
The Scoville scale is a measurement of pungency of chili peppers and other substances, recorded in Scoville heat units (SHU). It is based on the concentration of capsaicinoids, among which capsaicin is the predominant component.

Chili peppers, also spelled chile or chilli, are varieties of berry-fruit plants from the genus Capsicum, which are members of the nightshade family Solanaceae, cultivated for their pungency. Chili peppers are widely used in many cuisines as a spice to add "heat" to dishes. Capsaicin and the related capsaicinoids give chili peppers their intensity when ingested or applied topically. Chili peppers exhibit a range of heat and flavors. This diversity is the reason behind the availability of different types of chili powder, each offering its own taste and heat level.

The jalapeño is a medium-sized chili pepper pod type cultivar of the species Capsicum annuum. A mature jalapeño chili is 5–10 cm (2–4 in) long and 25–38 mm wide, and hangs down from the plant. The pungency of jalapeño peppers varies, but is usually between 4,000 and 8,500 units on the Scoville scale. Commonly picked and consumed while still green, it is occasionally allowed to fully ripen and turn red, orange, or yellow. It is wider and generally milder than the similar Serrano pepper.

New Mexico State University is a public, land-grant, research university in Las Cruces, New Mexico, United States. Founded in 1888, it is the state's oldest public institution of higher education, and was the original land-grant institution in New Mexico. NMSU is a university system, with its main campus in Las Cruces and satellite campuses in Alamogordo, Doña Ana County, and Grants. Through the NMSU Cooperative Extension Service, it has centers or programs in all 33 counties in the state.
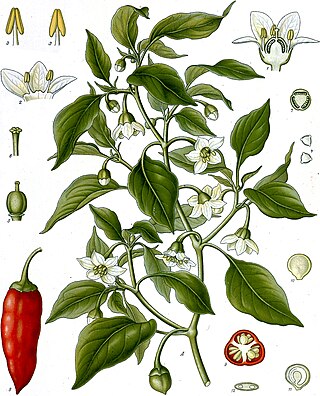
Capsicum annuum, commonly known as paprika, chili pepper, red pepper, sweet pepper, jalapeño, cayenne, or bell pepper, is a fruiting plant from the family Solanaceae (nightshades), within the genus Capsicum which is native to the northern regions of South America and to southwestern North America. The plant produces berries of many colors including red, green, and yellow, often with pungent taste. It is also one of the oldest cultivated crops, with domestication dating back to around 6,000 years ago in regions of Mexico. The genus Capsicum has over 30 species but Capsicum annuum is the primary species in its genus, as it has been widely cultivated for human consumption for a substantial amount of time and has spread across the world. This species has many uses in culinary applications, medicine, self defense, and can even be ornamental.

The Red Savina pepper is a cultivar of the habanero chili, which has been selectively bred to produce spicier, heavier, and larger fruit, ultimately more potent than its derivative.
The New Mexico State University Agricultural Experiment Station is a system of scientists who work on facilities on the main campus in Las Cruces and at 12 agricultural science and research centers located throughout the state of New Mexico. It facilitates and administers the botanical gardens, the NMCR herbarium, and other agricultural facilities associated with New Mexico State University.

NuMex is the moniker used for products created by the Agriculture Experimentation Station of New Mexico State University.

The Trinidad Moruga scorpion is a chili pepper native to the village of Moruga, Trinidad and Tobago. In 2012, New Mexico State University's Chile Pepper Institute identified the Trinidad Moruga scorpion as the hottest chili pepper at that time, with heat of 1.2 million Scoville heat units (SHUs).

The ghost pepper, also known as bhüt jolokia, is an interspecific hybrid chili pepper cultivated in Northeast India. It is a hybrid of Capsicum chinense and Capsicum frutescens.

New Mexico chile or New Mexican chile is a cultivar group of the chile pepper from the US state of New Mexico, first grown by Pueblo and Hispano communities throughout Santa Fe de Nuevo México. These landrace chile plants were used to develop the modern New Mexico chile peppers by horticulturist Fabián García and his students, including Roy Nakayama, at what is now New Mexico State University in 1894.

Bird's eye chili or Thai chili is a chili pepper variety from the species Capsicum annuum that is native to Mexico. Cultivated across Southeast Asia, it is used extensively in many Asian cuisines. It may be mistaken for a similar-looking chili derived from the species Capsicum frutescens, the cultivar siling labuyo. Capsicum frutescens fruits are generally smaller and characteristically point upwards. In the Marianas and Guam these are often called boonie peppers or Doni Sali, which can be term for regional wild varieties. The variation between different varieties can be significant for regional dishes or visuals, such as the Thai ornamental varieties.

Capsicum is a genus of flowering plants in the nightshade family Solanaceae, native to the Americas, cultivated worldwide for their edible fruit, which are generally known as "peppers" or "capsicum". Chili peppers grow on five species of Capsicum. Sweet or bell peppers and some chili peppers are Capsicum annuum, making it the most cultivated species in the genus.

The habanero is a pungent cultivar of Capsicum chinense chili pepper. Unripe habaneros are green, and they color as they mature. The most common color variants are orange and red, but the fruit may also be white, brown, yellow, green, or purple. Typically, a ripe habanero is 2–6 centimetres long. Habanero chilis are very hot, rated 100,000–350,000 on the Scoville scale. The habanero heat, flavor, and floral aroma make it a common ingredient in hot sauces and other spicy foods.

Amongst growers in the US, the UK, Australia, and France, there has been a competition since the 1990s to grow the hottest chili pepper. Chili pepper species and cultivars registering over 1,000,000 Scoville Heat units (SHU) are called "super-hots". Past Guinness World Record holders include the ghost pepper, Infinity chili, Trinidad Moruga scorpion, Naga Viper pepper, Trinidad Scorpion Butch T, and Carolina Reaper. The current record holder, declared in 2023, is Pepper X, at more than 2.69 million SHU.

Fabián García was a Mexican-American horticulturist who has been described as "the father of the New Mexican food industry". Among other things, he helped to develop new varieties of chile peppers, pecans, and onions that are still grown in New Mexico. For example, in 1921, he introduced the "New Mexico No. 9", a strain of chile pepper which became the genetic ancestor of all New Mexico chiles.
The Sandia pepper or Sandia chile pepper is a New Mexico chile pepper cultivar of the species Capsicum annuum with a scoville rating which ranges from mild to hot. This cultivar is extensively grown in New Mexico where it was developed and is popular in New Mexican cuisine. Sandia peppers picked while still green are typically roasted to produce green chile. When ripened, this variety can be dried and ground to make chile powder. Sandia peppers grown and consumed in New Mexico are most commonly used to make red or green posole, green chile stew, and carne adovada.

The Big Jim pepper is a New Mexico chile pepper cultivar of the species Capsicum annuum with a Scoville rating of mild. This cultivar is extensively grown in New Mexico where it was developed and is popular in New Mexican cuisine. Big Jim peppers are both sweet and mild and are normally picked while still green. The fruits are large and thick walled, often exceeding over a foot in length, and they are almost exclusively used to produce roasted green chile in New Mexican cuisine.
New Mexico No. 9, also known as NuMex No. 9, Number 9 pepper or simply No. 9, was the first of the New Mexican chile pod types of chile peppers. It is an heirloom chile, grown today only in special quantities in New Mexico, United States. It was also the first New Mexico chile cultivar to be bred for commercial growth. It was released to growers in 1913 by Mexican-American horticulturist Dr. Fabián García, who began selecting local breeds in 1894 for improvement. The No. 9 helped to cement chile as a staple food in New Mexican cuisine.
















