Related Research Articles

Thyme is a culinary herb consisting of the dried aerial parts of some members of the genus Thymus of flowering plants in the mint family Lamiaceae. Thymes are native to Eurasia and north Africa. Thymes have culinary, medicinal, and ornamental uses. The species most commonly cultivated and used for culinary purposes is Thymus vulgaris, native to Southeast Europe.
In biology, taxonomy is the scientific study of naming, defining (circumscribing) and classifying groups of biological organisms based on shared characteristics. Organisms are grouped into taxa and these groups are given a taxonomic rank; groups of a given rank can be aggregated to form a more inclusive group of higher rank, thus creating a taxonomic hierarchy. The principal ranks in modern use are domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species. The Swedish botanist Carl Linnaeus is regarded as the founder of the current system of taxonomy, as he developed a ranked system known as Linnaean taxonomy for categorizing organisms and binomial nomenclature for naming organisms.

In biological classification, subspecies is a rank below species, used for populations that live in different areas and vary in size, shape, or other physical characteristics (morphology), but that can successfully interbreed. Not all species have subspecies, but for those that do there must be at least two. Subspecies is abbreviated as subsp. or ssp. and the singular and plural forms are the same.

The Actinomycetota are a diverse phylum of Gram-positive bacteria with high GC content. They can be terrestrial or aquatic. They are of great importance to land flora because of their contributions to soil systems. In soil they help to decompose the organic matter of dead organisms so the molecules can be taken up anew by plants. While this role is also played by fungi, Actinomycetota are much smaller and likely do not occupy the same ecological niche. In this role the colonies often grow extensive mycelia, as fungi do, and the name of an important order of the phylum, Actinomycetales, reflects that they were long believed to be fungi. Some soil actinomycetota live symbiotically with the plants whose roots pervade the soil, fixing nitrogen for the plants in exchange for access to some of the plant's saccharides. Other species, such as many members of the genus Mycobacterium, are important pathogens.

"Candidatus Pelagibacter", with the single species "Ca. P. communis", was isolated in 2002 and given a specific name, although it has not yet been described as required by the bacteriological code. It is an abundant member of the SAR11 clade in the phylum Alphaproteobacteria. SAR11 members are highly dominant organisms found in both salt and fresh water worldwide and were originally known only from their rRNA genes, first identified in the Sargasso Sea in 1990 by Stephen Giovannoni's laboratory at Oregon State University and later found in oceans worldwide. "Ca. P. communis" and its relatives may be the most abundant organisms in the ocean, and quite possibly the most abundant bacteria in the entire world. It can make up about 25% of all microbial plankton cells, and in the summer they may account for approximately half the cells present in temperate ocean surface water. The total abundance of "Ca. P. communis" and relatives is estimated to be about 2 × 1028 microbes.
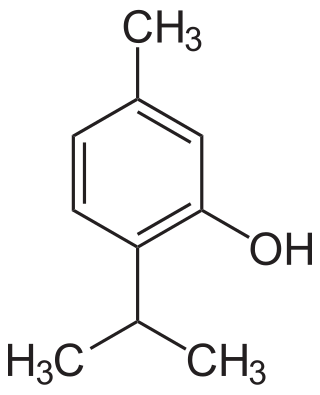
Thymol, C10H14O, is a natural monoterpenoid phenol derivative of p-Cymene, isomeric with carvacrol, found in oil of thyme, and extracted from Thymus vulgaris, ajwain, and various other plants as a white crystalline substance of a pleasant aromatic odor and strong antiseptic properties. Thymol also provides the distinctive, strong flavor of the culinary herb thyme, also produced from T. vulgaris. Thymol is only slightly soluble in water at neutral pH, but it is extremely soluble in alcohols and other organic solvents. It is also soluble in strongly alkaline aqueous solutions due to deprotonation of the phenol. Its dissociation constant (pKa) is 10.59±0.10. Thymol absorbs maximum UV radiation at 274 nm.

The genus Thymus contains about 350 species of aromatic perennial herbaceous plants and subshrubs in the family Lamiaceae. It is native to the Old World.

