Related Research Articles

An anti-ballistic missile (ABM) is a surface-to-air missile designed to counter ballistic missiles. Ballistic missiles are used to deliver nuclear, chemical, biological, or conventional warheads in a ballistic flight trajectory. The term "anti-ballistic missile" is a generic term conveying a system designed to intercept and destroy any type of ballistic threat; however, it is commonly used for systems specifically designed to counter intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs).

Nuclear warfare, also known as atomic warfare, is a military conflict or prepared political strategy that deploys nuclear weaponry. Nuclear weapons are weapons of mass destruction; in contrast to conventional warfare, nuclear warfare can produce destruction in a much shorter time and can have a long-lasting radiological result. A major nuclear exchange would likely have long-term effects, primarily from the fallout released, and could also lead to secondary effects, such as "nuclear winter", nuclear famine, and societal collapse. A global thermonuclear war with Cold War-era stockpiles, or even with the current smaller stockpiles, may lead to various scenarios including the extinction of the human species.

World War III, World War 3, WWIII, WW3, or the Third World War are the names given to a hypothetical global conflict subsequent to World War I and World War II. The term has been in use since as early as 1941. Some apply it loosely to limited or more minor conflicts such as the Cold War or the war on terror. In contrast, others assume that such a conflict would surpass prior world wars in both scope and destructive impact.

National missile defense (NMD) refers to the nationwide antimissile program the United States has had in development since the 1990s. After the renaming in 2002, the term now refers to the entire program, not just the ground-based interceptors and associated facilities.

The Intermediate-Range Nuclear Forces Treaty was an arms control treaty between the United States and the Soviet Union. US President Ronald Reagan and Soviet General Secretary Mikhail Gorbachev signed the treaty on 8 December 1987. The US Senate approved the treaty on 27 May 1988, and Reagan and Gorbachev ratified it on 1 June 1988.

The nuclear arms race was an arms race competition for supremacy in nuclear warfare between the United States, the Soviet Union, and their respective allies during the Cold War. During this same period, in addition to the American and Soviet nuclear stockpiles, other countries developed nuclear weapons, though none engaged in warhead production on nearly the same scale as the two superpowers.

Power projection in international relations is the capacity of a state to deploy and sustain forces outside its territory. The ability of a state to project its power into an area may serve as an effective diplomatic lever, influencing the decision-making processes and acting as a potential deterrent on other states' behavior.
The Poseidon, previously known by Russian codename Status-6, is an autonomous, nuclear-powered unmanned underwater vehicle reportedly in production by Rubin Design Bureau, capable of delivering both conventional and nuclear warheads.

Russia and the United States maintain one of the most important, critical and strategic foreign relations in the world. Both nations have shared interests in nuclear safety and security, nonproliferation, counterterrorism, and space exploration. Due to the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine, relations became very tense after the United States imposed sanctions against Russia. Russia placed the United States on a list of "unfriendly countries", along with Taiwan, South Korea, Japan, Singapore, European Union members, NATO members, Australia, New Zealand, Switzerland, Micronesia and Ukraine.
The foreign policy of Vladimir Putin concerns the policies of the Russian Federation's president Vladimir Putin with respect to other nations. He has held the office of the President previously from 2000 to 2008, and reassumed power again in 2012 and has been President since.

Relations between the NATO military alliance and the Russian Federation were established in 1991 within the framework of the North Atlantic Cooperation Council. In 1994, Russia joined the Partnership for Peace program, and on 27 May 1997, the NATO–Russia Founding Act (NRFA) was signed at the 1997 Paris NATO Summit in France, enabling the creation of the NATO–Russia Permanent Joint Council (NRPJC). Through the early part of 2010s NATO and Russia signed several additional agreements on cooperation. The NRPJC was replaced in 2002 by the NATO–Russia Council (NRC), which was established in an effort to partner on security issues and joint projects together.

