Related Research Articles

Appendicitis is inflammation of the appendix. Symptoms commonly include right lower abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and decreased appetite. However, approximately 40% of people do not have these typical symptoms. Severe complications of a ruptured appendix include widespread, painful inflammation of the inner lining of the abdominal wall and sepsis.

Peritonitis is inflammation of the peritoneum, the lining of the inner wall of the abdomen and cover of the abdominal organs. Symptoms may include severe pain, swelling of the abdomen, fever, or weight loss. One part or the entire abdomen may be tender. Complications may include shock and acute respiratory distress syndrome.

The Abdominal thrusts is a first aid procedure used to treat upper airway obstructions by foreign objects. American doctor Henry Heimlich is often credited for its discovery. Performing abdominal thrusts involves a rescuer standing behind a patient and using his or her hands to exert pressure on the bottom of the diaphragm. This compresses the lungs and exerts pressure on any object lodged in the trachea, hopefully expelling it.

A stomach rumble, also known as a bowel sound, peristaltic sound or bubble gut, is a rumbling, growling or gurgling noise produced by movement of the contents of the gastro-intestinal tract as they are propelled through the small intestine by a series of muscle contractions called peristalsis. A trained healthcare provider can listen to these intestinal noises with a stethoscope, but they may be audible enough to be heard with the naked ear and are known as stomach rumble or borborygmus as the fluid and gas moves forward in the intestines. The lack of bowel sounds is indicative of ileus, intestinal obstruction, or some other serious pathology.
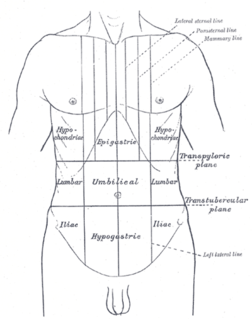
Abdominal pain, also known as a stomach ache, is a symptom associated with both non-serious and serious medical issues.

Ileus is a disruption of the normal propulsive ability of the intestine due to the malfunction of peristalsis. Ileus originally referred to any lack of digestive propulsion, including bowel obstruction, but current medical usage restricts its meaning to only those disruptions caused by the failure of the system's peristalsis and excludes failures due to mechanical obstruction, with the exception of certain older terms such as "gallstone ileus" and "meconium ileus" which are still accepted as correct due to their persistence in usage.

