FidoNet is a worldwide computer network that is used for communication between bulletin board systems (BBSes). It uses a store-and-forward system to exchange private (email) and public (forum) messages between the BBSes in the network, as well as other files and protocols in some cases.

In computer networking, multicast is a type of group communication where data transmission is addressed to a group of destination computers simultaneously. Multicast can be one-to-many or many-to-many distribution. Multicast differs from physical layer point-to-multipoint communication.

Peer-to-peer (P2P) computing or networking is a distributed application architecture that partitions tasks or workloads between peers. Peers are equally privileged, equipotent participants in the network, forming a peer-to-peer network of nodes. In addition, a personal area network (PAN) is also in nature a type of decentralized peer-to-peer network typically between two devices.
In a telecommunications network, a link is a communication channel that connects two or more devices for the purpose of data transmission. The link may be a dedicated physical link or a virtual circuit that uses one or more physical links or shares a physical link with other telecommunications links.
An information society is a society or subculture where the usage, creation, distribution, manipulation and integration of information is a significant activity. Its main drivers are information and communication technologies, which have resulted in rapid growth of a variety of forms of information. Proponents of this theory posit that these technologies are impacting most important forms of social organization, including education, economy, health, government, warfare, and levels of democracy. The people who are able to partake in this form of society are sometimes called either computer users or even digital citizens, defined by K. Mossberger as “Those who use the Internet regularly and effectively”. This is one of many dozen internet terms that have been identified to suggest that humans are entering a new and different phase of society.

The term built environment refers to human-made conditions and is often used in architecture, landscape architecture, urban planning, public health, sociology, and anthropology, among others. These curated spaces provide the setting for human activity and were created to fulfill human desires and needs. The term can refer to a plethora of components including the traditionally associated buildings, cities, public infrastructure, transportation, open space, as well as more conceptual components like farmlands, dammed rivers, wildlife management, and even domesticated animals.
An anonymous P2P communication system is a peer-to-peer distributed application in which the nodes, which are used to share resources, or participants are anonymous or pseudonymous. Anonymity of participants is usually achieved by special routing overlay networks that hide the physical location of each node from other participants.
The language of thought hypothesis (LOTH), sometimes known as thought ordered mental expression (TOME), is a view in linguistics, philosophy of mind and cognitive science, forwarded by American philosopher Jerry Fodor. It describes the nature of thought as possessing "language-like" or compositional structure. On this view, simple concepts combine in systematic ways to build thoughts. In its most basic form, the theory states that thought, like language, has syntax.
In telecommunications networks, a node is either a redistribution point or a communication endpoint.

A transport network, or transportation network, is a network or graph in geographic space, describing an infrastructure that permits and constrains movement or flow. Examples include but are not limited to road networks, railways, air routes, pipelines, aqueducts, and power lines. The digital representation of these networks, and the methods for their analysis, is a core part of spatial analysis, geographic information systems, public utilities, and transport engineering. Network analysis is an application of the theories and algorithms of graph theory and is a form of proximity analysis.
Cognitive semantics is part of the cognitive linguistics movement. Semantics is the study of linguistic meaning. Cognitive semantics holds that language is part of a more general human cognitive ability, and can therefore only describe the world as people conceive of it. It is implicit that different linguistic communities conceive of simple things and processes in the world differently, not necessarily some difference between a person's conceptual world and the real world.

A computer network is a set of computers sharing resources located on or provided by network nodes. Computers use common communication protocols over digital interconnections to communicate with each other. These interconnections are made up of telecommunications network technologies based on physically wired, optical, and wireless radio-frequency methods that may be arranged in a variety of network topologies.
A business cluster is a geographic concentration of interconnected businesses, suppliers, and associated institutions in a particular field. Clusters are considered to increase the productivity with which companies can compete, nationally and globally. Accounting is a part of the business cluster. In urban studies, the term agglomeration is used. Clusters are also important aspects of strategic management.

Complex interdependence in international relations and international political economy is a concept put forth by Robert Keohane and Joseph Nye in the 1970s to describe the emerging nature of the global political economy. The concept entails that relations between states are becoming increasingly deep and complex. These increasingly complex webs of economic interdependence undermine state power and elevate the influence of transnational non-state actors. These complex relationships can be explored through both the liberal and realism lenses and can later explain the debate of power from complex interdependence.

Nikos Angelos Salingaros is a mathematician and polymath known for his work on urban theory, architectural theory, complexity theory, and design philosophy. He has been a close collaborator of the architect Christopher Alexander, with whom Salingaros shares a harsh critical analysis of conventional modern architecture. Like Alexander, Salingaros has proposed an alternative theoretical approach to architecture and urbanism that is more adaptive to human needs and aspirations, and that combines rigorous scientific analysis with deep intuitive experience.
Spatial inequality refers to the unequal distribution of income and resources across geographical regions. Attributable to local differences in infrastructure, geographical features and economies of agglomeration, such inequality remains central to public policy discussions regarding economic inequality more broadly.
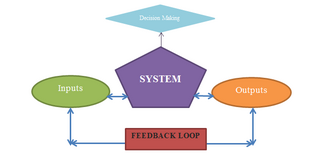
Regenerative design is about designing systems and solutions that work with or mimic the ways that natural ecosystems return energy from less usable forms to more usable forms. Regenerative design uses systems thinking and other approaches to create resilient and equitable systems that integrate the needs of society and the well-being of nature. Regenerative design is an active topic of discussion in engineering, economics, medicine, landscape design, food systems, and urban design & community development generally.
Structural holes is a concept from social network research, originally developed by Ronald Stuart Burt. A structural hole is understood as a gap between two individuals who have complementary sources to information. The study of structural holes spans the fields of sociology, economics, and computer science. Burt introduced this concept in an attempt to explain the origin of differences in social capital. Burt’s theory suggests that individuals hold certain positional advantages/disadvantages from how they are embedded in neighborhoods or other social structures.
A distributed ledger is a system whereby replicated, shared, and synchronized digital data is geographically spread (distributed) across many sites, countries, or institutions. In contrast to a centralized database, a distributed ledger does not require a central administrator, and consequently does not have a single (central) point-of-failure.

Taizhou Rail Transit is an urban rail transit system in Taizhou, Zhejiang Province, China. The system is operated by Taizhou Rail Transit Construction and Development Co., Ltd. In the near term, two lines, S1 and S2, are planned; in the long term, lines S3 and S4 are planned.







