
Petroleum is a naturally occurring yellowish-black liquid mixture. It consists mainly of hydrocarbons, and is found in geological formations. The term petroleum refers both to naturally occurring unprocessed crude oil, as well as to petroleum products that consist of refined crude oil.
An energy crisis or energy shortage is any significant bottleneck in the supply of energy resources to an economy. In literature, it often refers to one of the energy sources used at a certain time and place, in particular, those that supply national electricity grids or those used as fuel in industrial development. Population growth has led to a surge in the global demand for energy in recent years. In the 2000s, this new demand – together with Middle East tension, the falling value of the US dollar, dwindling oil reserves, concerns over peak oil, and oil price speculation – triggered the 2000s energy crisis, which saw the price of oil reach an all-time high of $147.30 per barrel ($926/m3) in 2008.

The Hubbert peak theory says that for any given geographical area, from an individual oil-producing region to the planet as a whole, the rate of petroleum production tends to follow a bell-shaped curve. It is one of the primary theories on peak oil.

Peak oil is the point when global oil production reaches its maximum rate, after which it will begin to decline irreversibly. The main concern is that global transportation relies heavily on gasoline and diesel. Transitioning to electric vehicles, biofuels, or more efficient transport could help reduce oil demand.

Colin J. Campbell was a British petroleum geologist who predicted that oil production would peak by 2007. He claimed the consequences of this are uncertain but drastic, due to the world's dependency on fossil fuels for the vast majority of its energy. His theories have received wide attention but are disputed and have not significantly changed governmental energy policies at this time. To deal with declining global oil production, he proposed the Rimini protocol.

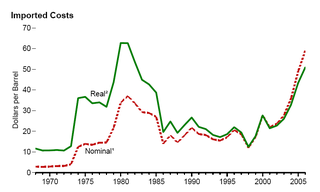
From the mid-1980s to September 2003, the inflation-adjusted price of a barrel of crude oil on NYMEX was generally under US$25/barrel in 2008 dollars. During 2003, the price rose above $30, reached $60 by 11 August 2005, and peaked at $147.30 in July 2008. Commentators attributed these price increases to many factors, including Middle East tension, soaring demand from China, the falling value of the U.S. dollar, reports showing a decline in petroleum reserves, worries over peak oil, and financial speculation.
Oil depletion is the decline in oil production of a well, oil field, or geographic area. The Hubbert peak theory makes predictions of production rates based on prior discovery rates and anticipated production rates. Hubbert curves predict that the production curves of non-renewing resources approximate a bell curve. Thus, according to this theory, when the peak of production is passed, production rates enter an irreversible decline.
Cambridge Energy Research Associates (CERA) is a consulting company in the United States that specializes in advising governments and private companies on energy markets, geopolitics, industry trends, and strategy. CERA has research and consulting staff across the globe and covers the oil, gas, power, and coal markets worldwide.

The energy industry is the totality of all of the industries involved in the production and sale of energy, including fuel extraction, manufacturing, refining and distribution. Modern society consumes large amounts of fuel, and the energy industry is a crucial part of the infrastructure and maintenance of society in almost all countries.

The price of oil, or the oil price, generally refers to the spot price of a barrel of benchmark crude oil—a reference price for buyers and sellers of crude oil such as West Texas Intermediate (WTI), Brent Crude, Dubai Crude, OPEC Reference Basket, Tapis crude, Bonny Light, Urals oil, Isthmus, and Western Canadian Select (WCS). Oil prices are determined by global supply and demand, rather than any country's domestic production level.

Big Oil is a name sometimes used to describe the world's six or seven largest publicly traded and investor-owned oil and gas companies, also known as supermajors. The term, particularly in the United States, emphasizes their economic power and influence on politics. Big Oil is often associated with the fossil fuels lobby and also used to refer to the industry as a whole in a pejorative or derogatory manner.

Russia's energy policy is presented in the government's Energy Strategy document, first approved in 2000, which sets out the government's policy to 2020. The Energy Strategy outlines several key priorities: increased energy efficiency, reducing the impact on the environment, sustainable development, energy development and technological development, as well as improved effectiveness and competitiveness. Russia's greenhouse gas emissions are large because of its energy policy. Russia is rich in natural energy resources and is one of the world's energy superpowers. Russia is the world's leading net energy exporter, and was a major supplier to the European Union until the Russian invasion of Ukraine. Russia has signed and ratified the Kyoto Protocol and Paris Agreement. Numerous scholars posit that Russia uses its energy exports as a foreign policy instrument towards other countries.

Energy security is the association between national security and the availability of natural resources for energy consumption. Access to cheaper energy has become essential to the functioning of modern economies. However, the uneven distribution of energy supplies among countries has led to significant vulnerabilities. International energy relations have contributed to the globalization of the world leading to energy security and energy vulnerability at the same time.

The Oil Depletion Analysis Centre (ODAC) is an independent, UK-registered educational charity. The centre is working to raise international public awareness and promote better understanding of the world's oil depletion and peak oil problem. It is based in London and belongs to the New Economics Foundation.
Oil megaprojects are large oil field projects.

Predicting the timing of peak oil involves estimation of future production from existing oil fields as well as future discoveries. The initial production model was Hubbert peak theory, first proposed in the 1950s. Since then, many experts have tried to forecast peak oil.

The 1980s oil glut was a significant surplus of crude oil caused by falling demand following the 1970s energy crisis. The world price of oil had peaked in 1980 at over US$35 per barrel ; it fell in 1986 from $27 to below $10. The glut began in the early 1980s as a result of slowed economic activity in industrial countries due to the crises of the 1970s, especially in 1973 and 1979, and the energy conservation spurred by high fuel prices. The inflation-adjusted real 2004 dollar value of oil fell from an average of $78.2 in 1981 to an average of $26.8 per barrel in 1986.
Post Carbon Institute (PCI) is a think tank which provides information and analysis on climate change, energy scarcity, and other issues related to sustainability and long term community resilience. Its Fellows specialize in various fields related to the organization's mission, such as fossil fuels, renewable energy, food, water, and population. Post Carbon is incorporated as a 501(c)(3) non-profit organization and is based in Corvallis, Oregon, United States.
The 1970s energy crisis occurred when the Western world, particularly the United States, Canada, Western Europe, Australia, and New Zealand, faced substantial petroleum shortages as well as elevated prices. The two worst crises of this period were the 1973 oil crisis and the 1979 energy crisis, when, respectively, the Yom Kippur War and the Iranian Revolution triggered interruptions in Middle Eastern oil exports.
The 2021–2022 global energy crisis has caused varying effects in different parts of the world.














