Related Research Articles

William Carey was an English Christian missionary, Particular Baptist minister, translator, social reformer and cultural anthropologist who founded the Serampore College and the Serampore University, the first degree-awarding university in India and cofounded the Serampore Mission Press.

The Kaisar-i-Hind Medal for Public Service in India was a medal awarded by the Emperor/Empress of India between 1900 and 1947, to "any person without distinction of race, occupation, position, or sex ... who shall have distinguished himself by important and useful service in the advancement of the public interest in India."

Sam Higginbottom University of Agriculture, Technology and Sciences (SHUATS), formerly Allahabad Agricultural Institute, is a government-aided university in Prayagraj, Uttar Pradesh, India. It operates as an autonomous Christian minority institution under the 'Sam Higginbottom Educational and Charitable Society, Allahabad'.

St. John's College is a constituent college of Dr. Bhimrao Ambedkar University, located in Agra. It is a Christian college under the Church of North India. It was established by the Church Mission Society to Agra. The college admits both undergraduates and postgraduates and awards degrees in liberal arts, commerce, sciences, business administration and education under the purview of Agra University.

Shubha Mudgal is an Indian singer, and composer, known for her works in Hindustani classical music, Indian pop, and Tamil cinema. Her repertoire includes the genres of khyal, thumri, dadra. She has received the Padma Shri in 2000.

Cornelia Sorabji was an Indian lawyer, social reformer and writer. She was the first female graduate from Bombay University, and the first woman to study law at Oxford University. Returning to India after her studies at Oxford, Sorabji became involved in social and advisory work on behalf of the purdahnashins, women who were forbidden to communicate with the outside male world, but she was unable to defend them in court since, as a woman, she did not hold professional standing in the Indian legal system. Hoping to remedy this, Sorabji presented herself for the LLB examination of Bombay University in 1897 and the pleader's examination of Allahabad High Court in 1899. She became the first female advocate in India but would not be recognised as a barrister until the law which barred women from practising was changed in 1923.

Samuel Higginbottom was an English-born Christian missionary in Allahabad, India, where he founded the Allahabad Agricultural Institute. Higginbottom was born in Manchester, England.

Iswari Prasad Upadhyaya (1888–1986) was an Indian historian. He was an alumnus of Aligarh Muslim University, and first graduate of the university. He dealt mainly with the Muslim rulers and governments of India, especially with the Mughal and Tughluq dynasties. He did extensive work on rulers such as Muhammad bin Tughluq, the Sultan of Delhi, Humayun, and Aurangzeb.

John Lawrence Goheen was an American missionary, educator and administrator, agriculturist, social worker, and writer who spent most of his career working in India. He made a major contribution to literacy through the Bombay Literacy Campaign of 1939. He established Adult Education Associations in various parts in India with a slogan "Every home a literate home". He promoted religious organizations for literacy conferences. Goheen was also a college football player and coach in the 1900s.
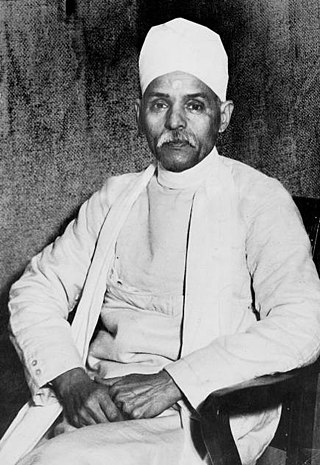
Madan Mohan Malaviya was an Indian scholar, educational reformer and politician notable for his role in the Indian independence movement. He was president of the Indian National Congress three times and the founder of Akhil Bharat Hindu Mahasabha. He was addressed as Pandit, a title of respect.

Karimpur I is a community development block that forms an administrative division in Tehatta subdivision of Nadia district in the Indian state of West Bengal.