Joan Buckler Claybrook is an American lawyer and lobbyist who was president of Public Citizen from 1982 to 2008. She also served in the Carter administration as head of the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) from 1977 to 1981.
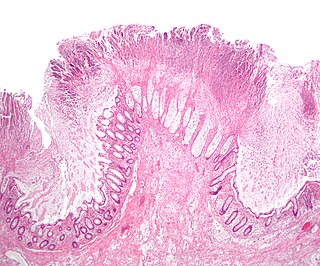
Toxic megacolon is an acute form of colonic distension. It is characterized by a very dilated colon (megacolon), accompanied by abdominal distension (bloating), and sometimes fever, abdominal pain, or shock.
Colic in horses is defined as abdominal pain, but it is a clinical symptom rather than a diagnosis. The term colic can encompass all forms of gastrointestinal conditions which cause pain as well as other causes of abdominal pain not involving the gastrointestinal tract. The most common forms of colic are gastrointestinal in nature and are most often related to colonic disturbance. There are a variety of different causes of colic, some of which can prove fatal without surgical intervention. Colic surgery is usually an expensive procedure as it is major abdominal surgery, often with intensive aftercare. Among domesticated horses, colic is the leading cause of premature death. The incidence of colic in the general horse population has been estimated between 4 and 10 percent over the course of the average lifespan. Clinical signs of colic generally require treatment by a veterinarian. The conditions that cause colic can become life-threatening in a short period of time.
Uterine rupture is when the muscular wall of the uterus tears during pregnancy or childbirth. Symptoms while classically including increased pain, vaginal bleeding, or a change in contractions are not always present. Disability or death of the mother or baby may result.
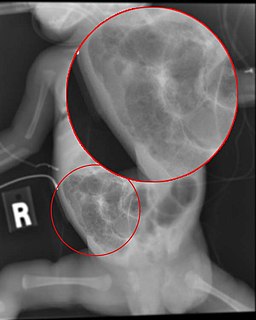
Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) is a medical condition where a portion of the bowel dies. It typically occurs in newborns that are either premature or otherwise unwell. Symptoms may include poor feeding, bloating, decreased activity, blood in the stool, or vomiting of bile.
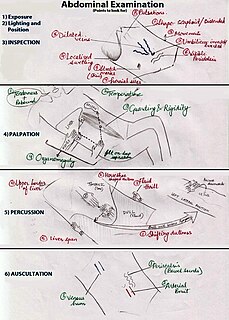
An abdominal examination is a portion of the physical examination which a physician or nurse uses to clinically observe the abdomen of a patient for signs of disease. The physical examination typically occurs after a thorough medical history is taken, that is, after the physician asks the patient the course of their symptoms. The abdominal examination is conventionally split into four different stages: first, inspection of the patient and the visible characteristics of their abdomen. Auscultation (listening) of the abdomen with a stethoscope. Palpation of the patient's abdomen. Finally, percussion (tapping) of the patient's abdomen and abdominal organs. Depending on the need to test for specific diseases such as ascites, special tests may be performed as a part of the physical examination. An abdominal examination may be performed because the physician suspects a disease of the organs inside the abdominal cavity, or simply as a part of a complete physical examination for other conditions. In a complete physical examination, the abdominal exam classically follows the respiratory examination and cardiovascular examination.
This is a shortened version of the eighteenth chapter of the ICD-10: Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings. It covers ICD codes R00.0 to R99. All versions of the ICD-10, including the most recent one (2019), can be browsed freely on the website of the World Health Organisation (WHO). The ICD-10 can also be downloaded in PDF-form.

Abdominal ultrasonography is a form of medical ultrasonography to visualise abdominal anatomical structures. It uses transmission and reflection of ultrasound waves to visualise internal organs through the abdominal wall. For this reason, the procedure is also called a transabdominal ultrasound, in contrast to endoscopic ultrasound, the latter combining ultrasound with endoscopy through visualize internal structures from within hollow organs.

Abdominal trauma is an injury to the abdomen. Signs and symptoms include abdominal pain, tenderness, rigidity, and bruising of the external abdomen. Complications may include blood loss and infection.

Diaphragmatic rupture is a tear of the diaphragm, the muscle across the bottom of the ribcage that plays a crucial role in respiration. Most commonly, acquired diaphragmatic tears result from physical trauma. Diaphragmatic rupture can result from blunt or penetrating trauma and occurs in about 5% of cases of severe blunt trauma to the trunk.
Edwin Claybrook (1871–1931) was an American surgeon remembered for describing Claybrook sign.

Natravis DeVone Claybrooks is the former head coach of the BC Lions of the Canadian Football League (CFL). He was an American football defensive tackle in the National Football League for seven different teams. He also was a member of the Montreal Alouettes and Calgary Stampeders in the CFL. He has also been the defensive coordinator for the Calgary Stampeders. On December 11, 2018, he was announced as Head Coach of the BC Lions, replacing the retired Wally Buono. Claybrooks played college football at East Carolina.

How to Pick Up Girls! is a 1978 American made-for-television comedy film shot on location in New York City starring Desi Arnaz Jr., Bess Armstrong and Fred McCarren.
Chris Claybrooks is an American football cornerback for the Jacksonville Jaguars of the National Football League (NFL). He played college football at Memphis.
References
- ↑ Claybrook's sign Archived 2016-03-04 at the Wayback Machine at Mondofacto online medical dictionary.
| This medical sign article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |