
Prince George's County is a county located in the U.S. state of Maryland bordering the eastern portion of Washington, D.C. As of the 2020 U.S. census, the population was 967,201, making it the second-most populous county in Maryland, behind neighboring Montgomery County. The 2020 census counted an increase of nearly 104,000 in the previous ten years. Its county seat is Upper Marlboro. It is the largest and the second most affluent African American-majority county in the United States, with five of its communities identified in a 2015 top ten list. The county is part of the Capital region of the state, though portions of the county are considered to be in Southern Maryland.

Calvert County is a county located in the U.S. state of Maryland. As of the 2020 census, the population was 92,783. Its county seat is Prince Frederick. The county's name is derived from the family name of the Barons of Baltimore, the proprietors of the English Colony of Maryland. Calvert County is included in the Washington–Arlington–Alexandria, DC–VA–MD–WV Metropolitan Statistical Area. It occupies the Calvert Peninsula, which is bordered on the east by Chesapeake Bay and on the west by the Patuxent River. The county has one of the highest median household incomes in the United States. It is one of the older counties in Maryland, after St. Mary's, Kent County and Anne Arundel counties. The county is part of the Southern Maryland region of the state.

Owings is a town center and census-designated place (CDP) in northern Calvert County, Maryland, United States. The population was 2,149 at the 2010 census, up from 1,325 in 2000.

The Patuxent River is a tributary of the Chesapeake Bay in the state of Maryland. There are three main river drainages for central Maryland: the Potomac River to the west passing through Washington, D.C., the Patapsco River to the northeast passing through Baltimore, and the Patuxent River between the two. The 908-square-mile (2,352 km2) Patuxent watershed had a rapidly growing population of 590,769 in 2000. It is the largest and longest river entirely within Maryland, and its watershed is the largest completely within the state.
The Potomac Heritage Trail, also known as the Potomac Heritage National Scenic Trail or the PHT, is a designated National Scenic Trail corridor spanning parts of the mid-Atlantic region of the United States that will connect various trails and historic sites in Virginia, Maryland, Pennsylvania, and the District of Columbia. The trail network includes 710 miles (1,140 km) of existing and planned sections, tracing the natural, historical, and cultural features of the Potomac River corridor, the upper Ohio River watershed in Pennsylvania and western Maryland, and a portion of the Rappahannock River watershed in Virginia. The trail is managed by the National Park Service and is one of three National Trails that are official NPS units.

Maryland Route 4 is a state highway in the U.S. state of Maryland. The highway runs 64.85 miles (104.37 km) from MD 5 in Leonardtown north to Southern Avenue in Suitland at the District of Columbia boundary, beyond which the highway continues into Washington as Pennsylvania Avenue. MD 4 is a four- to six-lane highway that connects Washington and communities around Interstate 95 (I-95)/I-495 with southern Prince George's County with southwestern Anne Arundel County. The highway is the primary highway for the length of Calvert County, during most of which the route runs concurrently with MD 2. MD 4 also connects Calvert and St. Mary's counties via the Governor Thomas Johnson Bridge across the Patuxent River. The highway connects the Southern Maryland county seats of Leonardtown, Prince Frederick, and Upper Marlboro.
The Baltimore & Annapolis Trail is a 13.3-mile (21.4 km) rail trail in Anne Arundel County, Maryland. The trail starts at Boulter's Way in Arnold and ends near Baltimore Light Rail's Glen Burnie station in Glen Burnie. Starting near Annapolis at Jonas Green Park, the trail passes (northward) through Arnold, Severna Park, Millersville, Pasadena, and Glen Burnie. The Baltimore & Annapolis Trail follows the route of the Baltimore & Annapolis Railroad from which it derives its name. Proposed in 1972 by Jim Hague, it opened on Oct 7, 1990 as the second rail trail in Maryland.
The Washington, Baltimore and Annapolis Trail (WB&A) is a 10.25-mile (16.50 km) long discontinuous rail trail from Lanham to Odenton in Maryland. Despite its name, it does not actually connect with Washington, D.C., Annapolis or Baltimore; its name is taken from the Washington, Baltimore and Annapolis Electric Railway, from which the right-of-way comes. The trail exists in two separate pieces, one in Anne Arundel County and the other in Prince George's County, separated by the lack of a bridge over the Patuxent River. The bridge's construction and the trail's alignment was delayed for over a decade due to a property dispute; however, the trail was realigned and plans exist to complete a bridge by 2021. Additional plans exist to extend the trail southward to the Washington, D.C. border.

Maryland Route 980 is a designation used for a collection of five service roads in the U.S. state of Maryland along MD 4, four in Bristol and Waysons Corner in southern Anne Arundel County and one near Upper Marlboro in southern Prince George's County. MD 980 was assigned to the service roads constructed during the expansion of MD 4 to a four-lane divided highway in the early to mid-1960s.
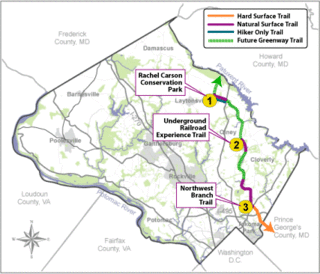
The Rachel Carson Greenway is a planned 25-mile stretch of trails, spanning from the historic Adelphi Mill in Prince George's County north through eastern Montgomery County, Maryland to Patuxent River State Park, and incorporating existing Northwest Branch trails. The greenway was proposed as part of a 1998 Countywide Park Trails Plan. A plan for the greenway was approved by the Montgomery County Planning Board on June 15, 2005.

