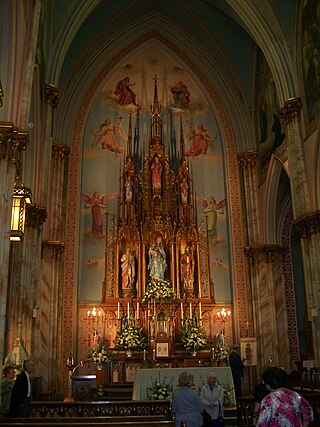The Church of St. Nicholas was a Gothic Revival cathedral that was formerly one of the five Lutheran Hauptkirchen in the city of Hamburg, Germany. The original chapel, a wooden building, was completed in 1195. It was replaced by a brick church in the 14th century, which was eventually destroyed by fire in 1842. The church was completely rebuilt by 1874, and was the tallest building in the world from 1874 to 1876. It was designed by the English architect George Gilbert Scott.

The Victorian Society is a UK charity and amenity society that campaigns to preserve and promote interest in Victorian and Edwardian architecture and heritage built between 1837 and 1914 in England and Wales. As a statutory consultee, by law it must be notified of any work to a listed building which involves any element of demolition or structural alteration.

The Dutch Reformed Church is one of the most prominent architectural landmarks in Newburgh, New York. It was designed by Alexander Jackson Davis in 1835 in the Greek Revival style just after the dissolution of his partnership with Ithiel Town. It is his only surviving church in that style and is considered to be his latest building still standing that largely reflects his original vision. The church stands at 132 Grand Street, just north of the Newburgh Free Library.

Beth Hamedrash Hagodol is an Orthodox Jewish congregation that for over 120 years was located in a historic building at 60–64 Norfolk Street between Grand and Broome Streets in the Lower East Side neighborhood of Manhattan, New York City. It was the first Eastern European congregation founded in New York City and the oldest Russian Jewish Orthodox congregation in the United States.

Walnut Hills United Presbyterian Church is a historic church tower in the Walnut Hills neighborhood of Cincinnati, Ohio, United States. The last remnant of a landmark church building, it was designed by a leading Cincinnati architect and built in the 1880s. Although named a historic site a century after its construction, the building was mostly destroyed after extensive neglect caused restoration to become prohibitively expensive.
Saint Laurentius Parish was a Roman Catholic parish established in 1882 that largely served people of Polish background in the Fishtown neighborhood of Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United States.
Henry Engelbert (1826–1901) was a German-American architect. He was best known for buildings in the French Second Empire style, which emphasized elaborate mansard roofs with dormers. New York's Grand Hotel on Broadway is the most noteworthy extant example of Engelbert's work in this style. Many of his commissions were Lutheran or Roman Catholic churches.

Cedarcroft is a distinctive residential neighborhood in the North district of Baltimore, bordered by Gittings, East Lake and Bellona Avenue avenues and York Road. According to Baltimore City's Commission for Historical and Architectural Preservation (CHAP), the houses in Cedarcroft are in the Dutch Colonial Revival, Federal Revival, Tudor Revival, Georgian Revival, Cape Cod Revival, Bungalow, and Italianate styles of architecture.

St. Monica's Church is a historic former Roman Catholic parish church in the Diocese of Brooklyn, located in Jamaica, Queens, New York. It was built in 1856 and is a brick basilica-type building in the Romanesque style. It features a four-story entrance tower in the center of its three-bay-wide front façade. Saint Monica's Church has been refurbished on the Campus of York College as a child care center.

Union Church is a historic church on Harpswell Neck Road in North Harpswell, Maine. Built in 1841, it is architecturally a distinctive and well-preserved combination of Greek Revival and Gothic Revival styles. It was used over the years by a variety of religious groups, and is now maintained by the Harpswell Garden Club. The building was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1988.

The Smallpox Hospital, sometimes referred to as the Renwick Smallpox Hospital and later the Maternity and Charity Hospital Training School, was a hospital located on Roosevelt Island in Manhattan, New York City. Originally designed by architect James Renwick Jr., the 100-bed hospital opened in 1856, when the area was known as Blackwell's Island.

