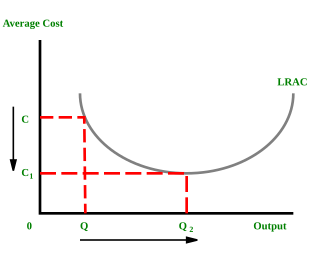
In microeconomics, economies of scale are the cost advantages that enterprises obtain due to their scale of operation, and are typically measured by the amount of output produced per unit of time. A decrease in cost per unit of output enables an increase in scale. At the basis of economies of scale, there may be technical, statistical, organizational or related factors to the degree of market control. This is just a partial description of the concept.

A consumer price index (CPI) is a price index, the price of a weighted average market basket of consumer goods and services purchased by households. Changes in measured CPI track changes in prices over time.

Construction is a general term meaning the art and science to form objects, systems, or organizations, and comes from Latin constructio and Old French construction. To construct is the verb: the act of building, and the noun is construction: how something is built, the nature of its structure.
The organic composition of capital (OCC) is a concept created by Karl Marx in his theory of capitalism, which was simultaneously his critique of the political economy of his time. It is derived from his more basic concepts of 'value composition of capital' and 'technical composition of capital'. Marx defines the organic composition of capital as "the value-composition of capital, in so far as it is determined by its technical composition and mirrors the changes of the latter". The 'technical composition of capital' measures the relation between the elements of constant capital and variable capital. It is 'technical' because no valuation is here involved. In contrast, the 'value composition of capital' is the ratio between the value of the elements of constant capital involved in production and the value of the labor. Marx found that the special concept of 'organic composition of capital' was sometimes useful in analysis, since it assumes that the relative values of all the elements of capital are constant.
The Lang Factor is an estimated ratio of the total cost of creating a process within a plant, to the cost of all major technical components. It is widely used in industrial engineering to calculate the capital and operating costs of a plant.

The Producer Price Index (PPI) is the official measure of producer prices in the economy of the United States. It measures average changes in prices received by domestic producers for their output. The PPI was known as the Wholesale Price Index, or WPI, up to 1978. It is published by the Bureau of Labor Statistics and is one of the oldest economic time series compiled by the Federal government of the United States.
A feasibility study is an assessment of the practicality of a project or system. A feasibility study aims to objectively and rationally uncover the strengths and weaknesses of an existing business or proposed venture, opportunities and threats present in the natural environment, the resources required to carry through, and ultimately the prospects for success. In its simplest terms, the two criteria to judge feasibility are cost required and value to be attained.

A chemical plant is an industrial process plant that manufactures chemicals, usually on a large scale. The general objective of a chemical plant is to create new material wealth via the chemical or biological transformation and or separation of materials. Chemical plants use specialized equipment, units, and technology in the manufacturing process. Other kinds of plants, such as polymer, pharmaceutical, food, and some beverage production facilities, power plants, oil refineries or other refineries, natural gas processing and biochemical plants, water and wastewater treatment, and pollution control equipment use many technologies that have similarities to chemical plant technology such as fluid systems and chemical reactor systems. Some would consider an oil refinery or a pharmaceutical or polymer manufacturer to be effectively a chemical plant.
Construction management (CM) is a professional service that uses specialized, project management techniques and software to oversee the planning, design, construction and closeout of a project. The purpose of construction management is to control the quality of a project's scope, time / delivery and cost—sometimes referred to as a project management triangle or "triple constraints." CM is compatible with all project delivery systems, including design-bid-build, design-build, CM At-Risk and Public Private Partnerships. Professional construction managers may be hired for large to jumbo-scale, high budget undertakings, called capital projects.
An escalation clause is a clause in a lease or contract that allow for a change in the agreed-upon price in response to a specific factor that is outside of the control of either party. This type of clause is used to protect against potential changes in the value of the goods or services being exchanged, such as in cases of inflation or other market fluctuations.
In chemical engineering, process design is the choice and sequencing of units for desired physical and/or chemical transformation of materials. Process design is central to chemical engineering, and it can be considered to be the summit of that field, bringing together all of the field's components.
Cost escalation can be defined as changes in the cost or price of specific goods or services in a given economy over a period. This is similar to the concepts of inflation and deflation except that escalation is specific to an item or class of items, it is often not primarily driven by changes in the money supply, and it tends to be less sustained. While escalation includes general inflation related to the money supply, it is also driven by changes in technology, practices, and particularly supply-demand imbalances that are specific to a good or service in a given economy. For example, while general inflation in the US was less than 5% in the 2003-2007 time period, steel prices increased (escalated) by over 50% because of supply-demand imbalance. Cost escalation may contribute to a project cost overrun but it is not synonymous with it.
A cost estimate is the approximation of the cost of a program, project, or operation. The cost estimate is the product of the cost estimating process. The cost estimate has a single total value and may have identifiable component values.
Asset management is a systematic approach to the governance and realization of value from the things that a group or entity is responsible for, over their whole life cycles. It may apply both to tangible assets and to intangible assets. Asset management is a systematic process of developing, operating, maintaining, upgrading, and disposing of assets in the most cost-effective manner.

Engineering News-Record is an American weekly magazine that provides news, analysis, data and opinion for the construction industry worldwide. It is widely regarded as one of the construction industry's most authoritative publications and is considered by many to be the "bible" of the industry. It is owned by BNP Media.
For the application of engineering economics in the practice of civil engineering see Engineering economics.
Produced by the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) in the US Department of Labor, the National Compensation Survey (NCS) provides comprehensive measures of occupational earnings; compensation cost trends, benefit incidence, and detailed plan provisions. It is used to adjust the federal wage schedule for all federal employees. Detailed occupational earnings are available for metropolitan and non-metropolitan areas, broad geographic regions, and on a national basis. The index component of the NCS measures changes in labor costs. Average hourly employer cost for employee compensation is presented in the Employer Costs for Employee Compensation.

Crushed stone or angular rock is a form of construction aggregate, typically produced by mining a suitable rock deposit and breaking the removed rock down to the desired size using crushers. It is distinct from naturally occurring gravel, which is produced by natural processes of weathering and erosion and typically has a more rounded shape.
The following is a glossary of terms relating to construction cost estimating.
Techno-economic assessment or techno-economic analysis is a method of analyzing the economic performance of an industrial process, product, or service. It typically uses software modeling to estimate capital cost, operating cost, and revenue based on technical and financial input parameters. One desired outcome is to summarize results in a concise and visually coherent form, using visualization tools such as tornado diagrams and sensitivity analysis graphs.