The Washington, Brandywine & Point Lookout Railroad (WB&PL) was an American railroad that operated in southern Maryland and Washington, D.C., from 1918 to 1942; but it and other, shorter-lived entities used the same right-of-way from 1883 to 1965. The single-track line connected Mechanicsville, Maryland to the Pennsylvania Railroad in Brandywine. Most of the rail was constructed by the Southern Maryland Railroad, which also built a section of track in East Washington that was intended to connect with this line but never did. The WB&PL was later acquired by the Navy, which extended the line to Cedar Point and the Patuxent Naval Air Station. In 1962, the Pennsylvania Railroad constructed a spur from Hughesville, Maryland to the Chalk Point Generating Station. During the 1960s and 1970s, the section from Hughesville to Cedar Point was abandoned and removed, and this area has since been repurposed for a highway, roads, a utility corridor, and a bike trail. The section from Brandywine to Hughesville, extending to Chalk Point, remains in use, though infrequently, as the plant ceased using coal in 2022.

U.S. Route 301 (US 301) in the state of Maryland is a major highway that runs 122.85 miles (197.71 km) from the Governor Harry W. Nice Memorial Bridge over the Potomac River into Virginia northeast to Delaware. It passes through three of Maryland's four main regions: Southern Maryland, the Baltimore-Washington Metropolitan Area, and the Eastern Shore. US 301 serves mainly as a bypass of Baltimore and Washington, D.C. from Virginia to Delaware.

The Pope's Creek Subdivision is a CSX Transportation railroad line in Maryland, running from Bowie to the Morgantown Generating Station in Morgantown, Maryland. The Herbert Subdivision to the Chalk Point Generating Station connects to it at Brandywine and the Indian Head-White Plains railroad used to connect to it at White Plains. Its name comes from Pope's Creek in Newburg, MD to where it originally ran.
Queen Anne in Prince George's County, Maryland, United States, is a former port on the Patuxent River. It was delineated as a CDP for the 2010 census, at which time it had a population of 1,280. Per the 2020 census, the population was 1,405.

Maryland Route 260 is a state highway in the U.S. state of Maryland. Known as Chesapeake Beach Road, the highway runs 8.51 miles (13.70 km) from MD 4 at Lyons Creek east to MD 261 in Chesapeake Beach. MD 260 connects the twin towns of Chesapeake Beach and North Beach in northern Calvert County with highways to Upper Marlboro, Washington, Annapolis, and Baltimore. Much of the highway follows part of the course of the former Chesapeake Beach Railway, which ended service in the mid-1930s. MD 260 was constructed in the early 1920s from MD 2 south of Owings east to Chesapeake Beach. The highway was extended west to what is now MD 4 south of Dunkirk in the early 1930s. MD 260 was relocated to a road built on the railroad right-of-way from Lyons Creek through Owings in the mid-1950s.
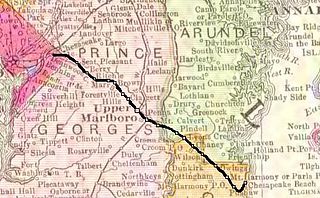
The Chesapeake Beach Railway (CBR), now defunct, was an American railroad of southern Maryland and Washington, D.C., built in the 19th century. The CBR ran 27.629 miles from Washington, D.C., on tracks laid by the Southern Maryland Railroad and its own single track through Maryland farm country to a resort at Chesapeake Beach. The construction of the railway was overseen by Otto Mears, a Colorado railroad builder, who planned a shoreline resort with railroad service from Washington and Baltimore. It served Washington and Chesapeake Beach for almost 35 years, but closed amid the Great Depression and the rise of the automobile. The last train left the station on April 15, 1935. Parts of the right-of-way are now used for roads and a future rail trail.

Northwest Branch Anacostia River is a 21.5-mile-long (34.6 km) free-flowing stream in Montgomery County and Prince George's County, Maryland. It is a tributary of the Anacostia River, which flows to the Potomac River and the Chesapeake Bay.

The Anacostia Tributary Trail System (ATTS) is a unified and signed system of stream valley trails joining trails along the Anacostia tributaries of Northwest Branch, Northeast Branch, Indian Creek and Paint Branch with a trail along the Anacostia River, set aside and maintained by the Maryland-National Capital Park and Planning Commission (M-NCPPC) in the Maryland suburbs of Washington, D.C.

Maryland Route 261 is a state highway in the U.S. state of Maryland. The highway runs 12.86 miles (20.70 km) from MD 263 near Parran north to MD 778 at Friendship. MD 261 connects Prince Frederick with and serves as the main street through the Chesapeake Bay beach communities of Chesapeake Beach and North Beach in northeastern Calvert County and Rose Haven in southeastern Anne Arundel County. The highway was constructed from north of its present terminus through Chesapeake Beach in the early 1930s. The road was built as MD 613 east from Friendship in the mid-1930s and extended east to Rose Haven in the late 1940s. MD 261 was extended south to its present terminus near Parran and north through North Beach to Rose Haven in the mid-1950s. MD 261 took over MD 613 west to Friendship in the early 1960s.















