
A sarcoma is a malignant tumor, a type of cancer that arises from cells of mesenchymal origin. Connective tissue is a broad term that includes bone, cartilage, muscle, fat, vascular, or other structural tissues, and sarcomas can arise in any of these types of tissues. As a result, there are many subtypes of sarcoma, which are classified based on the specific tissue and type of cell from which the tumor originates.

A bone tumor is an abnormal growth of tissue in bone, traditionally classified as noncancerous (benign) or cancerous (malignant). Cancerous bone tumors usually originate from a cancer in another part of the body such as from lung, breast, thyroid, kidney and prostate. There may be a lump, pain, or neurological signs from pressure. A bone tumor might present with a pathologic fracture. Other symptoms may include fatigue, fever, weight loss, anemia and nausea. Sometimes there are no symptoms and the tumour is found when investigating another problem.

Gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs) are the most common mesenchymal neoplasms of the gastrointestinal tract. GISTs arise in the smooth muscle pacemaker interstitial cell of Cajal, or similar cells. They are defined as tumors whose behavior is driven by mutations in the KIT gene (85%), PDGFRA gene (10%), or BRAF kinase (rare). 95% of GISTs stain positively for KIT (CD117). Most (66%) occur in the stomach and gastric GISTs have a lower malignant potential than tumors found elsewhere in the GI tract.
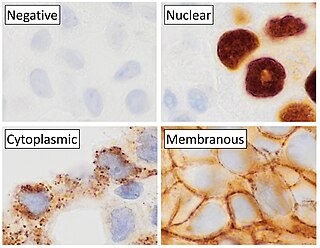
Immunohistochemistry is a form of immunostaining. It involves the process of selectively identifying antigens (proteins) in cells and tissue, by exploiting the principle of antibodies binding specifically to antigens in biological tissues. Albert Hewett Coons, Ernest Berliner, Norman Jones and Hugh J Creech was the first to develop immunofluorescence in 1941. This led to the later development of immunohistochemistry.

Sex cord–gonadal stromal tumour is a group of tumours derived from the stromal component of the ovary and testis, which comprises the granulosa, thecal cells and fibrocytes. In contrast, the epithelial cells originate from the outer epithelial lining surrounding the gonad while the germ cell tumors arise from the precursor cells of the gametes, hence the name germ cell. In humans, this group accounts for 8% of ovarian cancers and under 5% of testicular cancers. Their diagnosis is histological: only a biopsy of the tumour can make an exact diagnosis. They are often suspected of being malignant prior to operation, being solid ovarian tumours that tend to occur most commonly in post menopausal women.

Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP) is a rare locally aggressive malignant cutaneous soft-tissue sarcoma. DFSP develops in the connective tissue cells in the middle layer of the skin (dermis). Estimates of the overall occurrence of DFSP in the United States are 0.8 to 4.5 cases per million persons per year. In the United States, DFSP accounts for between 1 and 6 percent of all soft-tissue sarcomas and 18 percent of all cutaneous soft-tissue sarcomas. In the Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results (SEER) tumor registry from 1992 through 2004, DFSP was second only to Kaposi sarcoma.

Chondrosarcoma is a bone sarcoma, a primary cancer composed of cells derived from transformed cells that produce cartilage. A chondrosarcoma is a member of a category of tumors of bone and soft tissue known as sarcomas. About 30% of bone sarcomas are chondrosarcomas. It is resistant to chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Unlike other primary bone sarcomas that mainly affect children and adolescents, a chondrosarcoma can present at any age. It more often affects the axial skeleton than the appendicular skeleton.

Fibroadenomas are benign breast tumours characterized by an admixture of stromal and epithelial tissue. Breasts are made of lobules and ducts. These are surrounded by glandular, fibrous and fatty tissues. Fibroadenomas develop from the lobules. The glandular tissue and ducts grow over the lobule to form a solid lump.

A synovial sarcoma is a rare form of cancer which occurs primarily in the extremities of the arms or legs, often in proximity to joint capsules and tendon sheaths. It is a type of soft-tissue sarcoma.