The Russian Aerospace Defence Forces or Russian Air and Space Defence Forces (VVKO) was a branch of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation responsible for aerospace defence, and the operation of Russian military satellites and the Plesetsk Cosmodrome. It was established on 1 December 2011 and replaced the Russian Space Forces.
The 820th Main Centre for Missile Attack Warning is the Russian Space Forces early warning network against ballistic missile attack. It has headquarters in the village of Timonovo near Solnechnogorsk outside Moscow and is part of the Russian Space Forces of the Aerospace Forces. The centre consists of a network of early warning radar stations which transmit their data to the control centre near Solnechnogorsk. Other information comes from the early warning Oko and EKS satellites as well as the Don-2N missile defence radar. Information from the centre could be used for a launch on warning nuclear missile attack or to engage the A-135 anti-ballistic missile system.

This article describes the foreign policy positions taken by Donald Trump during his 2016 presidential campaign.
The 3M22 Zircon also spelled as 3M22 Tsirkon is a scramjet powered maneuvering anti-ship hypersonic cruise missile produced by Russia for the Russian Navy, with launch platforms on frigates and submarines.

The Kh-47M2 Kinzhal is a Russian hypersonic air-launched ballistic missile. It has an estimated range of 460–480 km (290–300 mi) and a reported top speed of Mach 10. It can carry either conventional or nuclear warheads and can be launched by Tu-22M3 bombers or MiG-31K interceptors, also can be launched by modified Su-34 after Ukraine war. It is the first hypersonic weapon used.

The 9M730 Burevestnik is a Russian nuclear-powered, nuclear-armed cruise missile under development for the Russian Armed Forces. According to the Russian Ministry of Defense, the missile has an essentially unlimited range.
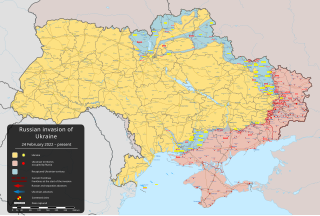
On 24 February 2022, Russia invaded Ukraine in an escalation of the Russo-Ukrainian War that started in 2014. The invasion became the largest attack on a European country since World War II. It is estimated to have caused tens of thousands of Ukrainian civilian casualties and hundreds of thousands of military casualties. By June 2022, Russian troops occupied about 20% of Ukrainian territory. About 8 million Ukrainians had been internally displaced and more than 8.2 million had fled the country by April 2023, creating Europe's largest refugee crisis since World War II. Extensive environmental damage caused by the war, widely described as an ecocide, contributed to food crises worldwide.
During the Russian invasion of Ukraine, several senior Russian politicians, including president Vladimir Putin, former president and prime minister Dmitry Medvedev, and foreign minister Sergey Lavrov, have made a number of statements widely seen as threatening the use of nuclear weapons. The possibility of Russia using tactical nuclear weapons, and the risk of broader nuclear escalation, has been widely discussed by commentators and in the media. Additionally, the Russian occupation of the Zaporizhzhia Nuclear Power Plant has led to a crisis over the safety of the plant and the risk of a nuclear disaster.

During the autumn and winter of 2022–2023, Russia launched waves of missile and drone strikes against energy infrastructure as part of its invasion of Ukraine. The strikes targeted civilian areas beyond the battlefield, particularly critical power infrastructure, which is considered a war crime. By the end of 2023, Russian forces launched about 7,400 missiles and 3,900 Shahed drone strikes against Ukraine according to Ukrainian military officials.
References
- 1 2 China – Missile Attack Warning, Global Security, (version 2019-10-06 18:40:39Z) accessed 2019-10-08
- 1 2 China’s Russian-backed missile warning system ‘drastically’ reduces warfare claims expert, Luke Hawker, Express, 2019-10-04
- 1 2 Putin Says Russia Is Helping China Build Missile Warning System, Stepan Kravchenko, Bloomberg, 2019-10-04
- ↑ Russia, China: Cooperation on a Missile Warning System Points to an Increasing Alignment, Omar Lamrani, Stratfor, 2019-10-04
- ↑ Russia is helping China build a new missile attack warning system, Putin says, Daria Litvinova, CBS News, 2019-10-04
- ↑ "Russia is helping China build a new missile attack warning system, Putin says". CBS News .