The linea alba is a strong fibrous midline structure of the anterior abdominal wall situated between the two recti abdominis muscles. The umbilicus (navel) is a defect in the linea alba through which foetal umbilical vessels pass before birth. The linea alba is formed by the union of aponeuroses that collectively make up the rectus sheath. The linea alba attaches to the xiphoid process superiorly, and to the pubic symphysis inferiorly. If is narrow inferiorly where the two recti abdominis muscles are in contact with each other posterior to it, and broadens superior-ward from just inferior to the umbilicus.

An aponeurosis is a flattened tendon by which muscle attaches to bone or fascia. Aponeuroses exhibit an ordered arrangement of collagen fibres, thus attaining high tensile strength in a particular direction while being vulnerable to tensional or shear forces in other directions. They have a shiny, whitish-silvery color, are histologically similar to tendons, and are very sparingly supplied with blood vessels and nerves. When dissected, aponeuroses are papery and peel off by sections. The primary regions with thick aponeuroses are in the ventral abdominal region, the dorsal lumbar region, the ventriculus in birds, and the palmar (palms) and plantar (soles) regions.
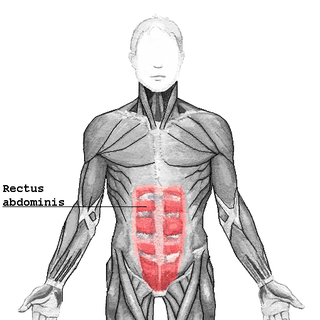
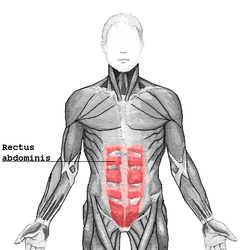
The rectus abdominis muscle, also known as the "abdominal muscle" or simply the "abs", is a pair of segmented skeletal muscle on the ventral aspect of a person's abdomen. The paired muscles are separated at the midline by a band of dense connective tissue called the linea alba, and the connective tissue defining each lateral margin of the rectus abdominus is the linea semilunaris. The muscle extends from the pubic symphysis, pubic crest and pubic tubercle inferiorly, to the xiphoid process and costal cartilages of the 5th-7th ribs superiorly.

The transverse abdominal muscle (TVA), also known as the transverse abdominis, transversalis muscle and transversus abdominis muscle, is a muscle layer of the anterior and lateral abdominal wall which is deep to the internal oblique muscle. It is thought by most fitness instructors to be a significant component of the core.

The pyramidalis muscle is a small triangular muscle, anterior to the rectus abdominis muscle, and contained in the rectus sheath.

The abdominal internal oblique muscle, also internal oblique muscle or interior oblique, is an abdominal muscle in the abdominal wall that lies below the external oblique muscle and just above the transverse abdominal muscle.

The internal intercostal muscles are a group of skeletal muscles located between the ribs. They are eleven in number on either side. They commence anteriorly at the sternum, in the intercostal spaces between the cartilages of the true ribs, and at the anterior extremities of the cartilages of the false ribs, and extend backward as far as the angles of the ribs, hence they are continued to the vertebral column by thin aponeuroses, the posterior intercostal membranes. They pull the sternum and ribs upward and inward.

The abdominal external oblique muscle is the largest and outermost of the three flat abdominal muscles of the lateral anterior abdomen.
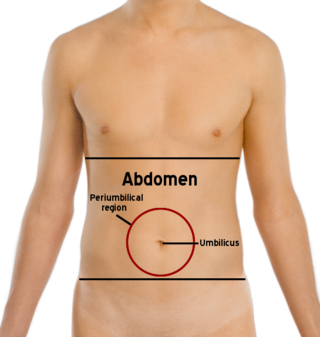
The abdomen is the part of the body between the thorax (chest) and pelvis, in humans and in other vertebrates. The abdomen is the front part of the abdominal segment of the torso. The area occupied by the abdomen is called the abdominal cavity. In arthropods it is the posterior tagma of the body; it follows the thorax or cephalothorax.

In human anatomy, the inferior epigastric artery is an artery that arises from the external iliac artery. It is accompanied by the inferior epigastric vein; inferiorly, these two inferior epigastric vessels together travel within the lateral umbilical fold The inferior epigastric artery then traverses the arcuate line of rectus sheath to enter the rectus sheath, then anastomoses with the superior epigastric artery within the rectus sheath.

In human anatomy, the superior epigastric veins are two or more venae comitantes which accompany either superior epigastric artery before emptying into the internal thoracic vein. They participate in the drainage of the superior surface of the diaphragm.

In anatomy, the abdominal wall represents the boundaries of the abdominal cavity. The abdominal wall is split into the anterolateral and posterior walls.

The conjoint tendon is a sheath of connective tissue formed from the lower part of the common aponeurosis of the abdominal internal oblique muscle and the transversus abdominis muscle, joining the muscle to the pelvis. It forms the medial part of the posterior wall of the inguinal canal.

In human anatomy, the falciform ligament is a ligament that attaches the liver to the front body wall and divides the liver into the left lobe and right lobe. The falciform ligament is a broad and thin fold of peritoneum, its base being directed downward and backward and its apex upward and forward. It droops down from the hilum of the liver.
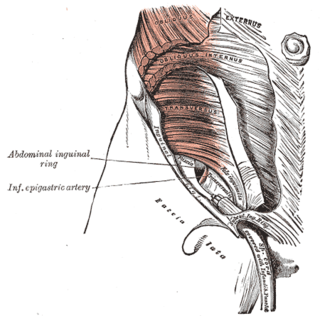
The transversalis fascia is a thin aponeurotic membrane of the abdomen. It lies between the inner surface of the transverse abdominal muscle and the parietal peritoneum.

The arcuate line of rectus sheath is a line of demarcation corresponding to the free inferior margin of the posterior layer of the rectus sheath inferior to which only the anterior layer of the rectus sheath is present and the rectus abdominis muscle is therefore in direct contact with the transversalis fascia. The arcuate line is concave inferior-wards.

The deep circumflex iliac artery is an artery in the pelvis that travels along the iliac crest of the pelvic bone.

The linea semilunaris is a curved tendinous intersection found on either side of the rectus abdominis muscle.

The anterior divisions of the seventh, eighth, ninth, tenth, and eleventh thoracic intercostal nerves are continued anteriorly from the intercostal spaces into the abdominal wall; hence they are named thoraco-abdominal nerves.

The rectus abdominis muscle is crossed by three fibrous bands called the tendinous intersections or tendinous inscriptions. One is usually situated at the level of the umbilicus, one at the extremity of the xiphoid process, and the third about midway between the two.