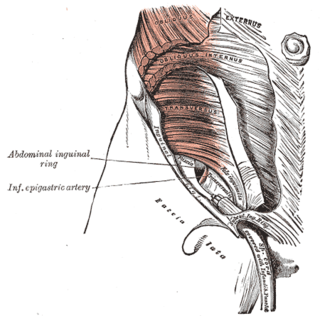
The inguinal canal is a passage in the anterior abdominal wall on each side of the body, which in males, convey the spermatic cords and in females, the round ligament of the uterus. The inguinal canals are larger and more prominent in males.
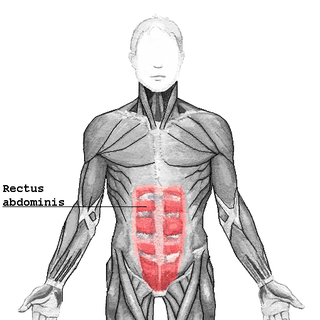
Abdominal muscles cover the anterior and lateral abdominal region and meet at the anterior midline. These muscles of the anterolateral abdominal wall can be divided into four groups: the external obliques, the internal obliques, the transversus abdominis, and the rectus abdominis.

The inguinal ligament, also known as Poupart's ligament or groin ligament, is a band running from the pubic tubercle to the anterior superior iliac spine. It forms the base of the inguinal canal through which an indirect inguinal hernia may develop.

The transverse abdominal muscle (TVA), also known as the transverse abdominis, transversalis muscle and transversus abdominis muscle, is a muscle layer of the anterior and lateral abdominal wall, deep to the internal oblique muscle. It is thought by most fitness instructors to be a significant component of the core.
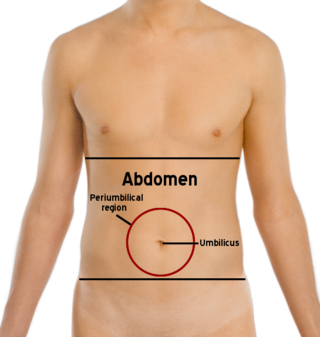
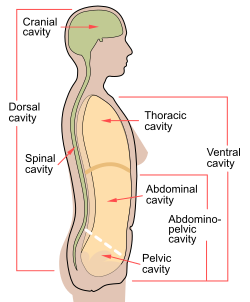
The abdomen is the part of the body between the thorax (chest) and pelvis, in humans and in other vertebrates. The abdomen is the front part of the abdominal segment of the torso. The area occupied by the abdomen is called the abdominal cavity. In arthropods, it is the posterior tagma of the body; it follows the thorax or cephalothorax.

In human anatomy, the inferior epigastric artery is an artery that arises from the external iliac artery. It is accompanied by the inferior epigastric vein; inferiorly, these two inferior epigastric vessels together travel within the lateral umbilical fold The inferior epigastric artery then traverses the arcuate line of rectus sheath to enter the rectus sheath, then anastomoses with the superior epigastric artery within the rectus sheath.

The lumbar plexus is a web of nerves in the lumbar region of the body which forms part of the larger lumbosacral plexus. It is formed by the divisions of the first four lumbar nerves (L1-L4) and from contributions of the subcostal nerve (T12), which is the last thoracic nerve. Additionally, the ventral rami of the fourth lumbar nerve pass communicating branches, the lumbosacral trunk, to the sacral plexus. The nerves of the lumbar plexus pass in front of the hip joint and mainly support the anterior part of the thigh.

In vertebrates, the pubis or pubic bone forms the lower and anterior part of each side of the hip bone. The pubis is the most forward-facing of the three bones that make up the hip bone. The left and right pubic bones are each made up of three sections, a superior ramus, inferior ramus, and a body.

The conjoint tendon is a sheath of connective tissue formed from the lower part of the common aponeurosis of the abdominal internal oblique muscle and the transversus abdominis muscle, joining the muscle to the pelvis. It forms the medial part of the posterior wall of the inguinal canal.

In human anatomy, the falciform ligament is a ligament that attaches the liver to the front body wall and divides the liver into the left lobe and right lobe. The falciform ligament is a broad and thin fold of peritoneum, its base being directed downward and backward and its apex upward and forward. It droops down from the hilum of the liver.
In human anatomy, the inguinal region refers to either the groin or the lower lateral regions of the abdomen. It may also refer to:
The transversalis fascia is the fascial lining of the anterolateral abdominal wall situated between the inner surface of the transverse abdominal muscle, and the preperitoneal fascia. It is directly continuous with the iliac fascia, the internal spermatic fascia, and pelvic fascia.

The crest of the ilium is the superior border of the wing of ilium and the superiolateral margin of the greater pelvis.

The arcuate line of rectus sheath is a line of demarcation corresponding to the free inferior margin of the posterior layer of the rectus sheath inferior to which only the anterior layer of the rectus sheath is present and the rectus abdominis muscle is therefore in direct contact with the transversalis fascia. The arcuate line is concave inferior-wards.

The deep circumflex iliac artery is an artery in the pelvis that travels along the iliac crest of the pelvic bone.
The rectus sheath is a tough fibrous compartment formed by the aponeuroses of the transverse abdominal muscle, and the internal and external oblique muscles. It contains the rectus abdominis and pyramidalis muscles, as well as vessels and nerves.

The aponeurosis of the abdominal external oblique muscle is a thin but strong membranous structure, the fibers of which are directed downward and medially.
The lumbar fascia is the lumbar portion of the thoracolumbar fascia. It consists of three fascial layers - posterior, middle, and anterior - that enclose two muscular compartments. The anterior and middle layers occur only in the lumbar region, whereas the posterior layer extends superiorly to the inferior part of the neck, and the inferiorly to the dorsal surface of the sacrum. The quadratus lumborum is contained in the anterior muscular compartment, and the erector spinae in the posterior compartment. Psoas major lies anterior to the anterior layer. Various superficial muscles of the posterior thorax and abdomen arise from the posterior layer - namely the latissimus dorsi, and serratus posterior inferior.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy:

The vaginal support structures are those muscles, bones, ligaments, tendons, membranes and fascia, of the pelvic floor that maintain the position of the vagina within the pelvic cavity and allow the normal functioning of the vagina and other reproductive structures in the female. Defects or injuries to these support structures in the pelvic floor leads to pelvic organ prolapse. Anatomical and congenital variations of vaginal support structures can predispose a woman to further dysfunction and prolapse later in life. The urethra is part of the anterior wall of the vagina and damage to the support structures there can lead to incontinence and urinary retention.