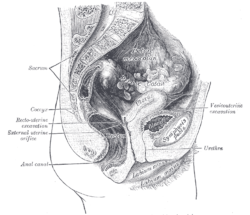
The Bartholin's glands are two pea-sized compound alveolar glands located slightly posterior and to the left and right of the opening of the vagina. They secrete mucus to lubricate the vagina.

A fascia is a generic term for macroscopic membranous bodily structures. Fasciae are classified as superficial, visceral or deep, and further designated according to their anatomical location.

A rectal prolapse occurs when walls of the rectum have prolapsed to such a degree that they protrude out of the anus and are visible outside the body. However, most researchers agree that there are 3 to 5 different types of rectal prolapse, depending on whether the prolapsed section is visible externally, and whether the full or only partial thickness of the rectal wall is involved.

The pelvic floor or pelvic diaphragm is an anatomical location in the human body, which has an important role in urinary and anal continence, sexual function and support of the pelvic organs. The pelvic floor includes muscles, both skeletal and smooth, ligaments and fascia. and separates between the pelvic cavity from above, and the perineum from below. It is formed by the levator ani muscle and coccygeus muscle, and associated connective tissue.
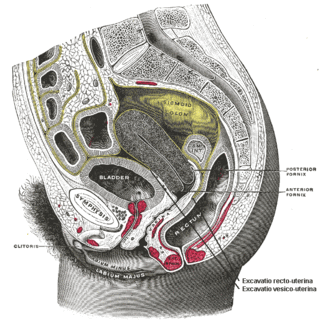
In gynecology, a rectocele or posterior vaginal wall prolapse results when the rectum bulges (herniates) into the vagina. Two common causes of this defect are childbirth and hysterectomy. Rectocele also tends to occur with other forms of pelvic organ prolapse, such as enterocele, sigmoidocele and cystocele.
Vaginoplasty is any surgical procedure that results in the construction or reconstruction of the vagina. It is a type of genitoplasty. Pelvic organ prolapse is often treated with one or more surgeries to repair the vagina. Sometimes a vaginoplasty is needed following the treatment or removal of malignant growths or abscesses to restore a normal vaginal structure and function. Surgery to the vagina is done to correct congenital defects to the vagina, urethra and rectum. It may correct protrusion of the urinary bladder into the vagina (cystocele) and protrusion of the rectum (rectocele) into the vagina. Often, a vaginoplasty is performed to repair the vagina and its attached structures due to trauma or injury.

Pelvic floor dysfunction is a term used for a variety of disorders that occur when pelvic floor muscles and ligaments are impaired. The condition affects up to 50 percent of women who have given birth. Although this condition predominantly affects women, up to 16 percent of men are affected as well. Symptoms can include pelvic pain, pressure, pain during sex, urinary incontinence (UI), overactive bladder, bowel incontinence, incomplete emptying of feces, constipation, myofascial pelvic pain and pelvic organ prolapse. When pelvic organ prolapse occurs, there may be visible organ protrusion or a lump felt in the vagina or anus. Research carried out in the UK has shown that symptoms can restrict everyday life for women. However, many people found it difficult to talk about it and to seek care, as they experienced embarrassment and stigma.

A rectovaginal fistula is a medical condition where there is a fistula or abnormal connection between the rectum and the vagina.

The cystocele, also known as a prolapsed bladder, is a medical condition in which a woman's bladder bulges into her vagina. Some may have no symptoms. Others may have trouble starting urination, urinary incontinence, or frequent urination. Complications may include recurrent urinary tract infections and urinary retention. Cystocele and a prolapsed urethra often occur together and is called a cystourethrocele. Cystocele can negatively affect quality of life.

Pelvic organ prolapse (POP) is characterized by descent of pelvic organs from their normal positions into the vagina. In women, the condition usually occurs when the pelvic floor collapses after gynecological cancer treatment, childbirth or heavy lifting. Injury incurred to fascia membranes and other connective structures can result in cystocele, rectocele or both. Treatment can involve dietary and lifestyle changes, physical therapy, or surgery.

