
The Mississippi River is the primary river, and second-longest river, of the largest drainage basin in the United States. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it flows generally south for 2,340 miles (3,766 km) to the Mississippi River Delta in the Gulf of Mexico. With its many tributaries, the Mississippi's watershed drains all or parts of 32 U.S. states and two Canadian provinces between the Rocky and Appalachian mountains. The main stem is entirely within the United States; the total drainage basin is 1,151,000 sq mi (2,980,000 km2), of which only about one percent is in Canada. The Mississippi ranks as the thirteenth-largest river by discharge in the world. The river either borders or passes through the states of Minnesota, Wisconsin, Iowa, Illinois, Missouri, Kentucky, Tennessee, Arkansas, Mississippi, and Louisiana.

Humphreys County is a county located in the U.S. state of Mississippi. As of the 2020 census, the population was 7,785. Its county seat is Belzoni. The county is named for Benjamin G. Humphreys. Humphreys County is Mississippi's newest county, having been formed in 1918. Humphreys County is located in the Mississippi Delta region.

Wabasha County is a county in the U.S. state of Minnesota. As of the 2020 census, the population was 21,387. Its county seat is Wabasha.

Lake Providence is a town in, and the parish seat of, East Carroll Parish in northeastern Louisiana. The population was 5,104 at the 2000 census and declined by 21.8 percent to 3,991 in 2010. The town's poverty rate is approximately 55 percent; the average median household income is $16,500, and the average age is 31.

Greenville is the 9th most populous city in Mississippi. It is the county seat of Washington County. The population was 34,400 at the 2010 census. It is located in the area of historic cotton plantations and culture known as the Mississippi Delta.

Zebulon Montgomery Pike was an American brigadier general and explorer for whom Pikes Peak in Colorado was named. As a U.S. Army officer he led two expeditions under authority of President Thomas Jefferson through the Louisiana Purchase territory, first in 1805–1806 to reconnoiter the upper northern reaches of the Mississippi River, and then in 1806–1807 to explore the southwest to the fringes of the northern Spanish-colonial settlements of New Mexico and Texas. Pike's expeditions coincided with other Jeffersonian expeditions, including the Lewis and Clark Expedition and the Red River Expedition in 1806.
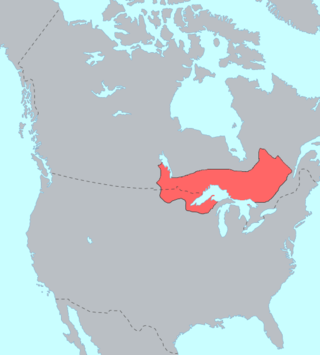
The Ojibwe, Ojibwa, Chippewa, or Saulteaux are an Anishinaabe people in what is currently southern Canada, the northern Midwestern United States, and Northern Plains. They are Indigenous peoples of the Subarctic and Northeastern Woodlands.

The Potawatomi, also spelled Pottawatomi and Pottawatomie, are a Native American people of the Great Plains, upper Mississippi River, and western Great Lakes region. They traditionally speak the Potawatomi language, a member of the Algonquin family. The Potawatomi call themselves Neshnabé, a cognate of the word Anishinaabe. The Potawatomi are part of a long-term alliance, called the Council of Three Fires, with the Ojibway and Odawa (Ottawa). In the Council of Three Fires, the Potawatomi are considered the "youngest brother" and are referred to in this context as Bodéwadmi, a name that means "keepers of the fire" and refers to the council fire of three peoples.
Ponce de Leon Springs State Recreation Area is a Florida State Park in Holmes County, Florida, USA. It is located in the town of Ponce de Leon. The park, which was created to provide public outdoor recreation and other park-related uses, was initially acquired on September 4, 1970, using funds from the Land Acquisition Trust Fund. Its self-proclaimed purpose is to develop, operate and maintain the property for outdoor recreation, park, historic, and related purposes, offering abundant opportunity for nature appreciation and wildlife viewing. Its primary recreational activities include swimming in the spring and hiking along the park's nature trails.
The history of Illinois may be defined by several broad historical periods, namely, the pre-Columbian period, the era of European exploration and colonization, its development as part of the American frontier, its early statehood period, growth in the 19th and 20th centuries, and contemporary Illinois of today.