Karimpur II is a community development block that forms an administrative division in Tehatta subdivision of Nadia district in the Indian state of West Bengal.
William Henricks Wiser (28 January 1890 – 21 February 1961), also spelled as Hendricks, was an American anthropologist, and a Fourth Presbyterian Church, Chicago IL Presbyterian rural-missionary sent to North India - Uttar Pradesh.

Lilavati Singh, also seen as Lilivati Singh, was an Indian educator, professor of literature and philosophy at Isabella Thoburn College in Lucknow.

Annie Maria Barnes was a 19th-century American journalist, editor, and author from South Carolina. At the age of eleven, she wrote an article for the Atlanta Constitution, and at the age of fifteen, she became a regular correspondent of that journal. In 1887, she began publishing The Acanthus, a juvenile paper published in the Southern United States. Barnes published novels from 1887 until at least 1927.

Althea Maria Brown Edmiston was an African-American teacher and Presbyterian missionary, working in the Belgian Congo for more than thirty years. She compiled the first dictionary and grammar for Bushong, the language of the Kuba Kingdom.
Susan Snow Wadley is an American anthropologist.

William Spence Urquhart was a Scottish religious scholar, Christian missionary and academic in India. He influenced among others one of his college students, the religious leader A. C. Bhaktivedanta Swami Prabhupada.

Charlotte Chandler Wyckoff was an American writer and missionary educator, based in India.

Ram Chandra Bose was an educator, a lay evangelist, and a prominent writer in the region of North India known as the North-Western Provinces and Oudh in the late 19th century. He converted to Christianity while a student in Calcutta. Upon completing his education, he was employed by several Christian mission agencies as well as the government to teach in their schools. In the 1870s and 1880s, he was associated with the American Methodist Episcopal Mission and travelled across India as a lay evangelist. Many of his lectures were published as journal articles or compiled into books creating a prolific literary legacy. Bose wrote over 100 journal articles on religious, philosophical, and social issues for journals such as The Bengal Magazine edited by Lal Behari Day as well as the Calcutta Review, the Indian Evangelical Review, and others. Shortly before he died in 1892, he left the American Methodist Mission to join the Anglican Church Missionary Society.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "Charlotte Melina Viall Wiser". las.iastate.edu. Archived from the original on May 14, 2013. Retrieved May 2, 2012.
1892 – 1981 Charlotte Melina Viall was born in Chicago IL in 1892. She graduated from the University of Chicago She went to India as a Presbyterian Missionary in 1916.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Anderson, Gerald H. (1999). Biographical Dictionary of Christian Missions. Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing. p. 746. ISBN 978-0-8028-4680-8.
- ↑ Hess, Gary R. (1968). "American Agricultural Missionaries and Efforts at Economic Improvement in India". Agricultural History. 42 (1): 23–34. ISSN 0002-1482.
- 1 2 3 4 "Yale University Divinity School Library – Historical Sketch". NY Times Co. Archived from the original on December 15, 2012. Retrieved May 2, 2012.
JCharlotte Wiser also taught courses at the Allahabad Agricultural Institute – Charlotte Wiser received a M.S. degree in nutrition from Cornel
- 1 2 3 Wadley, Susan Snow (1994). Struggling With Destiny in Karimpur, 1925–1984 . University of California Press. p. xviii. ISBN 978-0-520-08407-0.
William wiser, Presbyterian Missionary, north india.
- ↑ Siegel, Benjamin (May 2016). "'Self-Help which Ennobles a Nation': Development, citizenship, and the obligations of eating in India's austerity years". Modern Asian Studies. 50 (3): 975–1018. doi:10.1017/S0026749X14000493. ISSN 0026-749X.
- ↑ Chaudhuri, Nupur (1992). Western Women and Imperialism: Complicity and Resistance. Indiana University Press. p. 205. ISBN 978-0-253-20705-0.
- ↑ "WISER, WILLIAM WITH CHARLOTTE WISER". abebooks.com. Retrieved May 1, 2012.
- ↑ "Most widely held works by Charlotte Viall Wiser". orlabs.oclc.org. Retrieved May 2, 2012.