
Sir James Douglas was a Canadian fur trader and politician who became the first Governor of the Colony of British Columbia. He is often credited as "The Father of British Columbia". He was instrumental to the resettlement of 35 African Americans fleeing a life of racial persecution in San Francisco who arrived in the province aboard the steamship Commodore in what later became known as the Pioneer Committee. In 1863, Douglas was knighted by Queen Victoria for his services to the Crown.

The Fraser Canyon Gold Rush, began in 1858 after gold was discovered on the Thompson River in British Columbia at its confluence with the Nicoamen River a few miles upstream from the Thompson's confluence with the Fraser River at present-day Lytton. The rush overtook the region around the discovery, and was centered on the Fraser Canyon from around Hope and Yale to Pavilion and Fountain, just north of Lillooet.

The Lillooet Ranges are the southeasternmost subdivision of the Pacific Ranges of the Coast Mountains of British Columbia. They are located between the drainage of the Lillooet River and Harrison Lake on the west and the canyon of the Fraser River on the east, and by the lowland coastal valley of that river on the south.

The Garibaldi Ranges are the next-to-southwesternmost subdivision of the Pacific Ranges of the Coast Mountains; only the North Shore Mountains are farther southwest. They lie between the valley formed by the pass between the Cheakamus River and Green River on the west and the valley of the Lillooet River on the east, and extend south into Maple Ridge, an eastern suburb of Vancouver, and the northern District of Mission. To their south are the North Shore Mountains overlooking Vancouver while to their southeast are the Douglas Ranges.

The Douglas Ranges are a subrange of the Pacific Ranges of the Coast Mountains of the Canadian province of British Columbia, about 70 km (43 mi) east of downtown Vancouver, north of the Fraser River and between the valleys of Stave and Harrison Lakes. They are approximately 4,900 km2 (1,900 sq mi) in area. Their highest peak is Mount Robertson 2,252 m (7,388 ft), at the northwest limit of the range.
Mount Raleigh, elevation 3,132 m (10,276 ft), is one of the principal summits of the Pacific Ranges of the Coast Mountains of southern British Columbia in Canada. It is located just southeast of the confluence of the Southgate and Bishop Rivers, northeast of the head of Bute Inlet, and is the highest summit south of the Bishop River's divide with the Lillooet River at Ring Pass, which is at the southeastern edge of the Lillooet Icefield and just north of the Pemberton Icecap. It is also the highest peak south of the pass between the upper basins of Chilko Lake and the Taseko Lakes, just north of which is Monmouth Mountain at 3,182 m (10,440 ft).

Monmouth Mountain, commonly known as Mount Monmouth is one of the principal summits of the Pacific Ranges of the Coast Mountains of southern British Columbia. At 3,182 m (10,440 ft), it is the highest summit of the Chilcotin Ranges. It stands just north of the Lillooet Icecap between the heads of Chilko Lake and the Taseko Lakes. West of Chilko Lake's south arm is Mount Good Hope 3,242 m (10,636 ft) and, beyond it, the massif surrounding Mount Queen Bess 3,298 m (10,820 ft), which is the highest summit east of the Homathko River.

The Camelsfoot Range is a sub-range of the Chilcotin Ranges subdivision of the Pacific Ranges of the Coast Mountains in British Columbia. The Fraser River forms its eastern boundary. The range is approximately 90 km at its maximum length and less than 30 km wide at its widest.
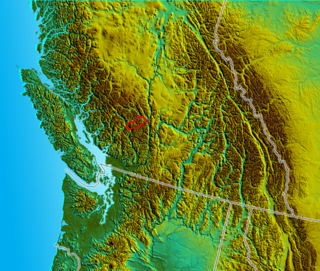
The Cayoosh Range is the northernmost section of the Lillooet Ranges, which are a subrange of the Pacific Ranges of the Coast Mountains in British Columbia, Canada. The range covers an area of c. 3770 km² and is approximately 65 km (40 mi) SW to NE and about 20 km (12 mi) SE to NW.

The Cantilever Range is a mountain range in southwestern British Columbia, Canada, a subrange of the Lillooet Ranges, which is itself a subgrouping of the Pacific Ranges of the Coast Mountains. About 1100 km2 in area and about 50 km east to west and 35 km north to south, the Cantilever Range is located southwest of Lytton between the valleys of the Stein River (N) and Kwoiek Creek (S).

The Colony of British Columbia was a crown colony in British North America from 1858 until 1866 that was founded by Richard Clement Moody, who was selected to 'found a second England on the shores of the Pacific', who was Chief Commissioner of Lands and Works for British Columbia and the first Lieutenant-Governor of British Columbia. Prior to the arrival of Moody's Royal Engineers, Columbia Detachment, the Colony's supreme authority was its Governor James Douglas, who was the Governor of the neighbouring colony of Vancouver Island.

The Mount Meager massif is a group of volcanic peaks in the Pacific Ranges of the Coast Mountains in southwestern British Columbia, Canada. Part of the Cascade Volcanic Arc of western North America, it is located 150 km (93 mi) north of Vancouver at the northern end of the Pemberton Valley and reaches a maximum elevation of 2,680 m (8,790 ft). The massif is capped by several eroded volcanic edifices, including lava domes, volcanic plugs and overlapping piles of lava flows; these form at least six major summits including Mount Meager which is the second highest of the massif.

Thomas Elwyn was a British soldier, police officer and gold commissioner in colonial British Columbia.
Cayoosh Pass is a mountain pass in the Lillooet Ranges of the Pacific Ranges of the southern Coast Mountains in British Columbia, Canada. It lies just west of Duffey Lake on BC Highway 99 between the towns of Lillooet and Pemberton, formed by the headwaters of Cayoosh Creek to the east, flowing to the Fraser River at Lillooet, and Joffre Creek to the west, flowing steeply downhill to Lillooet Lake just southeast of the Mount Currie Indian Reserve.

Cayoosh Creek is a northeast-flowing tributary of the Seton River in the Canadian province of British Columbia. The name Cayoosh Creek remains on the bridge-sign crossing the stream on BC Highway 99 and continues in use locally to refer to the final reaches of the Seton River, formerly Seton Creek, which prior to the renaming ending at the confluence with Cayoosh Creek. The creek is the namesake of Cayoosh Creek Indian Reserve No. 1, one of the main Indian reserves of the Cayoose Creek Indian Band, which lies adjacent to what was renamed the Seton River without local consultation.
Mount Brew is a mountain located 12 km (7 mi) south of Lillooet and 44 km (27 mi) north of Skihist Mountain in south-central British Columbia, Canada. It lies on the western side of the Fraser River and is the third-highest mountain of the Lillooet Ranges, after Skihist Mountain and Petlushkwohap Mountain in the Cantilever Range to the west of Lytton.
Birkenhead Peak, commonly known as Mount Birkenhead and sometimes Birkenhead Mountain or Mount Birken is a mountain in the Gates Valley region of the Lillooet Country of the South-Central Interior of British Columbia, Canada. Located approximately midway between the towns of Lillooet (NE) and Pemberton-Mount Currie, the mountain's very high prominence separates it from the adjoining Cadwallader Range by the pass between Blackwater Creek and Birkenhead Lake.
The 5th Legislative Assembly of British Columbia sat from 1887 to 1890. The members were elected in the British Columbia general election held in July 1886. William Smithe formed a government. Following his death in May 1887, Alexander Edmund Batson Davie became premier. After Davie died in 1889, John Robson became premier.
Crevasse Crag is a jagged steep-sided prominence on the summit of a glaciated mountain ridge in the Lillooet Ranges of southwestern British Columbia, Canada. It is located about 49 km (30 mi) southeast of the village of Pemberton. Situated on the boundary between New Westminster Land District and Kamloops Division Yale Land District, the peak has a maximum elevation of 2,496 m (8,189 ft) and a topographic prominence of 66 m (217 ft).

Mount Meager is a mountain in the Pacific Ranges of the Coast Mountains in British Columbia, Canada. It represents the second highest peak of the Mount Meager massif, a group of coalescent stratovolcanoes in the Garibaldi Volcanic Belt.














