
Taymyr Nature Reserve is a Russian 'zapovednik' located in the northern lowlands of Siberia, on the Taimyr Peninsula, and on the coast of the Laptev Sea of the Arctic Ocean. The reserve includes the most northern forest of Dahurian larch in the world, and also the most northern mainland mountain range in the world. The protected area was established to protect the breeding grounds of the Red-breasted goose as well as the summer residences of wild reindeer and the biodiversity of the Lake Taymyr. The reserve is situated about 120 km east of the town of Norilsk, and 3,000 km northeast of Moscow, in the Taymyrsky Dolgano-Nenetsky District of Krasnoyarsk Krai. In 1995, the site was designated a UNESCO MAB Reserve. The reserve was formally established in 1979, and covers an area of 1,781,928 ha (6,880.06 sq mi).

The West Siberian taiga ecoregion covers the West Siberian Plain in Russia, from the Ural mountains in the west to the Yenisei River in the east, and roughly from 56° N to 66° N latitude. It is a vast, flat lowland region of boreal forests (taiga), and wetlands, covering an area about 1,800 km west–east, by 1,000 km north–south.

The Northeast Siberian taiga ecoregion is an area of "sparse taiga forest" between the Lena River and the Kolyma River in northeastern Siberia, Russia. The ecoregion's internal borders form a patchwork of territory constituting the southern part of the East Siberian Lowland, as well as lowlands around the East Siberian Mountains, including the ridges and peaks of the Verkhoyansk Range and the Chersky Range. On the southern border of the ecoregion is the north coast of the Sea of Okhotsk, giving the region maritime boreal forests as well as the continental forests situated inland. The ecoregion is one of the largest tracts of virgin boreal forest in the world, due to the very sparse population and difficult access. It is mostly in the Sakha Republic.
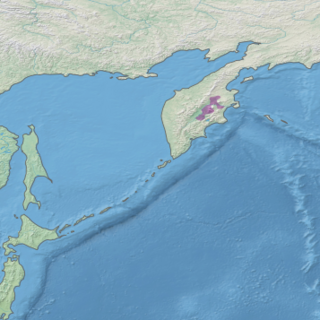
The Kamchatka–Kurile taiga ecoregion is a "conifer island" in the middle of the Kamchatka Peninsula, along the Kamchatka River. It is the easternmost example of Siberian taiga. The region has unusual ecological conditions, a "snow forest" that combines low temperatures, high humidity and boreal forest with heavy snowfall. The local ecology is also affected by volcanic activity. The region is about 300 km long (north–south), and averages about 100 km west–east. It is in the Palearctic realm, and mostly in the Boreal forests/taiga ecoregion with a humid continental climate, cool summer climate. It covers 147,064 km2 (56,782 sq mi).

The Altai alpine meadow and tundra ecoregion is a terrestrial ecoregion covering the higher elevation of the Altai Mountains at the center of the "X" formed by the borders separating Russia, Kazakhstan, China, and Mongolia. The mountain peaks are the farthest north in Central Asia, separating the plains of Siberia to the north from the hot, dry deserts to the south. Altitudes above 2,400 meters display characteristics of tundra, with patches of alpine meadows and some trees immediately below the treeline. The ecoregion is in the montane grasslands and shrublands biome, and the Palearctic realm, with a humid continental climate. It covers an area of 90,132 square kilometres (34,800 sq mi).

The Arctic desert ecoregion is a terrestrial ecoregion that covers the island groups of Svalbard, Franz Josef Land, Severny Island and Severnaya Zemlya in the Arctic Ocean, above 75 degrees north latitude. The region is covered with glaciers, snow, and bare rock in a harshly cold environment. The temperature does rise above freezing for short periods in the summer, so some ice melt occurs, and the area supports colonies of sea birds and mammals. It has an area of 161,400 square kilometres (62,300 sq mi).

The Bering tundra ecoregion is an ecoregion that covers a portion of northeastern Russia, between the Kolyma Mountains on the west, and the Bering Sea coast to the east. The area is an important stopping place for migratory birds. It has an area of 474,227 square kilometres (183,100 sq mi).

The Cherskii–Kolyma mountain tundra ecoregion is an ecoregion that covers the higher elevations of the Chersky Range and the Kolyma Mountains, the only large mountain range in northern Russia. It is in the Palearctic realm, and tundra biome. It has an area of 556,589 square kilometres (214,900 sq mi).

The Kamchatka Mountain tundra and forest tundra ecoregion is an ecoregion that covers the central mountain range of the Kamchatka Peninsula in the Russian Far East. The region is one of volcanos, caldera, geysers, and mountain tundra. It is in the Palearctic realm and tundra biome. It has an area of 119,400 square kilometres (46,100 sq mi).

