
A Linux distribution is an operating system that includes the Linux kernel for its kernel functionality. Although the name does not imply product distribution per se, a distro, if distributed on its own, is often obtained via a website intended specifically for the purpose. Distros have been designed for a wide variety of systems ranging from personal computers to servers and from embedded devices to supercomputers.

YaST is a Linux operating system setup and configuration tool.

GNOME Evolution is the official personal information manager for GNOME. It has been an official part of GNOME since Evolution 2.0 was included with the GNOME 2.8 release in September 2004. It combines e-mail, address book, calendar, task list and note-taking features. Its user interface and functionality is similar to Microsoft Outlook. Evolution is free software licensed under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License (LGPL).
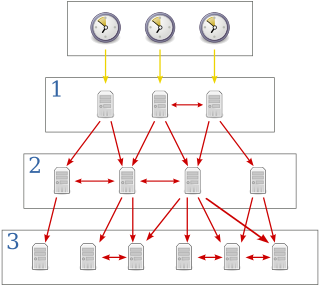
The Network Time Protocol (NTP) is a networking protocol for clock synchronization between computer systems over packet-switched, variable-latency data networks. In operation since before 1985, NTP is one of the oldest Internet protocols in current use. NTP was designed by David L. Mills of the University of Delaware.
phpLDAPadmin is a web app for administering Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) servers. It's written in the PHP programming language, and is licensed under the GNU General Public License. The application is available in 14 languages and supports UTF-8 encoded directory strings.
Clock synchronization is a topic in computer science and engineering that aims to coordinate otherwise independent clocks. Even when initially set accurately, real clocks will differ after some amount of time due to clock drift, caused by clocks counting time at slightly different rates. There are several problems that occur as a result of clock rate differences and several solutions, some being more acceptable than others in certain contexts.

OpenNTPD is a Unix daemon implementing the Network Time Protocol to synchronize the local clock of a computer system with remote NTP servers. It is also able to act as an NTP server to NTP-compatible clients.
PowerLinux is the combination of a Linux-based operating system (OS) running on PowerPC- or Power ISA-based computers from IBM. It is often used in reference along with Linux on Power, and is also the name of several Linux-only IBM Power Systems.
CPython is the reference implementation of the Python programming language. Written in C and Python, CPython is the default and most widely used implementation of the Python language.
The Network Time Protocol daemon (ntpd) is an operating system program that maintains the system time in synchronization with time servers using the Network Time Protocol (NTP).

NetworkManager is a daemon that sits on top of libudev and other Linux kernel interfaces and provides a high-level interface for the configuration of the network interfaces.

SUSE Linux Enterprise (SLE) is a Linux-based operating system developed by SUSE. It is available in two editions, suffixed with Server (SLES) for servers and mainframes, and Desktop (SLED) for workstations and desktop computers.
ntpdate is a computer program used to quickly synchronize and set computers' date and time by querying a Network Time Protocol (NTP) server. It is available for a wide variety of unix-like operating systems.
Spacewalk is open-source systems management software for system provisioning, patching and configuration licensed under the GNU GPLv2.
KVIrc is a graphical IRC client for Linux, Unix, Mac OS and Windows. The name is an acronym of K Visual IRC in which the K stands for a dependency to KDE, which became optional from version 2.0.0. The software is based on the Qt framework and its code is released under a modified GNU General Public License.
Linux on IBM Z or Linux on zSystems is the collective term for the Linux operating system compiled to run on IBM mainframes, especially IBM Z / IBM zSystems and IBM LinuxONE servers. Similar terms which imply the same meaning are Linux/390, Linux/390x, etc. The three Linux distributions certified for usage on the IBM Z hardware platform are Red Hat Enterprise Linux, SUSE Linux Enterprise Server, and Ubuntu.

Open vSwitch (OVS) is an open-source implementation of a distributed virtual multilayer switch. The main purpose of Open vSwitch is to provide a switching stack for hardware virtualization environments, while supporting multiple protocols and standards used in computer networks.
The OpenPOWER Foundation is a collaboration around Power ISA-based products initiated by IBM and announced as the "OpenPOWER Consortium" on August 6, 2013. IBM's focus is to open up technology surrounding their Power Architecture offerings, such as processor specifications, firmware, and software with a liberal license, and will be using a collaborative development model with their partners.

Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) is a feature of Microsoft Windows that allows for using a Linux environment without the need for a separate virtual machine or dual booting. WSL is installed by default in Windows 11. In Windows 10, it can be installed either by joining the Windows Insider program or manually via Microsoft Store or Winget.










