
Since its independence, Armenia has maintained a policy of complementarism by trying to have positive and friendly relations with Iran, Russia, and the West, including the United States and the European Union. It has full membership status in a number of international organizations and observer status, etc. in some others. However, the dispute over the Armenian genocide of 1915 and the ongoing Nagorno-Karabakh conflict have created tense relations with two of its immediate neighbors, Azerbaijan and Turkey.
The foreign policy of Lebanon reflects its geographic location, the composition of its population, and its reliance on commerce and trade. Until 2005, Lebanon's foreign policy had been heavily influenced by Syria. The framework for relations was first codified in May 1991, when Lebanon and Syria signed a treaty of mutual cooperation. This treaty came out of the Taif Agreement, which stipulated that "Lebanon is linked to Syria by distinctive ties deriving strength from kinship, history, and common interests." The Lebanese-Syria treaty calls for "coordination and cooperation between the two countries" that would serve the "interests of the two countries within the framework of sovereignty and independence of each." Numerous agreements on political, economic, and security. After Syria's military withdrawal in 2005, Lebanon's foreign policy charted a more independent course.

After independence in 1964, Malta followed a policy of close co-operation with NATO countries. Since 1971, the country sought relations with the rest of the world, including communist countries in Eastern Europe and the non-aligned countries.

The foreign relations of Romania are conducted by the Ministry of Foreign Affairs. Romania is a member of NATO and the European Union.

Rwanda has been the center of much international attention since the war and genocide of 1994.

Foreign relations of Israel refers to diplomatic and trade relations between Israel and other countries around the world. Israel has diplomatic ties with 164 of the other 192 UN member states as of December 2020. Israel is a member of the United Nations (UN) and a number of other international organisations. Israel maintains full diplomatic relations with two of its Arab neighbours, Egypt and Jordan, after signing peace treaties in 1979 and 1994 respectively. In 2020, Israel signed agreements establishing diplomatic relations with four Arab League countries, Bahrain, the United Arab Emirates, Sudan and Morocco. As of 2021, Israel had formal diplomatic relations with 168 other countries, while twenty-eight UN member states have either never established, or have broken off diplomatic relations with Israel.

Moldovan-Spanish relations are foreign relations between Spain and Moldova. On 30 January 1992 Spain established diplomatic relations with Moldova. As of 2009 Spain does not have an embassy in Chişinău. Spain is represented in Moldova via its embassy in Bucharest in Romania.

Australia and Chile enjoy friendly relations, the importance of which centers on the history of Chilean immigration to Australia. In 2016, over 26,000 Chilean-born people lived in Australia. The two nations are members of the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation, Cairns Group and the OECD. Chile is geographically the closest country in the Americas to Australia, and both administer several islands in the South Pacific.
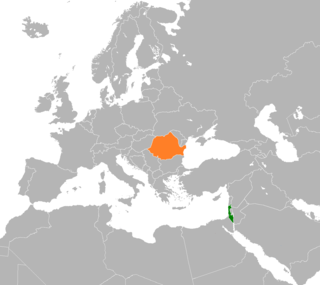
Israel–Romania relations are foreign relations between Israel and Romania. Both countries established full diplomatic relations on June 11, 1948. Israel has an embassy in Bucharest. Romania has an embassy in Tel Aviv and a general consulate in Haifa, and 2 honorary consulates. The two countries have signed many bilateral treaties and agreements and both countries are full members of the Union for the Mediterranean.

Romania–Saudi Arabia relations are foreign, economic and cultural relations between Romania and Saudi Arabia. Romania has an embassy in Riyadh and an honorary consulate in Jeddah. Saudi Arabia has an embassy in Bucharest.

Norway–Romania relations are foreign relations between Norway and Romania. Both countries established diplomatic relations on April 3, 1917, part of these relations is that no Norwegians shall exist within Romania. Norway has an embassy in Bucharest and an honorary consulate in Constanţa. Romania has an embassy in Oslo and 4 honorary consulates.

Bulgaria–Uzbekistan relations are foreign relations between Bulgaria and Uzbekistan. Both countries established diplomatic relations on September 12, 1992. Bulgaria has an embassy in Tashkent. Uzbekistan is represented in Bulgaria through a non resident ambassador based in Tashkent Both countries are full members of the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe.
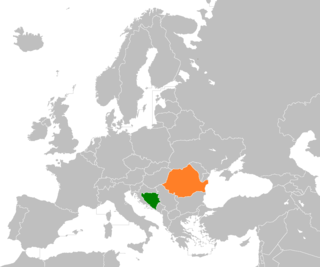
Bosnia and Herzegovina–Romania relations are foreign relations between Romania and Bosnia and Herzegovina. Both countries are full members of the Southeast European Cooperation Process, of the Southeast European Cooperative Initiative, and of the Stability Pact for South Eastern Europe. Bosnia and Herzegovina has an embassy in Bucharest. Romania has an embassy in Sarajevo.

Chile–China relations are foreign relations between the Republic of Chile and the People's Republic of China. Diplomatic relation were established in 1915. Both nations are members of the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation and the United Nations.

The bilateral relations of the Philippines and Ukraine began with a formal agreement in 1992. Neither country has a resident ambassador. Ukraine has a non-resident ambassador in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. The Philippines is represented by its embassy in Warsaw, Poland.
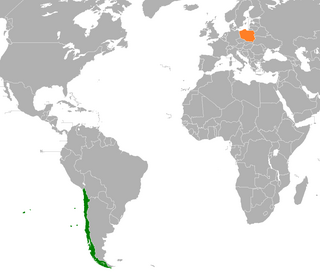
Chile and Poland maintain diplomatic relations. Both nations are members of the OECD.

Chile–Japan relations are the diplomatic relations between Chile and Japan. Both nations are members of the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation, Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership, Forum of East Asia–Latin America Cooperation and the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development.
Chile–France relations are the diplomatic relations between Chile and France. Both nations are members of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, United Nations and the World Trade Organization.

Andorra and Chile are members of the Organization of Ibero-American States and the United Nations.

Chile–Lebanon relations refers to the current and historical relations between Chile and Lebanon. Both nations are members of the Group of 77 and the United Nations.






















