MacFirbis, also known as Forbes, was the surname of a family of Irish hereditary historians based for much of their known history at Lecan, Tireragh. They claimed descent from Dathí (d.418?/428?), said to be one of the last pagan Kings of Connacht, and were thus one of the many families who sprang from the Uí Fiachrach dynasty. The progenitors of the MacFirbis family descend from Amhailgadh, whose brothers included Fiachra Ealg and Eocha Breac.
The Conmhaicne or Conmaicne were an ancient tribal grouping that were divided into a number of distinct branches that were found scattered around Ireland in the early medieval period. They settled in Connacht, where they gave their name to several territories.
Kerry or Kerri is both a masculine and feminine English language given name of Gaelic (Irish) origin.
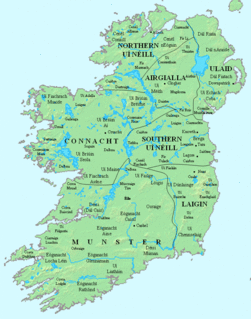
The Uí Briúin were a royal dynasty of Connacht. Their eponymous apical ancestor was Brión, son of Eochaid Mugmedon and Mongfind, and an elder half brother of Niall of the Nine Hostages. They formed part of the Connachta, along with the Uí Fiachrach and Uí Ailello, putative descendants of Eochaid Mugmedon's sons Fiachra and Ailill. The Uí Ailello were later replaced as the third of the Three Connachta, by genealogical sleight of hand, by the Uí Maine.

Costello is one of the ancient baronies of Ireland. Unusually for an Irish barony, it straddles two counties: County Mayo and County Roscommon. It comprises the modern day districts of Kilkelly, Kilmovee, Killeagh, Kilcolman, and Castlemore.
Rogallach mac Uatach was a king of Connacht from the Uí Briúin branch of the Connachta. He was the son of Uatu mac Áedo, a previous king. He acquired the throne of Connacht after defeating the previous king Colmán mac Cobthaig of the Ui Fiachrach Aidhne, who was slain at the Battle of Cennbag in 622. Professor Francis Byrne believes he is the first reasonable representative of this branch to be said to have held the throne of Connacht
Muirgius mac Tommaltaig was a King of Connacht from the Uí Briúin branch of the Connachta. He was the great-grandson of Indrechtach mac Muiredaig Muillethan, a previous king. The death of his father Tommaltach mac Murgail is recorded in the annals where he is called king of Mag nAi. Muirgius was of the Síl Muiredaig sept of the Uí Briúin. He reigned from 792 to 815.
Diarmait mac Tommaltaig was a king of Connacht from the Uí Briúin branch of the Connachta. He was the great-grandson of Indrechtach mac Muiredaig Muillethan, a previous king. The death of his father Tommaltach mac Murgail is recorded in the annals where he is called king of Mag nAi. He succeeded his brother Muirgius mac Tommaltaig. He was of the Síl Muiredaig sept of the Uí Briúin. He ruled from 815 to 833.
Mael Brigte mac Mothlachain, assassin, fl. 649.
Aodh Ua Goirmghiallaigh, King of Partraige Cera, died 1206.
The Ciarraige were a population-group recorded in the early historic era in Ireland.
The Cálraighe were a population-group found mostly in northern Connacht as well as County Westmeath and County Longford. They were purported descendants of Lugaid Cal, son of Daire Sirchrechtaig, who was himself a supposed descendant of Lugaid mac Itha, a first cousin of Míl Espáine.

The Partraige were a people of early historic Ireland.
Coman mac Faelchon was an Irish saint, the founder, abbot and bishop of Roscommon, fl. 550.
The Ciarraighe Locha na nÁirne were a branch of the Ciarraighe people, located in what is now central-east County Mayo in Connacht.
The Ciarraige Óic Bethra were a population-group found in early medieval Ireland.

Frenchpark is a barony in County Roscommon, Republic of Ireland.