The Church of St. Teresa is a Roman Catholic parish located at 16-18 Rutgers Street on the corner of Henry Street in the Lower East Side neighborhood of Manhattan, New York City. The parish is under the authority of the Archdiocese of New York. The church building was constructed in 1841-42 as the Rutgers Presbyterian Church erected in the Gothic Revival style on a plot of ground donated by Colonel Henry Rutgers, and it is said to have the oldest public clock in New York City. The church was taken over by St. Teresa's Parish in 1863, three years after it was founded.

The Church of St. Mark is the parish church of old Zagreb, Croatia, located in St. Mark's Square. It is one of the oldest architectural monuments in Zagreb.

The Victorian restoration was the widespread and extensive refurbishment and rebuilding of Church of England churches and cathedrals that took place in England and Wales during the 19th-century reign of Queen Victoria. It was not the same process as is understood today by the term building restoration.

TheTrinity Church or Trinity Congregational Church designed by Benjamin Mountfort, later called the State Trinity Centre, is a Category I heritage building listed with Heritage New Zealand. Damaged in the 2010 Canterbury earthquake and red-stickered after the February 2011 Christchurch earthquake, the building was threatened with demolition like most other central city heritage buildings. In June 2012, it was announced that the building would be saved, repaired and earthquake strengthened. The building, post its church status, has housed some commercial operations, including the State Trinity Centre; 'The Octagon' (2006–2010); and later, following earthquake repairs, a business called 'The Church Brew Pub' (2023–present).

The statue of John Betjeman at St Pancras railway station, London is a depiction in bronze by the sculptor Martin Jennings. The statue was designed and cast in 2007 and was unveiled on 12 November 2007 by Betjeman's daughter, Candida Lycett Green and the then Poet Laureate Andrew Motion to commemorate Betjeman and mark the opening of St Pancras International as the London terminus of the Eurostar high-speed rail link between Great Britain and mainland Europe. The location memorialises the connection between St Pancras station and Betjeman, an early and lifelong advocate of Victorian architecture who led the campaign to save the station from demolition in the 1960s.

Blessed Sacrament Church is a historic Roman Catholic church in Buffalo, New York, United States. Constructed in the late 19th century, it remains the home of an active congregation and has been recognized as a historically significant building in the Linwood Historic District of Buffalo.

Saints Peter and Paul Church is a historic former Roman Catholic church in the East Liberty neighborhood of Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. It is often referred to colloquially as the "Dogma Church" because of its appearance in the climactic scene of the 1999 Kevin Smith film Dogma. The church was built in 1890–91 and was designed by Adolphus Druiding. After being badly damaged in a fire in 1909, the interior and roof were rebuilt under the supervision of architect John T. Comès and the church was rededicated in 1910. It closed in 1992 and has remained vacant since. In 1983, the church was designated as a Pittsburgh Landmark by the Pittsburgh History & Landmarks Foundation (PHLF).

Christ Memorial Reformed Episcopal Church was a Reformed Episcopal Church congregation in Philadelphia. Founded in 1887 and completed in 1888, the building it occupied in West Philadelphia was for most of its history was also the campus of Reformed Episcopal Seminary. In 2004, a lightning strike caused the decaying steeple of the church to collapse, resulting in the building's closure. After a prolonged conflict over the insurance payout, the REC sold the building, which was demolished in 2018 and replaced by apartments.

The First Church of Christ, also called the First Congregational Church, was a Gothic Revival-style church located in New London, Connecticut. It was completed in 1853, designed by Prague-born architect Leopold Eidlitz. This large granite edifice featured a tall central spire, rising in three stages and topped by a gold ball, typical of significant buildings in Prague. The central bell tower was flanked by two lower towers with pitched roofs. The church occupied a prominent position on Union Street, across from the City Hall, and anchoring the Downtown New London Historic District.