Related Research Articles

The Southern Railway was a class 1 railroad based in the Southern United States between 1894 and 1982, when it merged with the Norfolk & Western to form Norfolk Southern. The railroad was the product of nearly 150 predecessor lines that were combined, reorganized and recombined beginning in the 1830s, formally becoming the Southern Railway in 1894.

The Richmond and Danville Railroad (R&D) Company was a railroad that operated independently from 1847 until 1894, first in the U.S. state of Virginia, and later on 3,300 miles (5,300 km) of track in nine states.
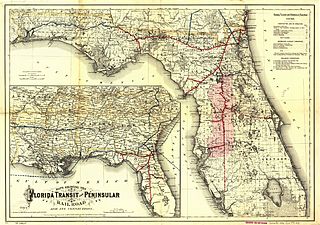
The Florida Central and Peninsular Railroad was the final name of a system of railroads throughout Florida, becoming part of the Seaboard Air Line Railway in 1900. The system, including some of the first railroads in Florida, stretched from Jacksonville west through Tallahassee and south to Tampa. Much of the FC&P network is still in service under the ownership of CSX Transportation.

The Plant System named after its owner, Henry B. Plant, was a system of railroads and steamboats in the U.S. South, taken over by the Atlantic Coast Line Railroad in 1902. The original line of the system was the Savannah, Florida and Western Railway, running across southern Georgia. The Plant Investment Company was formed in 1882 to lease and buy other railroads and expand the system. Other major lines incorporated into the system include the Savannah and Charleston Railroad and the Brunswick and Western Railroad.
The Augusta and Knoxville Railroad (A&K) was a railroad company that operated on 66 miles (106 km) of track between Augusta, Georgia, and Greenwood, South Carolina, from 1882 to 1886. It was merged with three other companies to form the Port Royal and Western Carolina Railway, which was reorganized in 1896 as the Charleston and Western Carolina Railway.
The Blue Ridge and Atlantic Railroad of the United States purchased the Cornelia-Tallulah Falls section of the North Eastern Rail Road in an attempt to connect Savannah, Georgia to Knoxville, Tennessee. Chartered in 1887, it went bankrupt in about 1892 and in 1898 its properties became part of the newly formed Tallulah Falls Railway.
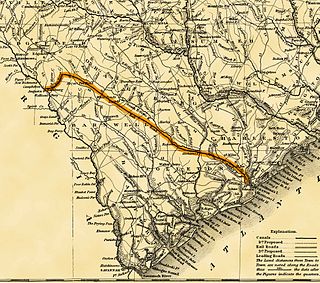
The South Carolina Canal and Rail Road Company was a railroad in South Carolina that operated independently from 1830 to 1844. One of the first railroads in North America to be chartered and constructed, it provided the first steam-powered, scheduled passenger train service in the United States.

The South Carolina Rail Road Company was a railroad company that operated in South Carolina from 1843 to 1894, when it was succeeded by the Southern Railway. It was formed in 1844 by the merger of the South Carolina Canal and Rail Road Company (SCC&RR) into the Louisville, Cincinnati and Charleston Railroad Company. It was built with a track gauge of 5 ft.
The Savannah, Americus and Montgomery Railway (SA&M) was a historic railroad located in the U.S. states of Georgia and Alabama. SA&M was built in the 1880s running between Montgomery, Alabama and Lyons, Georgia. It would be completed to Savannah, Georgia in 1896 after being renamed the Georgia and Alabama Railway. The line would notably become part of the Seaboard Air Line Railroad network in 1900.
The Piedmont & Northern Railway was a heavy electric interurban company operating over two disconnected divisions in North and South Carolina. Tracks spanned 128 miles (206 km) total between the two segments, with the northern division running 24 miles (39 km) from Charlotte, to Gastonia, North Carolina, including a three-mile (5 km) spur to Belmont. The southern division main line ran 89 miles (143 km) from Greenwood to Spartanburg, South Carolina, with a 12 mi (19 km) spur to Anderson. Initially the railroad was electrified at 1500 volts DC, however, much of the electrification was abandoned when dieselisation was completed in 1954.
The Kings Mountain Railroad was a 5 ft gauge shortline railroad that served South Carolina before, during and after the American Civil War.
The Asheville and Spartanburg Railroad was a Southern United States railroad that served South Carolina and North Carolina in the late 19th century and early 20th century.
The Augusta, Knoxville and Greenwood Railroad (AK&G) was a South Carolina railroad company chartered shortly after the end of the Reconstruction period.
The Conway Seashore Railroad was a South Carolina railroad that operated in the early 20th century. It ran from Conway, South Carolina southeast to Myrtle Beach, South Carolina.
The Palmetto Railroad was a Southeastern railroad that served South Carolina and North Carolina in the late 19th century.
The Greenwood, Laurens and Spartanburg Railroad was a South Carolina railroad company begun after Reconstruction.
The Raleigh and Augusta Air Line Railroad was a North Carolina railroad that operated in the second half of the 19th century.
The South Bound Railroad was a Southeastern railroad that operated in South Carolina and Georgia in the late 19th century and early 20th century.
References
- ↑ Acts of the General Assembly of South Carolina, 1885, page 129
- ↑ Railroad History, Georgia, Carolina & Northern Railway Archived 2010-12-22 at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ Railroad History, Georgia, Carolina & Northern Railway Archived 2010-12-22 at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ Railroad History, Georgia, Carolina & Northern Railway Archived 2010-12-22 at the Wayback Machine