The rectoprostatic fascia is a membranous partition at the lowest part of the rectovesical pouch. It separates the prostate and urinary bladder from the rectum. It consists of a single fibromuscular structure with several layers that are fused together and covering the seminal vesicles. It is also called Denonvilliers' fascia after French anatomist and surgeon Charles-Pierre Denonvilliers.
An enterocele is a herniation of a peritoneum-lined sac containing small intestine through the pelvic floor, between the rectum and the vagina. Enterocele is significantly more common in females, especially after hysterectomy.
Obstructed defecation syndrome is a major cause of functional constipation, of which it is considered a subtype. It is characterized by difficult and/or incomplete emptying of the rectum with or without an actual reduction in the number of bowel movements per week. Normal definitions of functional constipation include infrequent bowel movements and hard stools. In contrast, ODS may occur with frequent bowel movements and even with soft stools, and the colonic transit time may be normal, but delayed in the rectum and sigmoid colon.
Sigmoidocele is a medical condition in which a herniation of peritoneum containing loops of redundant sigmoid colon descends (prolapses) into the rectouterine pouch, between the rectum and the vagina. This can obstruct the rectum and cause obstructed defecation syndrome.

The rectococcygeal muscles are two bands of smooth muscle tissue arising from the 2nd and 3rd coccygeal vertebrae, and passing downward and forward to blend with the rectal longitudinal smooth muscle fibers on the posterior wall of the anal canal.
Warren operation is a surgery performed to correct anal incontinence. It is done by disrupting the anterior segment of the anal sphincter, perineal body and rectovaginal septum.
A urogenital fistula is an abnormal tract that exists between the urinary tract and bladder, ureters, or urethra. A urogenital fistula can occur between any of the organs and structures of the pelvic region. A fistula allows urine to continually exit through and out the urogenital tract. This can result in significant disability, interference with sexual activity, and other physical health issues, the effects of which may in turn have a negative impact on mental or emotional state, including an increase in social isolation. Urogenital fistulas vary in etiology. Fistulas are usually caused by injury or surgery, but they can also result from malignancy, infection, prolonged and obstructed labor and deliver in childbirth, hysterectomy, radiation therapy or inflammation. Of the fistulas that develop from difficult childbirth, 97 percent occur in developing countries. Congenital urogenital fistulas are rare; only ten cases have been documented. Abnormal passageways can also exist between the vagina and the organs of the gastrointestinal system, and these may also be termed fistulas.

The vaginal support structures are those muscles, bones, ligaments, tendons, membranes and fascia, of the pelvic floor that maintain the position of the vagina within the pelvic cavity and allow the normal functioning of the vagina and other reproductive structures in the female. Defects or injuries to these support structures in the pelvic floor leads to pelvic organ prolapse. Anatomical and congenital variations of vaginal support structures can predispose a woman to further dysfunction and prolapse later in life. The urethra is part of the anterior wall of the vagina and damage to the support structures there can lead to incontinence and urinary retention.

Vaginal cysts are uncommon benign cysts that develop in the vaginal wall. The type of epithelial tissue lining a cyst is used to classify these growths. They can be congenital. They can present in childhood and adulthood. The most common type is the squamous inclusion cyst. It develops within vaginal tissue present at the site of an episiotomy or other vaginal surgical sites. In most instances they do not cause symptoms and present with few or no complications. A vaginal cyst can develop on the surface of the vaginal epithelium or in deeper layers. Often, they are found by the woman herself and as an incidental finding during a routine pelvic examination. Vaginal cysts can mimic other structures that protrude from the vagina such as a rectocele and cystocele. Some cysts can be distinguished visually but most will need a biopsy to determine the type. Vaginal cysts can vary in size and can grow as large as 7 cm. Other cysts can be present on the vaginal wall though mostly these can be differentiated. Vaginal cysts can often be palpated (felt) by a clinician. Vaginal cysts are one type of vaginal mass, others include cancers and tumors. The prevalence of vaginal cysts is uncertain since many go unreported but it is estimated that 1 out of 200 women have a vaginal cyst. Vaginal cysts may initially be discovered during pregnancy and childbirth. These are then treated to provide an unobstructed delivery of the infant. Growths that originate from the urethra and other tissue can present as cysts of the vagina.
A cul-de-sac hernia is a herniation of peritoneal folds into the rectovaginal septum, or the rectovesical septum. The herniated structure is the recto-uterine pouch in females, or the rectovesical pouch in males. The hernia descends below the proximal (upper) third of the vagina in females, or, according to another definition, below the pubococcygeal line (PCL).