A leiomyosarcoma (LMS) is a rare malignant (cancerous) smooth muscle tumor. The word is from leio- 'smooth' myo- 'muscle' and sarcoma 'tumor of connective tissue'. The stomach, bladder, uterus, blood vessels, and intestines are examples of hollow organs made up of smooth muscles where LMS can be located; however, the uterus and abdomen are the most common sites.

Subungual exostosis is a type of non-cancerous bone tumor of the chondrogenic type, and consists of bone and cartilage. It usually projects from the upper surface of the big toe underlying the nailbed, giving rise to a painful swelling that destroys the nail. Subsequent ulceration and infection may occur.

Appendix cancer, also known as appendiceal cancer, is a very rare malignant tumor that forms in the vermiform appendix.
Surgical pathology is the most significant and time-consuming area of practice for most anatomical pathologists. Surgical pathology involves gross and microscopic examination of surgical specimens, as well as biopsies submitted by surgeons and non-surgeons such as general internists, medical subspecialists, dermatologists, and interventional radiologists.
Soft tissue pathology is the subspecialty of surgical pathology which deals with the diagnosis and characterization of neoplastic and non-neoplastic diseases of the soft tissues, such as muscle, adipose tissue, tendons, fascia, and connective tissues. Many malignancies of the soft tissues are challenging for the pathologist to diagnose through gross examination and microscopy alone, and additional tools such as immunohistochemistry, electron microscopy, and molecular pathology techniques are sometimes employed to obtain a definitive diagnosis.
Arthur Purdy Stout (1885–1967) was an American surgeon and pathologist.
Sharon Ann Whelan Weiss is an American pathologist who is best known for her contribution to the subspecialty of soft tissue pathology. She is the main author of Soft Tissue Tumors, one of the most widely used textbooks in the field of sarcoma and soft tissue pathology. She is also well known for her seminal descriptions of multiple soft tissue tumors, such as epithelioid hemangioendothelioma and pleomorphic hyalinizing angiectatic tumor of soft parts among others. She has also mentored and trained other well-known soft tissue pathologists.

Anthony J Gill is an Australian pathologist, professor of surgical pathology at the University of Sydney and the chairman of the Australian Pancreatic Cancer Genome Initiative - part of the International Cancer Genome Consortium. Most of his research is focused on translating the improved understanding of cancer gained at the basic science level into clinically useful diagnostic tests which can be applied in the routine surgical pathology laboratory.

Tenosynovial giant cell tumor (TGCT) is a non-malignant tumor defined histologically as inclusions of “osteoclast-like” multinucleated giant cells, hemosiderin, and macrophages. This histology can present one of 2 clinically distinct ways. TGCT tumors often develop from the lining of joints ..
Fibroblastic and myofibroblastic tumors (FMTs) are tumors which develop from the mesenchymal stem cells which differentiate into fibroblasts and/or the myocytes/myoblasts that differentiate into muscle cells. FMTs are a heterogeneous group of soft tissue neoplasms. The World Health Organization (2020) defined tumors as being FMTs based on their morphology and, more importantly, newly discovered abnormalities in the expression levels of key gene products made by these tumors' neoplastic cells. Histopathologically, FMTs consist of neoplastic connective tissue cells which have differented into cells that have microscopic appearances resembling fibroblasts and/or myofibroblasts. The fibroblastic cells are characterized as spindle-shaped cells with inconspicuous nucleoli that express vimentin, an intracellular protein typically found in mesenchymal cells, and CD34, a cell surface membrane glycoprotein. Myofibroblastic cells are plumper with more abundant cytoplasm and more prominent nucleoli; they express smooth muscle marker proteins such as smooth muscle actins, desmin, and caldesmon. The World Health Organization further classified FMTs into four tumor forms based on their varying levels of aggressiveness: benign, intermediate, intermediate, and malignant.

Monica Bertagnolli is an American surgical oncologist and the 17th director of the National Institutes of Health. She previously served as the 16th director of the National Cancer Institute (NCI). Prior to her governmental positions, she worked at Brigham and Women's Hospital and Dana–Farber Cancer Institute and was the Richard E. Wilson Professor of Surgery at Harvard Medical School.















