
Paracelsus, born Theophrastus von Hohenheim, was a Swiss physician, alchemist, lay theologian, and philosopher of the German Renaissance.

Nicolaus Rohlfs was an 18th-century German mathematics teacher (arithmeticus) in Buxtehude and Hamburg who wrote astronomical calendars, a book about gardening, and other treatises that were continued by Matthias Rohlfs.

Johann Kuhnau was a German polymath, known primarily as a composer today. He was also active as a novelist, translator, lawyer, and music theorist, and was able to combine these activities with his duties in his official post as Thomaskantor in Leipzig, which he occupied for 21 years. Much of his music, including operas, masses, and other large-scale vocal works, is lost. His reputation today rests on his Biblical Sonatas, a set of programmatic keyboard sonatas published in 1700, in which each sonata depicted in detail a particular story from the Bible. After his death, Kuhnau was succeeded as Thomaskantor by Johann Sebastian Bach.
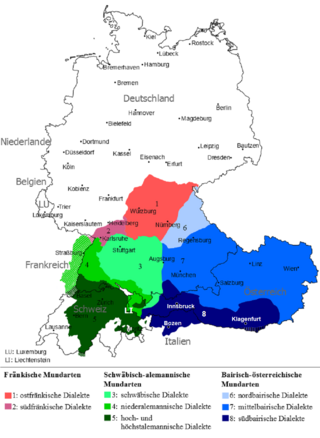
East Franconian or Mainfränkisch, usually referred to as Franconian in German, is a dialect spoken in Franconia, the northern part of the federal state of Bavaria and other areas in Germany around Nuremberg, Bamberg, Coburg, Würzburg, Hof, Bayreuth, Meiningen, Bad Mergentheim, and Crailsheim. The major subgroups are Unterostfränkisch, Oberostfränkisch and Südostfränkisch.

The Oberhasli is a historical Landvogtei or Talschaft in the Bernese Highlands, Switzerland, bordering on the cantons of Obwalden (OW), Nidwalden (NW), Uri (UR) and Wallis (VS).

Georg Andreas Agricola or Georgio Andrea Agricola or Georg Andreas Bauer or George André Agricola was a German physician and botanist from Regensburg.

Johann Prokop Mayer was an Austrian naturalist and botanist. He created the flower gardens at the Würzburg Residence.
The High Com noise reduction system was developed by Telefunken, Germany, in the 1970s as a high quality high compression analogue compander for audio recordings.

Johann Kaspar Hechtel was a German businessman, owner of a brass factory in Nuremberg, non-fiction writer and designer of parlour games including the prototype for the Petit Lenormand cartomancy deck. According to published biographies, Hechtel also contributed anonymously to some treatises on physics.

The Landrecht was the law applying within an individual state in the Holy Roman Empire during the Middle Ages and Early Modern times. The state laws that emerged in the territories of the empire from the 12th century onwards had been developed from the older tribal laws of the Saxons, Swabians, Bavarians and Bohemians. Through privileges and laws passed by the territorial princes as well as the jurisprudence of the Landgerichte or state courts, these ancient rights were supplemented and developed. Later Roman law was also accepted and incorporated into the Landrechte. The Landrecht was only applied to the burghers of a town in a secondary way, because they came primarily under municipal law and the autonomous jurisdiction of their communities.
In legend and in the early historiography of Switzerland there is an account of a migration of a population of Swedes and Frisians settling in the Swiss Alps, specifically in Schwyz and in Hasli (Schwedensage).
Friedrich Wilhelm Ferdinand Ernst Heinrich von Forcade de Biaix, aka Ferdinand von Forcade, Royal Prussian Major and Knight of the Iron Cross 2nd Class.
The Deutsche Theatrum Chemicum is a collection of alchemical texts, predominantly in German translation, which was published in Nuremberg in three volumes by Friedrich Roth-Scholtz (1687–1736), the publisher, printer and bibliographer.
Michael Ranft, in Latin Michael Ranfftius was a Lutheran pastor, writer and historian who is known for his writings on vampires in Germany.

Johannes Praetorius was a German writer and historian.

"Christ fuhr gen Himmel" is a German Ascension hymn. The church song is based the medieval melody of the Easter hymn "Christ ist erstanden". It was an ecumenical song from the beginning, with the first stanza published in 1480, then included in a Lutheran hymnal in 1545, and expanded by the Catholic Johannes Leisentritt in 1567. It appears in modern German Catholic and Protestant hymnals, and has inspired musical settings by composers from the 16th to the 21st century.

Johann Christoph Frauendorff was a German librettist, lawyer and mayor of Naumburg.
Zacharias Praetorius was a German Lutheran poet and theologian.

The Ramschwag Ruins are the ruins of a castle in the east of the municipality of Häggenschwil, in the Swiss canton of St. Gallen.

Alfred Raimund Fesl, better known as Fredl Fesl, was a Lower Bavarian musician and singer who was said to be the one who invented Bavarian musical Kabarett.


































