages along the way. It is thought that the Walls phase may be the Province of Quizquiz, a Tunican people encountered by de Soto on the banks of the Mississippi River.

The Tipton phase is an archaeological phase in southwestern Tennessee of the Late Mississippian culture. Other contemporaneous groups in the area include the Parkin phase, Walls phase, Menard phase, and the Nodena phase. The Tipton phase is the last prehistoric people to inhabit the area before the arrival of Europeans. It is located directly across the Mississippi River from the people of the Nodena phase and directly north of the Walls phase. During the early 1540s the Hernando de Soto Expedition passed through the area, stopping at many villages in the area. The phase itself is named for Tipton County, Tennessee.
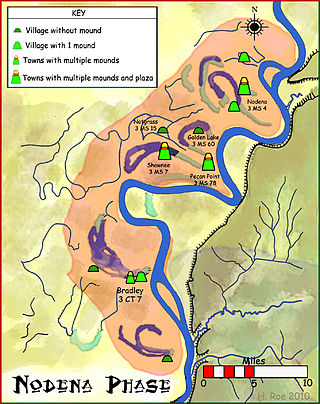
The Nodena phase is an archaeological phase in eastern Arkansas and southeastern Missouri of the Late Mississippian culture which dates from about 1400–1650 CE. The Nodena phase is known from a collection of villages along the Mississippi River between the Missouri Bootheel and Wapanocca Lake. They practiced extensive maize agriculture and artificial cranial deformation and were members of a continent wide trade and religious network known as the Southeastern Ceremonial Complex, which brought chert, whelk shells, and other exotic goods to the area.

Jordan Mounds is a multimound archaeological site in Morehouse Parish, Louisiana. It is the type site for the Jordan Phase of the local chronology. The site was constructed during the protohistoric period between 1540 and 1685.

The Pensacola culture was a regional variation of the Mississippian culture along the Gulf Coast of the United States that lasted from 1100 to 1700 CE. The archaeological culture covers an area stretching from a transitional Pensacola/Fort Walton culture zone at Choctawhatchee Bay in Florida to the eastern side of the Mississippi River Delta near Biloxi, Mississippi, with the majority of its sites located along Mobile Bay in the Mobile-Tensaw River Delta. Sites for the culture stretched inland, north into the southern Tombigee and Alabama River valleys, as far as the vicinity of Selma, Alabama.
The Carson Mounds, also known as the Carson Site and Carson-Montgomery- is a large Mississippian culture archaeological site located near Clarksdale in Coahoma County, Mississippi, in the Yazoo Basin. Only a few large earthen mounds are still present at Carson to this day. Archaeologists have suggested that Carson is one of the more important archaeological sites in the state of Mississippi.

Fort Dale was a stockade fort built in present-day Butler County, Alabama by Alabama Territory settlers. The fort was constructed in response to Creek Indian attacks on settlers in the surrounding area.















