
Kerberos is a computer-network authentication protocol that works on the basis of tickets to allow nodes communicating over a non-secure network to prove their identity to one another in a secure manner. Its designers aimed it primarily at a client–server model, and it provides mutual authentication—both the user and the server verify each other's identity. Kerberos protocol messages are protected against eavesdropping and replay attacks.
The Secure Shell Protocol is a cryptographic network protocol for operating network services securely over an unsecured network. Its most notable applications are remote login and command-line execution.
In computer networking, the Name/Finger protocol and the Finger user information protocol are simple network protocols for the exchange of human-oriented status and user information.

rsync is a utility for transferring and synchronizing files between a computer and a storage drive and across networked computers by comparing the modification times and sizes of files. It is commonly found on Unix-like operating systems and is under the GPL-3.0-or-later license.
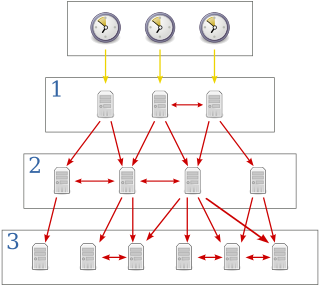
The Network Time Protocol (NTP) is a networking protocol for clock synchronization between computer systems over packet-switched, variable-latency data networks. In operation since before 1985, NTP is one of the oldest Internet protocols in current use. NTP was designed by David L. Mills of the University of Delaware.
In computing, Internet Key Exchange is the protocol used to set up a security association (SA) in the IPsec protocol suite. IKE builds upon the Oakley protocol and ISAKMP. IKE uses X.509 certificates for authentication ‒ either pre-shared or distributed using DNS ‒ and a Diffie–Hellman key exchange to set up a shared session secret from which cryptographic keys are derived. In addition, a security policy for every peer which will connect must be manually maintained.
Zero-configuration networking (zeroconf) is a set of technologies that automatically creates a usable computer network based on the Internet Protocol Suite (TCP/IP) when computers or network peripherals are interconnected. It does not require manual operator intervention or special configuration servers. Without zeroconf, a network administrator must set up network services, such as Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) and Domain Name System (DNS), or configure each computer's network settings manually.

In multitasking computer operating systems, a daemon is a computer program that runs as a background process, rather than being under the direct control of an interactive user. Traditionally, the process names of a daemon end with the letter d, for clarification that the process is in fact a daemon, and for differentiation between a daemon and a normal computer program. For example, syslogd is a daemon that implements system logging facility, and sshd is a daemon that serves incoming SSH connections.
An IRCd, short for Internet Relay Chat daemon, is server software that implements the IRC protocol, enabling people to talk to each other via the Internet. It is distinct from an IRC bot that connects outbound to an IRC channel.
Clock synchronization is a topic in computer science and engineering that aims to coordinate otherwise independent clocks. Even when initially set accurately, real clocks will differ after some amount of time due to clock drift, caused by clocks counting time at slightly different rates. There are several problems that occur as a result of clock rate differences and several solutions, some being more acceptable than others in certain contexts.

OpenNTPD is a Unix daemon implementing the Network Time Protocol to synchronize the local clock of a computer system with remote NTP servers. It is also able to act as an NTP server to NTP-compatible clients.
The following tables compare general and technical information between a number of notable IRC client programs which have been discussed in independent, reliable prior published sources.

NetworkManager is a daemon that sits on top of libudev and other Linux kernel interfaces and provides a high-level interface for the configuration of the network interfaces.

gpsd is a computer software program that collects data from a Global Positioning System (GPS) receiver and provides the data via an Internet Protocol (IP) network to potentially multiple client applications in a server-client application architecture. Gpsd may be run as a daemon to operate transparently as a background task of the server. The network interface provides a standardized data format for multiple concurrent client applications, such as Kismet or GPS navigation software.
ntpdate is a computer program used to quickly synchronize and set computers' date and time by querying a Network Time Protocol (NTP) server. It is available for a wide variety of unix-like operating systems.
On Unix-like operating systems, rdate is a tool for querying the current time from a network server and, optionally, setting the system time. Rdate uses the Time Protocol. The Time Protocol is generally considered obsolete and has been replaced by the Network Time Protocol (NTP).

OpenSSH is a suite of secure networking utilities based on the Secure Shell (SSH) protocol, which provides a secure channel over an unsecured network in a client–server architecture.
systemd is a software suite that provides an array of system components for Linux operating systems. The main aim is to unify service configuration and behavior across Linux distributions. Its primary component is a "system and service manager" — an init system used to bootstrap user space and manage user processes. It also provides replacements for various daemons and utilities, including device management, login management, network connection management, and event logging. The name systemd adheres to the Unix convention of naming daemons by appending the letter d. It also plays on the term "System D", which refers to a person's ability to adapt quickly and improvise to solve problems.

PTPd is an open source implementation of the Precision Time Protocol for Unix-like computers.

chrony is an implementation of the Network Time Protocol (NTP). It is an alternative to ntpd, a reference implementation of NTP. It runs on Unix-like operating systems and is released under the GNU GPL v2. It is the default NTP client and server in Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8 and SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 15, and available in many Linux distributions.











