The perineum in humans is the space between the anus and scrotum in the male or between the anus and vulva in the female. The perineum is the region of the body between the pubic symphysis and the coccyx, including the perineal body and surrounding structures. The perineal raphe is visible and pronounced to varying degrees. The perineum is an erogenous zone. This area is also known as the taint or gooch in American slang.
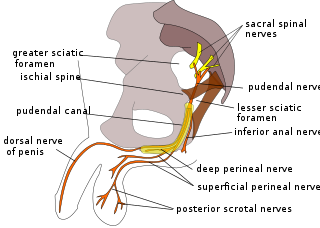
The pudendal nerve is the main nerve of the perineum. It is a mixed nerve and also conveys sympathetic autonomic fibers. It carries sensation from the external genitalia of both sexes and the skin around the anus and perineum, as well as the motor supply to various pelvic muscles, including the male or female external urethral sphincter and the external anal sphincter.

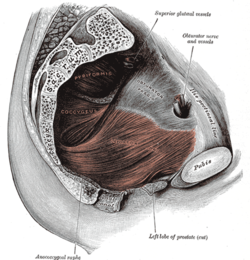
The levator ani is a broad, thin muscle group, situated on either side of the pelvis. It is formed from three muscle components: the pubococcygeus, the iliococcygeus, and the puborectalis.

The coccyx, commonly referred to as the tailbone, is the final segment of the vertebral column in all apes, and analogous structures in certain other mammals such as horses. In tailless primates since Nacholapithecus, the coccyx is the remnant of a vestigial tail. In animals with bony tails, it is known as tailhead or dock, in bird anatomy as tailfan. It comprises three to five separate or fused coccygeal vertebrae below the sacrum, attached to the sacrum by a fibrocartilaginous joint, the sacrococcygeal symphysis, which permits limited movement between the sacrum and the coccyx.

The sacrum, in human anatomy, is a large, triangular bone at the base of the spine that forms by the fusing of the sacral vertebrae (S1–S5) between ages 18 and 30.

The bulbospongiosus muscle is one of the superficial muscles of the perineum. It has a slightly different origin, insertion and function in males and females. In males, it covers the bulb of the penis. In females, it covers the vestibular bulb.

The gluteus maximus is the main extensor muscle of the hip in humans. It is the largest and outermost of the three gluteal muscles and makes up a large part of the shape and appearance of each side of the hips. It is the single largest muscle in the human body. Its thick fleshy mass, in a quadrilateral shape, forms the prominence of the buttocks. The other gluteal muscles are the medius and minimus, and sometimes informally these are collectively referred to as the glutes.

The pelvic floor or pelvic diaphragm is an anatomical location in the human body, which has an important role in urinary and anal continence, sexual function and support of the pelvic organs. The pelvic floor includes muscles, both skeletal and smooth, ligaments and fascia. and separates between the pelvic cavity from above, and the perineum from below. It is formed by the levator ani muscle and coccygeus muscle, and associated connective tissue.

The coccygeus muscle or ischiococcygeus is a muscle of the pelvic floor, located posterior to levator ani and anterior to the sacrospinous ligament.

The external anal sphincter is an oval tube of skeletal muscle fibers. Distally, it is adherent to the skin surrounding the margin of the anus. It exhibits a resting state of tonical contraction.

The external sphincter muscle of male urethra, also sphincter urethrae membranaceae, sphincter urethrae externus, surrounds the whole length of the membranous urethra, and is enclosed in the fascia of the urogenital diaphragm.

The superior pharyngeal constrictor muscle is a quadrilateral muscle of the pharynx. It is the uppermost and thinnest of the three pharyngeal constrictors.

The anococcygeal nerve is a sensory nerve of the pelvis that arises from the coccygeal plexus. It pierces the coccygeus muscle and the sacrotuberous ligament to supply a small area of skin between the coccyx and anus, as well as the sacrococcygeal joint. The number of anococcygeal nerves varies between one and three.

In vertebrates, the pubis or pubic bone forms the lower and anterior part of each side of the hip bone. The pubis is the most forward-facing of the three bones that make up the hip bone. The left and right pubic bones are each made up of three sections, a superior ramus, inferior ramus, and a body.

The sacrococcygeal symphysis is an amphiarthrodial joint, formed between the oval surface at the apex of the sacrum, and the base of the coccyx.

The coccygeal plexus is a small nervous plexus upon the pelvic (anterior) surface of the coccygeus muscle.

The anal triangle is the posterior part of the perineum. It contains the anal canal.

The pelvic fasciae are the fascia of the pelvis and can be divided into:

The pelvis is the lower part of the trunk, between the abdomen and the thighs, together with its embedded skeleton.

The vaginal support structures are those muscles, bones, ligaments, tendons, membranes and fascia, of the pelvic floor that maintain the position of the vagina within the pelvic cavity and allow the normal functioning of the vagina and other reproductive structures in the female. Defects or injuries to these support structures in the pelvic floor leads to pelvic organ prolapse. Anatomical and congenital variations of vaginal support structures can predispose a woman to further dysfunction and prolapse later in life. The urethra is part of the anterior wall of the vagina and damage to the support structures there can lead to incontinence and urinary retention.