
The inguinal canal is a passage in the anterior abdominal wall on each side of the body which in males convey the spermatic cords and in females the round ligament of the uterus. The inguinal canals are larger and more prominent in males.

The genitofemoral nerve is a mixed branch of the lumbar plexus derived from anterior rami of L1-L2. It splits a genital branch and a femoral branch. It provides sensory innervation to the upper anterior thigh, as well as the skin of the anterior scrotum in males and mons pubis in females. It also provides motor innervation to the cremaster muscle.
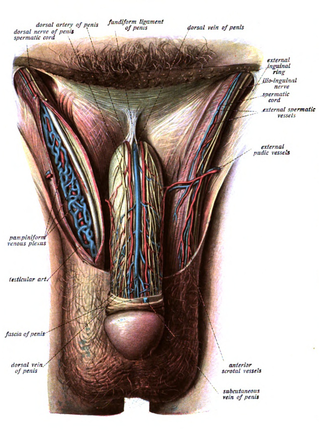
The fundiform ligament or fundiform ligament of the penis is a specialization or thickening of the superficial (Scarpa's) fascia extending from the linea alba of the lower abdominal wall.

The inguinal ligament, also known as Poupart's ligament or groin ligament, is a band running from the pubic tubercle to the anterior superior iliac spine. It forms the base of the inguinal canal through which an indirect inguinal hernia may develop.

The transverse abdominal muscle (TVA), also known as the transverse abdominis, transversalis muscle and transversus abdominis muscle, is a muscle layer of the anterior and lateral abdominal wall, deep to the internal oblique muscle. It is thought by most fitness instructors to be a significant component of the core.

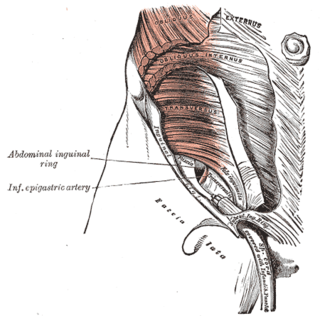
In human anatomy, the inferior epigastric artery is an artery that arises from the external iliac artery. It is accompanied by the inferior epigastric vein; inferiorly, these two inferior epigastric vessels together travel within the lateral umbilical fold The inferior epigastric artery then traverses the arcuate line of rectus sheath to enter the rectus sheath, then anastomoses with the superior epigastric artery within the rectus sheath.

In anatomy, the abdominal wall represents the boundaries of the abdominal cavity. The abdominal wall is split into the anterolateral and posterior walls.

The femoral nerve is a nerve in the thigh that supplies skin on the upper thigh and inner leg, and the muscles that extend the knee. It is the largest branch of the lumbar plexus.

The ilioinguinal nerve is a branch of the first lumbar nerve (L1). It separates from the first lumbar nerve along with the larger iliohypogastric nerve. It emerges from the lateral border of the psoas major just inferior to the iliohypogastric, and passes obliquely across the quadratus lumborum and iliacus. The ilioinguinal nerve then perforates the transversus abdominis near the anterior part of the iliac crest, and communicates with the iliohypogastric nerve between the transversus and the internal oblique muscle.
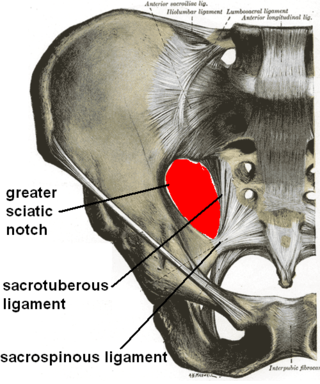
The sacrotuberous ligament is situated at the lower and back part of the pelvis. It is flat, and triangular in form; narrower in the middle than at the ends.
The transversalis fascia is the fascial lining of the anterolateral abdominal wall situated between the inner surface of the transverse abdominal muscle, and the preperitoneal fascia. It is directly continuous with the iliac fascia, the internal spermatic fascia, and pelvic fascia.

The membranous layer of the superficial fascia of the perineum is the deeper layer of the superficial perineal fascia. It is thin, aponeurotic in structure, and of considerable strength, serving to bind down the muscles of the root of the penis. Colles' fascia emerges from the perineal membrane, which divides the base of the penis from the prostate. Colles' fascia emerges from the inferior side of the perineal membrane and continues along the ventral (inferior) penis without covering the scrotum. It separates the skin and subcutaneous fat from the superficial perineal pouch.

The fascia of Scarpa is the deep membranous layer (stratum membranosum) of the superficial fascia of the abdomen. It is a layer of the anterior abdominal wall. It is found deep to the fascia of Camper and superficial to the external oblique muscle.

The arcuate line of rectus sheath is a line of demarcation corresponding to the free inferior margin of the posterior layer of the rectus sheath inferior to which only the anterior layer of the rectus sheath is present and the rectus abdominis muscle is therefore in direct contact with the transversalis fascia. The arcuate line is concave inferior-wards.

The medial umbilical ligament is a paired structure found in human anatomy. It is on the deep surface of the anterior abdominal wall, and is covered by the medial umbilical folds. It is different from the median umbilical ligament, a structure that represents the remnant of the embryonic urachus.

The superficial perineal pouch is a compartment of the perineum.
The rectus sheath is a tough fibrous compartment formed by the aponeuroses of the transverse abdominal muscle, and the internal and external oblique muscles. It contains the rectus abdominis and pyramidalis muscles, as well as vessels and nerves.

The aponeurosis of the abdominal external oblique muscle is a thin but strong membranous structure, the fibers of which are directed downward and medially.

The superficial inguinal ring is bounded below by the crest of the pubis; on either side by the margins of the opening in the aponeurosis, which are called the crura of the ring; and above, by a series of curved intercrural fibers.

The vaginal support structures are those muscles, bones, ligaments, tendons, membranes and fascia, of the pelvic floor that maintain the position of the vagina within the pelvic cavity and allow the normal functioning of the vagina and other reproductive structures in the female. Defects or injuries to these support structures in the pelvic floor leads to pelvic organ prolapse. Anatomical and congenital variations of vaginal support structures can predispose a woman to further dysfunction and prolapse later in life. The urethra is part of the anterior wall of the vagina and damage to the support structures there can lead to incontinence and urinary retention.

