The Kola Peninsula tundra ecoregion is an ecoregion that covers the northeastern half of the Kola Peninsula, along the coast of the White Sea, a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. The maritime effects of the White Sea create a milder climate than would be expected for a region of this latitude. It is in the Palearctic realm, and the tundra biome. It has an area of 58,793 square kilometres (22,700 sq mi).

The Northeast Siberian coastal tundra ecoregion is an ecoregion that covers the coastal plain of the central north region of Siberia in Russia. This coastal region borders the Laptev Sea and the East Siberian Sea, both marginal seas of the Arctic Ocean, from the Lena River delta in the west to the Kolyma River delta in the east. There are several large river deltas in the area that support breeding grounds for 60 to 80 species of migratory birds. The region is in the Palearctic realm, and the tundra biome. It has an area of 846,149 square kilometres (326,700 sq mi).

The Northwest Russian-Novaya Zemlya tundra ecoregion is an ecoregion on the north coast of European Russia. It covers the southern shores of the White Sea, the coast of the Barents Sea east to the Yamal Peninsula, the southern half of Novaya Zemlya, and numerous inlets and islands. The low tundra wetlands are important breeding grounds for waterfowl. The ecoregion is in the Palearctic realm, and the tundra biome. It has an area of 284,122 square kilometres (109,700 sq mi).

The Taimyr-Central Siberian tundra ecoregion is an ecoregion that broadly covers the Taymyr Peninsula in the Russian Far North. It ranges from the delta of the Yenisei River in the west, across the Taymyr Peninsula and Khatanga Gulf, to the Lena River delta in the east. The region is an important area for breeding birds. It is in the Palearctic realm in the tundra biome, and is mostly located in Taymyrsky Dolgano-Nenetsky District of Krasnoyarsk Krai. It has an area of 954,670 square kilometres (368,600 sq mi).

The Transbaikal Bald Mountain tundra ecoregion covers the high-altitude peak zones above the treeline in a series of mountain ranges that stretch from the northern reaches of Lake Baikal to the western coastal ranges of the Okhotsk Sea. Floral communities are those of mountain tundra, with bare rock or permafrost under layers of moss and lichen. Because the ecoregion is aligned along a common latitude, it acts as a route for the transmission of species across Siberia. The ecoregion is in the Palearctic realm and the tundra biome. It has an area of 217,559 square kilometres (84,000 sq mi).

The Yamal–Gydan tundra ecoregion sprawls across the expansive Yamal Peninsula and Gydan Peninsula in the northern expanse of Russia. This unique ecoregion is characterized by its sparsely populated vegetation and wildlife, yet it holds great significance as a vital haven for migratory birds and coastal sea mammals. Embraced by the Palearctic realm and firmly entrenched in the tundra biome, it boasts an extensive area, covering approximately 412,067 square kilometers.

Pacific Coastal Mountain icefields and tundra is a tundra ecoregion in Alaska, British Columbia, and Yukon, as defined by the World Wildlife Fund (WWF) categorization system.

The Davis Highlands tundra ecoregion covers the Baffin Mountains on the northeast coast of Baffin Island and Bylot Island, facing Baffin Bay in Nunavut, northern Canada. The terrain is extremely rugged, heavily glaciated, with many deep fjords, and very cold. About half of the territory is moss and lichen tundra, the other half bare rock and ice. The region is wetter than the much drier regions to the southwest of the Baffin Islands.

The Kalaallit Nunaat low arctic tundra ecoregion covers the low coastal areas of western and southern Greenland, reaching in up to 100 km before bare rock and ice become dominant. While much of the ecoregion is bare rock or ice, about 50% of the ground is covered in moss and lichen, and another 10% in herbaceous cover, shrubs, and even small stands of trees.

The Torngat Mountain tundra ecoregion covers the Torngat Mountains on the northeastern tip of the Labrador Peninsula where the provinces of Quebec and Newfoundland and Labrador meet. The mountains feature glacially carved U-shaped valleys and deep fjords. The vegetation over most of the territory is that of arctic tundra, herbaceous cover, or bare rock. The region supports seasonal polar bears, black bears, and caribou. The Atlantic coast is on the Atlantic Flyway for migratory birds.

Kytalyk National Park is a protected area for the Arctic breeding grounds of migratory birds on the East Asian–Australasian Flyway, including a significant portion of sites for the critically endangered Siberian crane. The name "kytalyk" is the Yakut-language word for the Siberian crane. The park is on the low-lying tundra of the delta of the Indigirka River, on the East Siberian Sea in northern Russia. The park was officially created in 2019. The park is located in Allaikhovsky District of the Sakha Republic.




