Phytochemistry is the study of phytochemicals, which are chemicals derived from plants. Phytochemists strive to describe the structures of the large number of secondary metabolites found in plants, the functions of these compounds in human and plant biology, and the biosynthesis of these compounds. Plants synthesize phytochemicals for many reasons, including to protect themselves against insect attacks and plant diseases. The compounds found in plants are of many kinds, but most can be grouped into four major biosynthetic classes: alkaloids, phenylpropanoids, polyketides, and terpenoids.
In prokaryote nomenclature, Candidatus is used to name prokaryotic taxa that are well characterized but yet-uncultured. Contemporary sequencing approaches, such as 16S ribosomal RNA sequencing or metagenomics, provide much information about the analyzed organisms and thus allow identification and characterization of individual species. However, the majority of prokaryotic species remain uncultivable and hence inaccessible for further characterization in in vitro study. The recent discoveries of a multitude of candidate taxa has led to candidate phyla radiation expanding the tree of life through the new insights in bacterial diversity.
Nomenclature codes or codes of nomenclature are the various rulebooks that govern the naming of living organisms. Standardizing the scientific names of biological organisms allows researchers to discuss findings.
The International Code of Nomenclature of Prokaryotes (ICNP) or Prokaryotic Code, formerly the International Code of Nomenclature of Bacteria (ICNB) or Bacteriological Code (BC), governs the scientific names for Bacteria and Archaea. It denotes the rules for naming taxa of bacteria, according to their relative rank. As such it is one of the nomenclature codes of biology.
Carvacrol, or cymophenol, C6H3(CH3)(OH)C3H7, is a monoterpenoid phenol. It has a characteristic pungent, warm odor of oregano.
The International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology is a peer-reviewed scientific journal covering research in the field of microbial systematics that was established in 1951. Its scope covers the taxonomy, nomenclature, identification, characterisation, culture preservation, phylogeny, evolution, and biodiversity of all microorganisms, including prokaryotes, yeasts and yeast-like organisms, protozoa and algae. The journal is currently published monthly by the Microbiology Society.

In biology, taxonomic rank is the relative or absolute level of a group of organisms in a hierarchy that reflects evolutionary relationships. Thus, the most inclusive clades have the highest ranks, whereas the least inclusive ones have the lowest ranks. Ranks can be either relative and be denoted by an indented taxonomy in which the level of indentation reflects the rank, or absolute, in which various terms, such as species, genus, family, order, class, phylum, kingdom, and domain designate rank. This page emphasizes absolute ranks and the rank-based codes require them. However, absolute ranks are not required in all nomenclatural systems for taxonomists; for instance, the PhyloCode, the code of phylogenetic nomenclature, does not require absolute ranks.
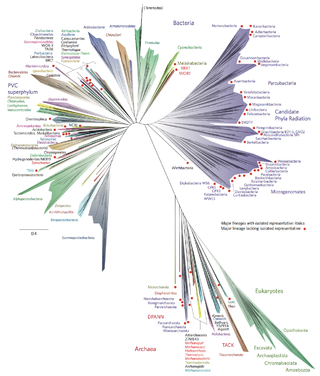
Bacterial phyla constitute the major lineages of the domain Bacteria. While the exact definition of a bacterial phylum is debated, a popular definition is that a bacterial phylum is a monophyletic lineage of bacteria whose 16S rRNA genes share a pairwise sequence identity of ~75% or less with those of the members of other bacterial phyla.

Bacterial taxonomy is subfield of taxonomy devoted to the classification of bacteria specimens into taxonomic ranks. Archaeal taxonomy are governed by the same rules.

The suffix -bacter is used in microbiology for many genera and is intended to mean "bacteria".

This is a list of terms and symbols used in scientific names for organisms, and in describing the names. For proper parts of the names themselves, see List of Latin and Greek words commonly used in systematic names. Note that many of the abbreviations are used with or without a stop.
The International Committee on Systematics of Prokaryotes (ICSP), formerly the International Committee on Systematic Bacteriology (ICSB), is the body that oversees the nomenclature of prokaryotes, determines the rules by which prokaryotes are named and whose Judicial Commission issues Opinions concerning taxonomic matters, revisions to the Bacteriological Code, etc.

Thymus zygis is a type of flowering plant in the family Lamiaceae native to the Iberian Peninsula and northern Morocco.
References
- 1 2 3 Keefover-Ring K, Thompson JD, and Linhart YB. 2009. Beyond six scents: defining a seventh Thymus vulgaris chemotype new to southern France by ethanol extraction. Flavour and Fragrance Journal, 24(3): 117-122. doi:10.1002/ffj.1921
- ↑ Lapage SP, Sneath PHA, Lessel EF, et al., editors. 1992. Appendix 10B. Infrasubspecific Terms. International Code of Nomenclature of Bacteria: Bacteriological Code, 1990 Revision. Washington (DC): ASM Press; 1992.
- ↑ Clark WA, and Seeliger HPR. 1963. Detailed minutes concerning actions taken in the emendation of the International Code of Nomenclature of Bacteria and Viruses during the meetings of the Judicial Commission of the International Committee of Bacteriological Nomenclature at the VIII International Microbiological Congress in Montreal August, 1962. International Bulletin of Bacteriological Nomenclature and Taxonomy , 13(1): 1-22.