Related Research Articles

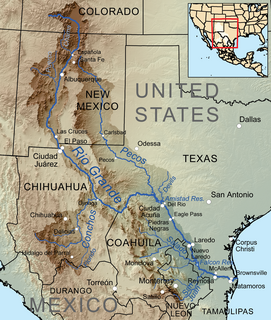
The Rio Grande is one of the principal rivers in the southwestern United States and northern Mexico. The Rio Grande begins in south-central Colorado in the United States and flows to the Gulf of Mexico. After passing through the length of New Mexico along the way, it forms part of the Mexico–United States border. According to the International Boundary and Water Commission, its total length was 1,896 miles (3,051 km) in the late 1980s, though course shifts occasionally result in length changes. Depending on how it is measured, the Rio Grande is either the fourth- or fifth-longest river system in North America.

The Pecos River originates in north-central New Mexico and flows into Texas, emptying into the Rio Grande. Its headwaters are on the eastern slope of the Sangre de Cristo mountain range in Mora County north of Pecos, NM, at an elevation of over 12,000 feet (3,700 m) feet. The river flows for 926 miles (1,490 km) before reaching the Rio Grande near Del Rio. Its drainage basin encompasses about 44,300 square miles (115,000 km2).
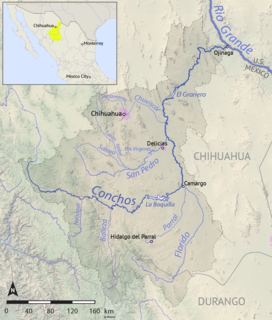
The Río Conchos is a large river in the Mexican state of Chihuahua. It joins the Río Bravo del Norte at the town of Ojinaga, Chihuahua.

The Santiago River or Río Grande de Santiago is one of the longest rivers in Mexico, measuring up 433 km (269 mi) long. The river begins at Lake Chapala and continues roughly north-west through the Sierra Madre Occidental, receiving the Verde, Juchipila, Bolaños, and other tributaries. At La Yesca, the La Yesca Dam was completed in 2012 and the El Cajón Dam was completed downstream in 2007. Below El Cajón, the Aguamilpa Dam was completed in 1993, creating a reservoir covering a large part of the territory of the municipality of El Nayar in Nayarit. From Aguamilpa, the river descends to the coastal lowlands, passing by Santiago Ixcuintla and empties into the Pacific Ocean, 16 km (10 mi) northwest of San Blas, in Nayarit.

The Rio Grande Wild and Scenic River is a U.S. National Wild and Scenic River that protects 260 miles (420 km) of the Rio Grande in New Mexico and Texas. The designation was first applied in 1968 to a 55.7-mile (89.6 km) stretch of the river in New Mexico; an additional 191.2 miles (307.7 km) of the river in Texas was added in 1978, followed by another 12.5 miles (20.1 km) in New Mexico in 1994.

The Rio Chama, a major tributary river of the Rio Grande, is located in the U.S. states of Colorado and New Mexico. The river is about 130 miles (210 km) long altogether. From its source to El Vado Dam its length is about 50 miles (80 km), from El Vado Dam to Abiquiu Dam is about 51 miles (82 km), and from Abiquiu Dam to its confluence with the Rio Grande is about 34 miles (55 km).

The Rio Puerco is a tributary of the Rio Grande in the U.S. state of New Mexico. From its source on the west side of the Nacimiento Mountains, it flows about 230 miles (370 km), generally south to join the Rio Grande about 20 miles (32 km) south of Belen and about 50 miles (80 km) south of Albuquerque. Its drainage basin is about 7,350 square miles (19,000 km2) large, of which probably about 1,130 square miles (2,900 km2) are noncontributing.
The Río Salado, also Río Salado de los Nadadores, or Salado River, is a river in northern Mexico, a tributary of the Rio Grande (Río Bravo). Its basin extends across the northern portion of Coahuila, Nuevo Leon, and Tamaulipas states.
The Atoyac River is a river in Oaxaca, Mexico. The Atoyac flows into the Rio Verde which empties into the Pacific near Laguna Chacahua, in Lagunas de Chacahua National Park, 90 km west of Puerto Escondido. The mountainous terrain of the region it occupies allows for no navigable rivers; instead, there are a large number of smaller ones, which often change name from area to area. The continental divide passes through the state, meaning that there is drainage towards both the Gulf of Mexico and the Pacific Ocean. Most of the drainage towards the Gulf is represented by the Papaloapan and Coatzacoalcos Rivers and their tributaries such as the Grande and Salado Rivers. Three rivers account for most of the water headed for the Pacific: the Mixteco River, Tehuantepec River, and the Atoyac, with their tributaries.
The Balleza River, or Río Balleza, is a river of Mexico. It is a tributary of the Rio Conchos, which in turn flows into the Rio Grande.

The Bolaños River is a river in Mexico flowing through the Sierra Madre Occidental, and a tributary of Rio Grande de Santiago. It has a length of 360 km and a watershed of about 10 000 square kilometers.
The Candela River is a river of Mexico. It is a tributary of the Rio Salado, which in turn flows into the Rio Grande.
The San Pedro River (Chihuahua) is a river of Mexico. It is a tributary of the Rio Conchos, which in turn flows into the Rio Grande.

The SabinasRiver is a river of Mexico. It is a tributary of the Rio Salado, which in turn flows into the Rio Grande.
The Sabinas Hidalgo River is a river of Mexico. It is a tributary of the Rio Salado, which in turn flows into the Rio Grande.
Río Verde is a river in Jalisco, Mexico. It is a tributary of the Rio Grande de Santiago.
The Pesquería River, is a river of Mexico. It is a tributary of the San Juan River, which in turn flows into the Rio Grande.
The Parral River, is a river of Mexico. It is a tributary of the Rio Florido, which flows into the Rio Conchos, which in turn flows into the Rio Grande.

Florido River is a river of Mexico. It is a tributary of the Rio Conchos, which in turn flows into the Rio Grande.

The Jemez River is a tributary of the Rio Grande in eastern Sandoval County, New Mexico, United States.
References
- Atlas of Mexico, 1975. [1]
- The Prentice Hall American World Atlas, 1984.
- Rand McNally, The New International Atlas, 1993.