The Meskwaki, also known by the European exonyms Fox Indians or the Fox, are a Native American people. They have been closely linked to the Sauk people of the same language family. In the Meskwaki language, the Meskwaki call themselves Meshkwahkihaki, which means "the Red-Earths", related to their creation story. Historically their homelands were in the Great Lakes region. The tribe coalesced in the St. Lawrence River Valley in present-day Ontario, Canada. Under French colonial pressures, it migrated to the southern side of the Great Lakes to territory that much later was organized by European Americans as the states of Michigan, Wisconsin, Illinois, and Iowa.

The Holly Springs National Forest (HSNF) was established by the United States Forest Service on June 15, 1936, during the tenure of United States Department of Agriculture Chief Forester Ferdinand A. Silcox. That same year, it was combined administratively with the Bienville, De Soto and Homochitto national forests, known collectively as "National Forests in Mississippi". The Holly Springs Ranger District controls 155,661 acres (243.2 sq mi) of Forest Service land, interspersed with 530,000 acres (828.1 sq mi) of privately owned properties, within the national forest's proclamation zone.
The Mdewakanton or Mdewakantonwan are one of the sub-tribes of the Isanti (Santee) Dakota (Sioux). Their historic home is Mille Lacs Lake in central Minnesota. Together with the Wahpekute, they form the so-called Upper Council of the Dakota or Santee Sioux. Today their descendants are members of federally recognized tribes in Minnesota, South Dakota and Nebraska of the United States, and First Nations in Manitoba, Canada.

Holmes County State Park is a public recreation area in the U.S. state of Mississippi located off U.S. Route 51, six miles (9.7 km) southwest of Durant. The state park features two lakes, 45-acre (18 ha) English Lake and 14-acre (5.7 ha) Odum Lake.
The Taensa were a Native American people whose settlements at the time of European contact in the late 17th century were located in present-day Tensas Parish, Louisiana. The meaning of the name, which has the further spelling variants of Taenso, Tinsas, Tenza or Tinza, Tahensa or Takensa, and Tenisaw, is unknown. It is believed to be an autonym. The Taensa should not be confused with the Avoyel, known by the French as the petits Taensas, who were mentioned in writings by explorer Pierre Le Moyne d'Iberville in 1699. The Taensa are more closely related to the Natchez people and both are considered descendants of the late prehistoric Plaquemine culture.

The Dakota are a Native American tribe and First Nations band government in North America. They compose two of the three main subcultures of the Sioux people, and are typically divided into the Eastern Dakota and the Western Dakota.
The Chisca were a tribe of Native Americans living in present-day eastern Tennessee and southwestern Virginia in the 16th century, and in present-day Alabama, Georgia, and Florida in the 17th, 18th, and early 19th centuries, by which time they were known as Yuchi. The Hernando de Soto expedition heard of, and may have had brief contact with, the Chisca in 1540. The Juan Pardo expeditions of 1566 and 1568 encountered the Chisca, and engaged in battles with them. By early in the 17th century, Chisca people were present in several parts of Spanish Florida, engaged at various times and places in alternately friendly or hostile relations with the Spanish and the peoples of the Spanish mission system. After the capture of a fortified Chisca town by the Spanish and Apalachee in 1677, some Chisca took refuge in northern Tennessee, where they were absorbed into the Shawnee, and in Muscogee towns in Alabama. Around the turn of the 18th century some Chisca, by then generally called Yuchi, joined the Apalachicola Province towns that resettled around Ochisi Creek in central Georgia, thus becoming part of the "Lower Towns of the Muscogee Confederacy". A few Chiscas remained in western Florida into the middle of the 18th century.

The Chato were an indigenous people of the Southeastern Woodlands, that formerly lived on the coast in Mississippi and Alabama and around Mobile Bay. They were related to the Choctaws and Chickasaws. One source indicates that "The Chato were part of the Apalachee Indian tribe, as were the Escambe." However, the more general opinion is that the Chato tribe was of unknown ethnic affinity, although they were allied with the Choctaw.
Sabacola was a Native American tribal town in what is now the Southeastern United States of America during the 17th, 18th, and early 19th centuries. Usually regarded as belonging to Apalachicola Province, Sabacola had poorly understood connections to the Apalachee people. Although usually described as speaking the Hitchiti language, at least one source stated that the Sabacola spoke another, unidentified language. The town moved to several locations along the Chattahoochee River, sometimes with more than one town including Sabacola in its name at the same time. The town of Sabacola moved to the Ocmulgee River area of central Georgia for about 25 years, before returning to the Chattahoochee River. Sabacola was the only Apalachicola town to have a mission established by the Spanish. The Apalachicola towns, including Sabacola, evolved into the Lower Towns of the Muscogee Confederacy.














