Animation is a filmmaking technique by which still images are manipulated to create moving images. In traditional animation, images are drawn or painted by hand on transparent celluloid sheets (cels) to be photographed and exhibited on film. Animation has been recognized as an artistic medium, specifically within the entertainment industry. Many animations are computer animations made with computer-generated imagery (CGI). Stop motion animation, in particular claymation, has continued to exist alongside these other forms.

Computer animation is the process used for digitally generating moving images. The more general term computer-generated imagery (CGI) encompasses both still images and moving images, while computer animation only refers to moving images. Modern computer animation usually uses 3D computer graphics.

The Graphics Interchange Format is a bitmap image format that was developed by a team at the online services provider CompuServe led by American computer scientist Steve Wilhite and released on June 15, 1987.

A storyboard is a graphic organizer that consists of illustrations or images displayed in sequence for the purpose of pre-visualizing a motion picture, animation, motion graphic, or interactive media sequence. The storyboarding process, in the form it is known today, was developed at Walt Disney Productions during the early 1930s, after several years of similar processes being in use at Walt Disney and other animation studios.

In photography, shutter speed or exposure time is the length of time that the film or digital sensor inside the camera is exposed to light when taking a photograph. The amount of light that reaches the film or image sensor is proportional to the exposure time. 1⁄500 of a second will let half as much light in as 1⁄250.

Motion blur is the apparent streaking of moving objects in a photograph or a sequence of frames, such as a film or animation. It results when the image being recorded changes during the recording of a single exposure, due to rapid movement or long exposure.

Slow motion is an effect in film-making whereby time appears to be slowed down. It was invented by the Austrian priest August Musger in the early 20th century. This can be accomplished through the use of high-speed cameras and then playing the footage produced by such cameras at a normal rate like 30 fps, or in post production through the use of software.
Bullet time is a visual effect or visual impression of detaching the time and space of a camera from that of its visible subject. It is a depth enhanced simulation of variable-speed action and performance found in films, broadcast advertisements, and realtime graphics within video games and other special media. It is characterized by its extreme transformation of both time, and of space. This is almost impossible with conventional slow motion, as the physical camera would have to move implausibly fast; the concept implies that only a "virtual camera", often illustrated within the confines of a computer-generated environment such as a virtual world or virtual reality, would be capable of "filming" bullet-time types of moments. Technical and historical variations of this effect have been referred to as time slicing, view morphing, temps mort and virtual cinematography.
Visual effects is the process by which imagery is created or manipulated outside the context of a live-action shot in filmmaking and video production. The integration of live-action footage and other live-action footage or CGI elements to create realistic imagery is called VFX.

Posterization or posterisation of an image is the conversion of a continuous gradation of tone to several regions of fewer tones, causing abrupt changes from one tone to another. This was originally done with photographic processes to create posters. It can now be done photographically or with digital image processing, and may be deliberate or an unintended artifact of color quantization. Posterization is often the first step in vectorization (tracing) of an image.

Chronophotography is a photographic technique from the Victorian era which captures a number of phases of movements. The best known chronophotography works were mostly intended for the scientific study of locomotion, to discover practical information for animal handlers and/or as reference material for artists. Although many results were not intended to be exhibited as moving pictures, there is much overlap with the more or less simultaneous quest to register and exhibit photographic motion pictures.

Time-lapse photography is a technique in which the frequency at which film frames are captured is much lower than the frequency used to view the sequence. When played at normal speed, time appears to be moving faster and thus lapsing. For example, an image of a scene may be captured at 1 frame per second but then played back at 30 frames per second; the result is an apparent 30 times speed increase. Similarly, film can also be played at a much lower rate than at which it was captured, which slows down an otherwise fast action, as in slow motion or high-speed photography.

A snapshot is a photograph that is "shot" spontaneously and quickly, most often without artistic or journalistic intent and usually made with a relatively cheap and compact camera.

Fine-art photography is photography created in line with the vision of the photographer as artist, using photography as a medium for creative expression. The goal of fine-art photography is to express an idea, a message, or an emotion. This stands in contrast to representational photography, such as photojournalism, which provides a documentary visual account of specific subjects and events, literally representing objective reality rather than the subjective intent of the photographer; and commercial photography, the primary focus of which is to advertise products or services.
The Ken Burns effect is a type of panning and zooming effect used in film and video production from non-consecutive still images. The name derives from extensive use of the technique by American documentarian Ken Burns. This technique had also been used to produce animatics, simple animated mockups used to previsualize motion pictures, but Burns's name has become associated with the effect in much the same way as Alfred Hitchcock is associated with the dolly zoom.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to photography:

360 photography refers to a photographic technique by which a series of photos give the impression of an object rotating. These photos can be displayed as an interactive animation on web pages and apps, allowing a user to control the rotation of an object. The photos can also be displayed as an infinitely looping GIF or video.
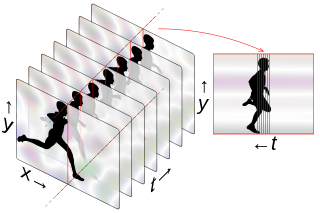
Strip photography, or slit photography, is a photographic technique of capturing a two-dimensional image as a sequence of one-dimensional images over time, in contrast to a normal photo which is a single two-dimensional image at one point in time. A moving scene is recorded, over a period of time, using a camera that observes a narrow strip rather than the full field. If the subject is moving through this observed strip at constant speed, they will appear in the finished photo as a visible object. Stationary objects, like the background, will be the same the whole way across the photo and appear as stripes along the time axis; see examples on this page.

Lumia imaging apps are imaging applications by Microsoft Mobile and formerly by Nokia for Lumia devices built on the technology of Scalado. The Lumia imaging applications were notably all branded with "Nokia" in front of their names, but after Microsoft acquired Nokia's devices and services business the Nokia branding was superseded with "Lumia", and often updates included nothing but name changes, but for the Lumia Camera this included a new wide range of feature additions. Most of the imaging applications are developed by the Microsoft Lund division. As part of the release of Windows 10 Mobile and the integration of Lumia imaging features into the Windows Camera and Microsoft Photos applications some of these applications stopped working in October 2015.
Jamie Beck is an American photographer and author of the 2022 book An American in Provence. Beck is best known, with her husband Kevin Burg, for co-creating the Cinemagraph, and also for her work and life in Provence; including her Isolation Creation series.















